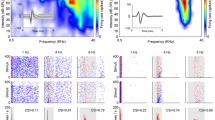
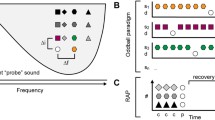
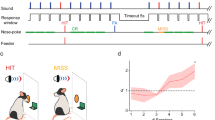
Abstract
Using oddball stimulus with pure tones, researchers have extensively investigated stimulus-specific adaptation (SSA), which has been regarded as a method of novelty detection, from the inferior colliculus (IC) to the auditory cortex (AC). However, until now, it is not clear whether SSA is preserved for natural sounds or whether it exists for spatial cues in the AC. Moreover, it is also unclear whether SSA integrates different types of cues within a single modality such as sound location and sound identity. Here, we addressed these issues using two natural sounds presented at two different locations while simultaneously performing extracellular recordings in the AC of awake rats. Our data showed that SSA was present in the AC for the natural sounds, the pure tones, and the spatial locations in the neuronal population. We also found that the AC response to a double deviant stimulus (a deviant sound at a deviant location) was stronger than that to a single (either a deviant sound or the same sound at a deviant location); this finding suggests that detecting unexpected events benefits from the integration of different cues within the same modality.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSA:
-
Stimulus-specific adaptation
- AC:
-
Auditory cortex
- IC:
-
Inferior colliculus
- A1:
-
Primary auditory cortex
- AAF:
-
Anterior auditory filed
- CF:
-
Characteristic frequencies
- FRA:
-
Frequency response area
- IOP:
-
Integrative oddball paradigm
- SCO:
-
Sound comparison oddball
- FM:
-
Frequency-modulated
- CSI:
-
Common stimulus-specific index
- DII:
-
Double-identity index
- DSI:
-
Double-spatial index
- PSTHs:
-
Peri-stimulus time histograms
- DD:
-
Double deviant
- SID:
-
Single identity deviant
- SSD:
-
Single spatial deviant
References
Anderson LA, Malmierca MS (2013) The effect of auditory cortex deactivation on stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the rat. Eur J Neurosci 37:52–62
Anderson LA, Christianson GB, Linden JF (2009) Stimulus-specific adaptation occurs in the auditory thalamus. J Neurosci 29:7359–7363
Antunes FM, Malmierca MS (2014) An overview of stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory thalamus. Brain Topogr 27:480–499
Antunes FM, Nelken I, Covey E, Malmierca MS (2010) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory thalamus of the anesthetized rat. PLoS One 5:e14071
Ayala YA, Malmierca Dr MS (2012) Stimulus-specific adaptation and deviance detection in the inferior colliculus. Front Neural Circuits 6:89
Ayala YA, Perez-Gonzalez D, Duque D, Nelken I, Malmierca MS (2012) Frequency discrimination and stimulus deviance in the inferior colliculus and cochlear nucleus. Front Neural Circuits 6:119
Bäuerle P, von der Behrens W, Kössl M, Gaese BH (2011) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the gerbil primary auditory thalamus is the result of a fast frequency-specific habituation and is regulated by the corticofugal system. J Neurosci 31:9708–9722
Bregman AS (1990) Auditory scene analysis: the perceptual organization of sound. MIT Press, Cambridge
Duque D, Malmierca MS, Caspary DM (2014) Modulation of stimulus-specific adaptation by GABAA receptor activation or blockade in the medial geniculate body of the anaesthetized rat. J Physiol 592:729–743
Duque D, Wang X, Nieto-Diego J, Krumbholz K, Malmierca MS (2016) Neurons in the inferior colliculus of the rat show stimulus-specific adaptation for frequency, but not for intensity. Sci Rep 6:24114
Farley BJ, Quirk MC, Doherty JJ, Christian EP (2010) Stimulus-specific adaptation in auditory cortex is an NMDA-independent process distinct from the sensory novelty encoded by the mismatch negativity. J Neurosci 30:16475–16484
Fishman YI, Steinschneider M (2012) Searching for the mismatch negativity in primary auditory cortex of the awake monkey: deviance detection or stimulus specific adaptation? J Neurosci 32:15747–15758
Horikawa J, Ito S, Hosokawa Y, Homma T, Murata K (1988) Tonotopic representation in the rat auditory-cortex. Proc Jpn Acad B Phys 64:260–263
Khouri L, Nelken I (2015) Detecting the unexpected. Curr Opin Neurobiol 35:142–147
Klein C, von der Behrens W, Gaese BH (2014) Stimulus-specific adaptation in field potentials and neuronal responses to frequency-modulated tones in the primary auditory cortex. Brain Topogr 27:599–610
Malmierca MS, Cristaudo S, Pérez-González D, Covey E (2009) Stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus of the anesthetized rat. J Neurosci 29:5483–5493
Malmierca MS, Sanchez-Vives MV, Escera C, Bendixen A (2014) Neuronal adaptation, novelty detection and regularity encoding in audition. Front Syst Neurosci 8:111
Nelken I, Yaron A, Polterovich A, Hershenhoren I (2013) Stimulus-specific adaptation beyond pure tones. Adv Exp Med Biol 787:411–418
Nieto-Diego J, Malmierca MS (2016) Topographic distribution of stimulus-specific adaptation across auditory cortical fields in the anesthetized rat. PLoS Biol 14:e1002397
Parras GG, Nieto-Diego J, Carbajal GV, Valdes-Baizabal C, Escera C, Malmierca MS (2017) Neurons along the auditory pathway exhibit a hierarchical organization of prediction error. Nat Commun 8:2148
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 5th edn. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam
Pérez-González D, Hernández O, Covey E, Malmierca MS (2012) GABA A-mediated inhibition modulates stimulus-specific adaptation in the inferior colliculus. PLoS One 7:e34297
Polterovich A, Jankowski MM, Nelken I (2018) Deviance sensitivity in the auditory cortex of freely moving rats. PLoS One 13:e0197678
Profant O, Burianova J, Syka J (2013) The response properties of neurons in different fields of the auditory cortex in the rat. Hear Res 296:51–59
Reches A, Gutfreund Y (2008) Stimulus-specific adaptations in the gaze control system of the barn owl. J Neurosci 28:1523–1533
Reches A, Netser S, Gutfreund Y (2010) Interactions between stimulus-specific adaptation and visual auditory integration in the forebrain of the barn owl. J Neurosci 30:6991–6998
Richardson BD, Hancock KE, Caspary DM (2013) Stimulus-specific adaptation in auditory thalamus of young and aged awake rats. J Neurophysiol 110:1892–1902
Rodriguez-Nodal F, Bajo-Lorenzana VM (2012) The role of the auditory cortex in the spatial information processing. Rev de Neurol 55:91–100
Roman N, Wang D, Brown GJ (2003) Speech segregation based on sound localization. J Acoust Soc Am 114:2236–2252
Rui YY, He J, Zhai YY, Sun ZH, Yu X (2018) Frequency-dependent stimulus-specific adaptation and regularity sensitivity in the rat auditory thalamus. Neuroscience 392:13–24
Schwarz C, Hentschke H, Butovas S, Haiss F, Stuttgen MC, Gerdjikov TV, Bergner CG, Waiblinger C (2010) The head-fixed behaving rat–procedures and pitfalls. Somatosens Mot Res 27:131–148
Sollini J, Mill R, Sumner CJ (2017) Spatial processing is frequency specific in auditory cortex but not in the midbrain. J Neurosci 37:6588–6599
Szymanski FD, Garcia-Lazaro JA, Schnupp JWH (2009) Current source density profiles of stimulus-specific adaptation in rat auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol 102:1483–1490
Taaseh N, Yaron A, Nelken I (2011) Stimulus-specific adaptation and deviance detection in the rat auditory cortex. PLoS One 6:e23369
Ulanovsky N, Las L, Nelken I (2003) Processing of low-probability sounds by cortical neurons. Nat Neurosci 6:391–398
Von Der Behrens W, Bäuerle P, Kössl M, Gaese BH (2009) Correlating stimulus-specific adaptation of cortical neurons and local field potentials in the awake rat. J Neurosci 29:13837–13849
Wang F, Liu J, Zhang J (2019) Early postnatal noise exposure degrades the stimulus-specific adaptation of neurons in the rat auditory cortex in adulthood. Neuroscience 404:1–13
Wasmuht DF, Pena JL, Gutfreund Y (2017) Stimulus-specific adaptation to visual but not auditory motion direction in the barn owl’s optic tectum. Eur J Neurosci 45:610–621
Xu X, Yu X, He J, Nelken I (2014) Across-ear stimulus-specific adaptation in the auditory cortex. Front Neural Circuits 8:89
Xu XX, Zhai YY, Kou XK, Yu X (2017) Adaptation facilitates spatial discrimination for deviant locations in the thalamic reticular nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience 365:1–11
Yu XJ, Xu XX, He S, He J (2009) Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons. Nat Neurosci 12:1165–1170
Zhao L, Liu Y, Shen L, Feng L, Hong B (2011) Stimulus-specific adaptation and its dynamics in the inferior colliculus of rat. Neuroscience 181:163–174
Funding
All experiments were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript. XY designed the experiments and analyzed and interpreted the data; YYZ, ZHS, YMG, and YT collected and analyzed the data. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution (ZJU20160246).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, YY., Sun, ZH., Gong, YM. et al. Integrative stimulus-specific adaptation of the natural sounds in the auditory cortex of the awake rat. Brain Struct Funct 224, 1753–1766 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01880-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01880-2