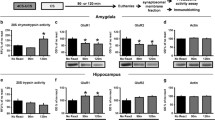
Abstract
Degradation of the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of the extracellular matrix (ECM) by injections of the bacterial enzyme chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) does not impair fear memory formation but accelerates its extinction and disrupts its reactivation. These observations suggest that the treatment might selectively interfere with the post-extinction features of neurons that mediate the reinstatement of fear. Here, we report that ChABC mice show regular fear memory and memory-driven c-fos activation and dendritic spine formation in the BLA. These mice then rapidly extinguish their fear response and exhibit a post-extinction concurrent reduction in c-fos activation and large dendritic spines that extends to the anterior cingulate cortex 7 days later. At this remote time point, fear renewal and fear retrieval are impaired. These findings show that a non-cellular component of the brain tissue controls post-extinction levels of neuronal activity and spine enlargement in the regions sequentially remodelled during the formation of recent and remote fear memory. By preventing BLA and aCC neurons to retain neuronal features that serve to reactivate an extinguished fear memory, ECM digestion might offer a therapeutic strategy for durable attenuation of traumatic memories.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 September 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-022-02567-x
References
Aceti M, Vetere G, Novembre G, Restivo L, Ammassari-Teule M (2015) Progression of activity and structural changes in the anterior cingulate cortex during remote memory formation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 123:67–71
Bauer EP, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2002) NMDA receptors and L-type voltage-gated calcium channels contribute to long-term potentiation and different components of fear memory formation in the lateral amygdala. J Neurosci 22:5239–5249
Dansie LE, Ethell IM (2011) Casting a net on dendritic spines: the extracellular matrix and its receptors. Dev Neurobiol 71(11):956–981
Ganguly K, Rejmak E, Mikosz M, Nikolaev E, Knapska E, Kaczmarek L (2013) Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 9 transcription in mouse brain induced by fear learning. J Biol Chem 288(29):20978–20991
Gibb R, Kolb B (1998) A method for vibratome sectioning of Golgi–Cox stained whole rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 79(1):1–4
Gogolla N, Caroni P, Lüthi A, Herry C (2009) Perineuronal nets protect fear memories from erasure. Science 325(5945):1258–1261
Happel MF, Niekisch H, Castiblanco Rivera LL, Ohl FW, Deliano M, Frischknecht R (2014) Enhanced cognitive flexibility in reversal learning induced by removal of the extracellular matrix in auditory cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(7):2800–2805
Heinrichs SC, Leite-Morris KA, Guy MD, Goldberg LR, Young AJ, Kaplan GB (2013) Dendritic structural plasticity in the basolateral amygdala after fear conditioning and its extinction in mice. Behav Brain Res 248:80–84
Hylin MJ, Orsi SA, Moore AN, Dash P (2013) Disruption of the perineuronal net in the hippocampus or medial prefrontal cortex impairs fear conditioning. Learn Mem 20(5):267–273
Kasai H, Matsuzaki M, Noguchi J, Yasumatsu N, Nakahara H (2003) Structure-stability-function relationships of dendritic spines. Trends Neurosci 26(7):360–368
Konur S, Rabinowitz D, Fenstermaker VL, Yuste R (2003) Systematic regulation of spine sizes and densities in pyramidal neurons. J Neurobiol 56(2):95–112
Lesburguères E, Gobbo OL, Alaux-Cantin S, Hambucken A, Trifilieff P, Bontempi B (2011) Early tagging of cortical networks is required for the formation of enduring associative memory. Science 331(6019):924–928
Levy AD, Omar MH, Koleske AJ (2014) Extracellular matrix control of dendritic spine and synapse structure and plasticity in adulthood. Front Neuroanat 8:116
Matsuo N, Reijmers L, Mayford M (2008) Spine-type-specific recruitment of newly synthesized AMPA receptors with learning. Science 319(5866):1104–1107
Miao QL, Ye Q, Zhang XH (2014) Perineuronal net, CSPG receptor and their regulation of neural plasticity. Sheng Li Xue Bao 66(4):387–389
Montag-Sallaz M, Montag D (2003) Severe cognitive and motor corrdination deficits in tenascin-R-deficient mice. Genes Brain Behav 2(1):20–31
Morellini F, Sivukhina E, Stoenica L, OuliANOVA E, Bukalo O, Jkovcevski I, Dityatev A, Irintchev A, Schachner M (2010) Improved reversal learning and working memory and enhanced reactivity to novelty in mice with enhanced GABAergic innervation in the dentate gyrus. Cereb Cortex 20(11):2712–2722
Pape HC, Paré D (2010) Plastic synaptic networks of the amygdala for the acquisition, expression, and extinction of conditioned fear. Physiol Rev 90(2):419–463
Phelps EA, LeDoux JE (2005) Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: from animal models to human behavior. Neuron 48(2):175–187
Pignataro A, Ammassari-Teule M (2015) Post-extinction selective persistence of large dendritic spines in fear remodeled circuits may serve to reactivate fear. Curr Opin Neurobiol 35:1–5
Pignataro A, Middei S, Borreca A, Ammassari-Teule M (2013) Indistinguishable pattern of amygdala and hippocampus rewiring following tone or contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Front Behav Neurosci 7:156
Restivo L, Vetere G, Bontempi B, Ammassari-Teule M (2009) The formation of recent and remote memory is associated with time-dependent formation of dendritic spines in the hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex. J Neurosci 29(25):8206–8214
Romberg C, Yang S, Melani R, Andrews MR, Horner AE, Spillantini MG, Bussey TJ, Fawcett JW, Pizzorusso T, Saksida LM (2013) Depletion of perineuronal nets enhances recognition memory and long-term depression in the perirhinal cortex. J Neurosci 33(16):7057–7065
Royer S, Paré D (2002) Bidirectional synaptic plasticity in intercalated amygdala neurons and the extinction of conditioned fear responses. Neuroscience 115(2):455–462
Tashiro A, Yuste R (2003) Structure and molecular organization of dendritic spines. Histol Histopathol 18(2):617–634
Vetere G, Restivo L, Cole CJ, Ross PJ, Ammassari-Teule M, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW (2011a) Spine growth in the anterior cingulate cortex is necessary for the consolidation of contextual fear memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(20):8456–8460
Vetere G, Restivo L, Novembre G, Aceti M, Lumaca M, Ammassari-Teule M (2011b) Extinction partially reverts structural changes associated with remote fear memory. Learn Mem 18(9):554–557
Vetere G, Piserchia V, Borreca A, Novembre G, Aceti M, Ammassari-Teule M (2013) Reactivating fear memory under propranolol resets pre-trauma levels of dendritic spines in basolateral amygdala but not dorsal hippocampus neurons. Front Behav Neurosci 7:211
Wright JW, Kramár EA, Meighan SE, Harding JW (2002) Extracellular matrix molecules, long-term potentiation, memory consolidation and the brain angiotensin system. Peptides 23(1):221–246
Xue YX, Xue LF, Liu JF, He J, Deng JH, Sun SC, Han HB, Luo YX, Xu LZ, Wu P, Lu L (2014) Depletion of perineuronal nets in the amygdala to enhance the erasure of drug memories. J Neurosci 34(19):6647–6658
Yang S, Cacquevel M, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ, Schneider BL, Aebischer P, Melani R, Pizzorusso T, Fawcett JW, Spillantini MG (2015) Perineuronal net digestion with chondroitinase restores memory in mice with tau pathology. Exp Neurol 265:48–58
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CNR-National Research Council of Italy (AGESPAN Project), Fondazione Santa Lucia, and Ministry of Health (Progetto di ricerca finalizzata No. RF-2009-153607).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
429_2017_1440_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary Fig. 5 Confirming that the treatment did not interfere with the formation of the tone-shock association, ChABC- and PBS-injected mice showed the same amount of freezing during the first minute of exposure to the CS alone on the first extinction trial (PDF 438 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pignataro, A., Pagano, R., Guarneri, G. et al. Extracellular matrix controls neuronal features that mediate the persistence of fear. Brain Struct Funct 222, 3889–3898 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1440-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1440-0