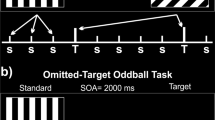
Abstract
Functional neuroimaging studies suggest that the insular cortex—and more especially the anterior insula (aI)—is involved in attentional processes and plays a crucial role in the “salience network”. However, its specific role in attentional processing remains unclear, which is partly attributable to the low temporal resolution of non-invasive neuroimaging techniques. This study aims to examine the spatio-temporal dynamics of visual target processing using intracranial EEG recorded directly from the insula. Eight epileptic patients (four women, age 18–44 years) completed a three-stimulus visual oddball task during the extraoperative invasive intracranial EEG (iEEG) monitoring of their drug-resistant seizures. Depth electrodes were implanted in ten insular lobes (5 left and 5 right) and provided a total of 59 recording contacts in the insula. Event-related potentials (ERPs) and high-gamma-band responses (GBRs) were processed offline. Permutation analyses were performed to compare ERP signals across conditions during the P300 (225–400) interval, and modulations of GBRs (70−150 Hz) were computed for separate 100 ms time windows (from 0 to 1000 ms post-stimulus) and compared across conditions using non-parametric Wilcoxon test. Target stimuli were associated with a P300 (250–338 ms) component for 39% of contacts implanted in the aI, most probably reflecting voluntary attentional processing. Amplitude was significantly greater for target than for standard stimuli for all of these contacts, and was greater than for novel stimuli for 72%. In the posterior insula (pI), 16% of contacts showed preferential responses to target stimulus in the P300 interval. Increased GBRs in response to targets were observed in 53% of aI contacts (from ≈ 200 to 300 ms) and in 43% of pI contacts (from ≈ 400 to 500 ms). This study is the first to characterize the spatio-temporal dynamics of visual target processing in the insula using iEEG. Results suggest that visual targets elicit a P300 in the aI which corresponds in latency to the P3b component, suggesting that this region is involved in top–down processing of task-relevant information. GBRs to visual targets occur earlier in the aI than in the pI, further characterizing their respective roles in voluntary attentional processing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardekani BA, Choi SJ, Hossein-Zadeh GA, Porjesz B, Tanabe JL, Lim KO, Begleiter H (2002) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of brain activity in the visual oddball task. Cogn Brain Res 14(3):347–356
Baudena P, Halgren E, Heit G, Clarke JM (1995) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. III. Frontal cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94(4):251–264
Bernat EM, Malone SM, Williams WJ, Patrick CJ, Iacono WG (2007) Decomposing delta, theta, and alpha time–frequency ERP activity from a visual oddball task using PCA. Int J Psychophysiol 64(1):62–74
Berntson GG, Norman GJ, Bechara A, Bruss J, Tranel D, Cacioppo JT (2011) The insula and evaluative processes. Psychol Sci 22(1):80–86
Boucher O, D’hondt F, Tremblay J, Lepore F, Lassonde M, Vannasing P et al (2015) Spatiotemporal dynamics of affective picture processing revealed by intracranial high-gamma modulations. Hum Brain Mapp 36(1):16–28
Brázdil M, Dobšík M, Mikl M, Hluštík P, Daniel P, Pažourková M et al (2005) Combined event-related fMRI and intracerebral ERP study of an auditory oddball task. Neuroimage 26(1):285–293
Britton JC, Taylor SF, Sudheimer KD, Liberzon I (2006) Facial expressions and complex IAPS pictures: common and differential networks. Neuroimage 31(2):906–919
Burneo JG, Kuzniecky RI, Bebin M, Knowlton RC (2004) Cortical reorganization in malformations of cortical development a magnetoencephalographic study. Neurology 63(10):1818–1824
Cauda F, D’agata F, Sacco K, Duca S, Geminiani G, Vercelli A (2011) Functional connectivity of the insula in the resting brain. Neuroimage 55(1):8–23
Cereda C, Ghika J, Maeder P, Bogousslavsky J (2002) Strokes restricted to the insular cortex. Neurology 59(12):1950–1955
Clark VP, Fannon S, Lai S, Benson R, Bauer L (2000) Responses to rare visual target and distractor stimuli using event-related fMRI. J Neurophysiol 83(5):3133–3139
Clarke JM, Halgren E, Chauvel P (1999) Intracranial ERPs in humans during a lateralized visual oddball task: II. Temporal, parietal, and frontal recordings. Clin Neurophysiol 110:1224–1225
Craig AD (2003) Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13(4):500–505
Demiralp T, Ademoglu A, Istefanopulos Y, Başar-Eroglu C, Başar E (2001) Wavelet analysis of oddball P300. Int J Psychophysiol 39(2–3):221–227
Downar J, Crawley AP, Mikulis DJ, Davis KD (2000) A multimodal cortical network for the detection of changes in the sensory environment. Nat Neurosci 3(3):277–283
Galán L, Biscay R, Rodríguez JL, Pérez-Abalo MC, Rodriguez R (1997) Testing topographic differences between event related brain potentials by using non-parametric combinations of permutation tests. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 102(3):240–247
Ghaziri J, Tucholka A, Girard G, Houde JC, Boucher O, Gilbert G et al (2017) The corticocortical structural connectivity of the human insula. Cereb Cortex 27(2):1216–1228
Gondo K, Kira R, Tokunaga Y, Harashima C, Tobimatsu S, Yamamoto T, Hara T (2000) Reorganization of the primary somatosensory area in epilepsy associated with focal cortical dysplasia. Dev Med Child Neurol 42(12):839–842
Guger C, Edlinger G, Krausz G (2011) Hardware/software components and applications of BCIs. In: Fazel R (ed.) recent advances in brain-computer interface systems. ISBN: 978-953-307-175-6, InTech, Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/recent-advances-in-brain-computer-interface-systems/hardware-software-components-and-applications-of-bcis
Gurtubay IG, Alegre M, Labarga A, Malanda A, Iriarte J, Artieda J (2001) Gamma band activity in an auditory oddball paradigm studied with the wavelet transform. Clin Neurophysiol 112(7):1219–1228
Halgren E, Baudena P, Clarke JM, Heit G, Liégeois C, Chauvel P, Musolino A (1995a) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. I. Superior temporal plane and parietal lobe. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94(3):191–220
Halgren E, Baudena P, Clarke JM, Heit G, Marinkovic K, Devaux B et al (1995b) Intracerebral potentials to rare target and distractor auditory and visual stimuli. II. Medial, lateral and posterior temporal lobe. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 94(4):229–250
Halgren E, Marinkovic K, Chauvel P (1998) Generators of the late cognitive potentials in auditory and visual oddball tasks. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106(2):156–164
Isnard J, Guénot M, Sindou M, Mauguiere F (2004) Clinical manifestations of insular lobe seizures: a stereo-electroencephalographic study. Epilepsia 45(9):1079–1090
Jensen O, Kaiser J, Lachaux JP (2007) Human gamma-frequency oscillations associated with attention and memory. Trends Neurosci 30(7):317–324
Kiehl KA, Laurens KR, Duty TL, Forster BB, Liddle PF (2001) Neural sources involved in auditory target detection and novelty processing: an event-related fMRI study. Psychophysiology 38(1):133–142
Kishima H, Saitoh Y, Osaki Y, Nishimura H, Kato A, Hatazawa J, Yoshimine T (2007) Motor cortex stimulation in patients with deafferentation pain: activation of the posterior insula and thalamus. J Neurosurg 107(1):43–48
Kolev V, Demiralp T, Yordanova J, Ademoglu A, Isoglu-Alkaç Ü (1997) Time–frequency analysis reveals multiple functional components during oddball P300. NeuroReport 8(8):2061–2065
Kurth F, Zilles K, Fox PT, Laird AR, Eickhoff SB (2010) A link between the systems: functional differentiation and integration within the human insula revealed by meta-analysis. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):519–534
Lachaux JP, Rudrauf D, Kahane P (2003) Intracranial EEG and human brain mapping. J Physiol Paris 97(4):613–628
Lachaux JP, Axmacher N, Mormann F, Halgren E, Crone NE (2012) High-frequency neural activity and human cognition: past, present and possible future of intracranial EEG research. Prog Neurobiol 98(3):279–301
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L et al (2000) Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10(3):120–131
Liberati G, Klöcker A, Algoet M, Mulders D, Maia Safronova M, Ferrao Santos S et al (2017) Gamma-band oscillations preferential for nociception can be recorded in the human insula. Cereb Cortex 28(10):3650–3664
Linden DE, Prvulovic D, Formisano E, Völlinger M, Zanella FE, Goebel R, Dierks T (1999) The functional neuroanatomy of target detection: an fMRI study of visual and auditory oddball tasks. Cereb Cortex 9(8):815–823
Lindín M, Zurrón M, Díaz F (2004) Changes in P300 amplitude during an active standard auditory oddball task. Biol Psychol 66(2):153–167
Mazzola L, Lopez C, Faillenot I, Chouchou F, Mauguiere F, Isnard J (2014) Vestibular responses to direct stimulation of the human insular cortex. Ann Neurol 76(4):609–619
Menon V, Uddin LQ (2010) Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):655–667
Milner R, Rusiniak M, Lewandowska M, Wolak T, Ganc M, Piątkowska-Janko E et al (2014) Towards neural correlates of auditory stimulus processing: a simultaneous auditory evoked potentials and functional magnetic resonance study using an odd-ball paradigm. Med Sci Monit 20:35
Mulert C, Jäger L, Schmitt R, Bussfeld P, Pogarell O, Möller HJ et al (2004) Integration of fMRI and simultaneous EEG: towards a comprehensive understanding of localization and time-course of brain activity in target detection. Neuroimage 22(1):83–94
Müsch K, Hamamé CM, Perrone-Bertolotti M, Minotti L, Kahane P, Engel AK, Schneider TR (2014) Selective attention modulates high-frequency activity in the face-processing network. Cortex 60:34–51
Nelson SM, Dosenbach NU, Cohen AL, Wheeler ME, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2010) Role of the anterior insula in task-level control and focal attention. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):669–680
Nguyen DK, Nguyen DB, Malak R, Leroux JM, Carmant L, Saint-Hilaire JM et al (2009) Revisiting the role of the insula in refractory partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 50(3):510–520
Obaid S, Zerouali Y, Nguyen DK (2017) Insular Epilepsy: Semiology and Noninvasive Investigations. J Clin Neurophysiol 34(4):315–323
Oppenheimer SM, Gelb A, Girvin JP, Hachinski VC (1992) Cardiovascular effects of human insular cortex stimulation. Neurology 42(9):1727
Parvizi J, Kastner S (2018) Promises and limitations of human intracranial electroencephalography. Nature Neuroscience 21(4):474–483
Paulus MP, Rogalsky C, Simmons A, Feinstein JS, Stein MB (2003) Increased activation in the right insula during risk-taking decision making is related to harm avoidance and neuroticism. Neuroimage 19(4):1439–1448
Phan KL, Taylor SF, Welsh RC, Ho SH, Britton JC, Liberzon I (2004) Neural correlates of individual ratings of emotional salience: a trial-related fMRI study. Neuroimage 21(2):768–780
Phillips ML, Young AW, Senior C, Brammer M, Andrew C, Calder AJ et al (1997) A specific neural substrate for perceiving facial expressions of disgust. Nature 389(6650):495
Polich J (2007) Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin Neurophysiol 118(10):2128–2148
Posner MI, Snyder CR, Davidson BJ (1980) Attention and the detection of signals. J Exp Psychol Gen 109(2):160
Ray S, Niebur E, Hsiao SS, Sinai A, Crone NE (2008) High-frequency gamma activity (80–150 Hz) is increased in human cortex during selective attention. Clin Neurophysiol 119(1):116–133
Scharfman HE (2002) Epilepsy as an example of neural plasticity. The Neuroscientist 8(2):154–173
Snyder E, Hillyard SA (1976) Long-latency evoked potentials to irrelevant, deviant stimuli. Behavioral Biology 16(3):319–331
Snyder E, Hillyard SA, Galambos R (1980) Similarities and differences among the P3 waves to detected signals in three modalities. Psychophysiology 17(2):112–122
Squires NK, Squires KC, Hillyard SA (1975) Two varieties of long-latency positive waves evoked by unpredictable auditory stimuli in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 38(4):387–401
Stevens AA, Skudlarski P, Gatenby JC, Gore JC (2000) Event-related fMRI of auditory and visual oddball tasks. Magn Reson Imaging 18(5):495–502
Surbeck W, Bouthillier A, Weil AG, Crevier L, Carmant L, Lortie A et al (2011) The combination of subdural and depth electrodes for intracranial EEG investigation of suspected insular (perisylvian) epilepsy. Epilepsia 52(3):458–466
Terasawa Y, Kurosaki Y, Ibata Y, Moriguchi Y, Umeda S (2015) Attenuated sensitivity to the emotions of others by insular lesion. Front Psychol 6:1314
Türe U, Yaşargil DC, Al-Mefty O, Yaşargil MG (1999) Topographic anatomy of the insular region. J Neurosurg 90(4):720–733
Uddin LQ (2015) Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(1):1–7
Uddin LQ, Nomi JS, Hébert-Seropian B, Ghaziri J, Boucher O (2017) Structure and function of the human insula. J Clin Neurophysiol 34(4):300–306
Vidal JR, Ossandón T, Jerbi K, Dalal SS, Minotti L, Ryvlin P et al (2010) Category-specific visual responses: an intracranial study comparing gamma, beta, alpha, and ERP response selectivity. Front Hum Neurosci 4:195
Volpe U, Mucci A, Bucci P, Merlotti E, Galderisi S, Maj M (2007) The cortical generators of P3a and P3b: a LORETA study. Brain Res Bull 73(4):220–230
Ward LM (2003) Synchronous neural oscillations and cognitive processes. Trends Cogn Sci 7(12):553–559
Zhang Y, Zhou W, Wang S, Zhou Q, Wang H, Zhang B et al (2018) The roles of subdivisions of human insula in emotion perception and auditory processing. Cereb Cortex 29(2):517–528
Funding
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR)—Project Grant (148563-DKN, FL, OB); CIHR Postdoctoral Grant (MFE-115520–OB); Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)—Discovery Grant (RGPIN-2016-05216-DKN, FL, KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Citherlet, D., Boucher, O., Tremblay, J. et al. Role of the insula in top–down processing: an intracranial EEG study using a visual oddball detection paradigm. Brain Struct Funct 224, 2045–2059 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01892-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01892-y