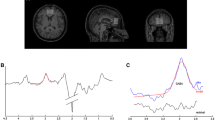
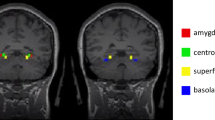
Abstract
The amygdala-medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) circuit plays a key role in social behavior. The amygdala and mPFC are bidirectionally connected, functionally and anatomically, via the uncinate fasciculus. Recent evidence suggests that GABA-ergic neurotransmission within the mPFC could be central to the regulation of amygdala activity related to emotions and anxiety processing. However, the functional and neurochemical interactions within amygdala-mPFC circuits are unclear. In the current study, multimodal magnetic resonance imaging techniques were combined to investigate effective connectivity within the amygdala-mPFC network and its relationship with mPFC neurotransmission in 22 healthy subjects aged between 41 and 88 years. Effective connectivity in the amygdala-mPFC circuit was assessed on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data using spectral dynamic causal modelling. State and trait anxiety were also assessed. The mPFC was shown to be the target of incoming outputs from the amygdalae and the source of exciting inputs to the limbic system. The amygdalae were reciprocally connected by excitatory projections. About half of the variance relating to the strength of top–down endogenous connection between right amygdala and mPFC was explained by mPFC GABA levels. State anxiety was correlated with the strength of the endogenous connections between right amygdala and mPFC. We suggest that mPFC GABA content predicts variability in the effective connectivity within the mPFC-amygdala circuit, providing new insights on emotional physiology and the underlying functional and neurochemical interactions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 June 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
Abbreviations
- GABA:
-
γ-Aminobutyric acid
- GM:
-
Grey matter
- STAI:
-
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory scale (Y1 = subscale-1, Y2 = subscale-2).
References
Abbate C, Luzzatti C, Vergani C (2007) Test delle matrici: velocità e accuratezza della ricerca visiva nel corso dell’invecchiamento. G Gerontol 55:11–20
Adhikari A, Lerner TN, Finkelstein J, Pak S, Jennings JH, Davidson TJ, Ferenczi E, Gunaydin LA, Mirzabekov JJ, Ye L, Kim SY, Lei A, Deisseroth K (2015) Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of anxiety and fear. Nature 527:179–185. doi:10.1038/nature15698
Adolphs R, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio A (1996) Cortical systems for the recognition of emotion in facial expressions. J Neurosci 16:7678–7687
Akirav I, Maroun M (2007) The role of the medial prefrontal cortex-amygdala circuit in stress effects on the extinction of fear. Neural Plast 2007:1–11. doi:10.1155/2007/30873
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association. doi:10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596
Andersen SL, Teicher MH (1999) Serotonin laterality in amygdala predicts performance in the elevated plus maze in rats. NeuroReport 10:3497–3500
Appollonio I, Leone M, Isella V, Piamarta F, Consoli T, Villa ML, Forapani E, Russo A, Nichelli P (2005) The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB): normative values in an Italian population sample. Neurol Sci 26:108–116. doi:10.1007/s10072-005-0443-4
Baddeley A, Wilson BA (2002) Prose recall and amnesia: Implications for the structure of working memory. Neuropsychologia 40:1737–1743. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(01)00146-4
Baker KB, Kim JJ (2004) Amygdalar lateralization in fear conditioning: evidence for greater involvement of the right amygdala. Behav Neurosci 118:15–23. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.118.1.15
Bastos-Leite AJ, Ridgway GR, Silveira C, Norton A, Reis S, Friston KJ (2015) Dysconnectivity within the default mode in first-episode schizophrenia: a stochastic dynamic causal modeling study with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Schizophr Bull 41:144–153. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbu080
Bishop SJ (2007) Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: an integrative account. Trends Cogn Sci 11:307–316. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2007.05.008
Blair K, Shaywitz J, Smith BW, Rhodes R, Geraci M, Jones M, McCaffrey D, Vythilingam M, Finger E, Jacobs M, Charney DS, Blair RJ, Drevets WC, Pine DS (2008) Response to emotional expressions in generalized social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder: evidence for separate disorders. Am J Psychiatry 165:1193–1202. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.07071060
Bogner W, Gruber S, Doelken M, Stadlbauer A, Ganslandt O, Boettcher U, Trattnig S, Doerfler A, Stefan H, Hammen T (2010) In vivo quantification of intracerebral GABA by single-voxel (1)H-MRS-How reproducible are the results? Eur J Radiol 73:526–531. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.01.014
Bonifazi P, Goldin M, Picardo MA, Jorquera I, Cattani A, Bianconi G, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y, Cossart R (2009) GABAergic hub neurons orchestrate synchrony in developing hippocampal networks. Science 326:1419–1424. doi:10.1126/science.1175509
Bowers D, Blonder LX, Feinberg T, Heilman KM (1991) Differential impact of right and left hemisphere lesions on facial emotion and object imagery. Brain 114:2593–2609. doi:10.1093/brain/114.6.2593
Bracht T, Tüscher O, Schnell S, Kreher B, Rüsch N, Glauche V, Lieb K, Ebert D, Il’yasov KA, Hennig J, Weiller C, van Elst LT, Saur D (2009) Extraction of prefronto-amygdalar pathways by combining probability maps. Psychiatry Res 174:217–222. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.05.001
Calhoon GG, Tye KM (2015) Resolving the neural circuits of anxiety. Nat Neurosci 18:1394–1404. doi:10.1038/nn.4101
Canli T, Desmond JE, Zhao Z, Glover G, Gabrieli JDE (1998) Hemispheric asymmetry for emotional stimuli detected with fMRI. NeuroReport 9:3233–3239
Chefer VI, Wang R, Shippenberg TS (2011) Basolateral amygdala-driven augmentation of medial prefrontal cortex GABAergic neurotransmission in response to environmental stimuli associated with cocaine administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:2018–2029. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.89
Constantinidis C, Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic (2002) A role for inhibition in shaping the temporal flow of information in prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci 5:175–180. doi:10.1038/nn799
Courtin J, Chaudun F, Rozeske RR, Karalis N, Gonzalez-Campo C, Wurtz H, Abdi A, Baufreton J, Bienvenu TC, Herry C (2014) Prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons shape neuronal activity to drive fear expression. Nature 505:92–96. doi:10.1038/nature12755
Crone JS, Schurz M, Höller Y, Bergmann J, Monti M, Schmid E, Trinka E, Kronbichler M (2015) Impaired consciousness is linked to changes in effective connectivity of the posterior cingulate cortex within the default mode network. Neuroimage 110:101–109. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.01.037
Crone JS, Lutkenhoff ES, Bio BJ, Laureys S, Monti MM (2017) Testing proposed neuronal models of effective connectivity within the Cortico-basal Ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop during loss of consciousness. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhw112 (In press)
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9:179–194. doi:10.1006/nimg.1998.0395
De Bondt T, De Belder F, Vanhevel F, Jacquemyn Y, Parizel PM (2015) Prefrontal GABA concentration changes in women-influence of menstrual cycle phase, hormonal contraceptive use, and correlation with premenstrual symptoms. Brain Res 1597:129–138. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.11.051
Declaration of Helsinki (1997) Recommendation Guiding Physicians in Biomedical Research involving human subjects. JAMA 277:925–926. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540350075038
Delli Pizzi S, Padulo C, Brancucci A, Bubbico G, Edden RA, Ferretti A, Franciotti R, Manippa V, Marzoli D, Onofrj M, Sepede G, Tartaro A, Tommasi L, Puglisi-Allegra S, Bonanni L (2016) GABA content within the ventromedial prefrontal cortex is related to trait anxiety. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 11:758–766. doi:10.1093/scan/nsv155
Delli Pizzi S, Chiacchiaretta P, Mantini D, Bubbico G, Edden RA, Di Giulio C, Onofrj M, Bonanni L (2017) Functional and neurochemical interactions within the amygdala-medial prefrontal cortex circuit and their relevance to emotional processing. Brain Struct Funct. doi:10.1007/s00429-016-1276-z
Donahue MJ, Near J, Blicher JU, Jezzard P (2010) Baseline GABA concentration and fMRI response. Neuroimage 53:392–398. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.017
Duncan NW, Enzi B, Wiebking C, Northoff G (2011) Involvement of glutamate in rest-stimulus interaction between perigenual and supragenual anterior cingulate cortex: a combined fMRI-MRS study. Hum Brain Mapp 32:2172–2182. doi:10.1002/hbm.21179
Duncan NW, Wiebking C, Northoff G (2014) Associations of regional GABA and glutamate with intrinsic and extrinsic neural activity in humans-a review of multimodal imaging studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:36–52. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.07.016
Edden RA, Barker PB (2007) Spatial effects in the detection of gamma-aminobutyric acid: improved sensitivity at high fields using inner volume saturation. Magn Reson Med 58:1276–1282. doi:10.1002/mrm.21383
Edden RA, Puts NA, Harris AD, Barker PB, Evans CJ (2014) Gannet: a batch-processing tool for the quantitative analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy spectra. J Magn Reson Imaging 40:1445–1452. doi:10.1002/jmri.24478
Edden RA, Oeltzschner G, Harris AD, Puts NA, Chan KL, Boer VO, Schär M, Barker PB (2016) Prospective frequency correction for macromolecule-suppressed GABA editing at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging. doi:10.1002/jmri.25304
Etkin A, Prater KE, Schatzberg AF, Menon V, Greicius MD (2009) Disrupted amygdalar subregion functional connectivity and evidence of a compensatory network in generalized anxiety disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:1361–1372. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2009.104
Falkenberg LE, Westerhausen R, Specht K, Hugdahl K (2012) Resting-state glutamate level in the anterior cingulate predicts blood-oxygen level-dependent response to cognitive control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:5069–5073. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115628109
Friston KJ (2011) Functional and effective connectivity: a review. Brain Connect 1:13–36. doi:10.1089/brain.2011.0008
Friston KJ, Frith CD, Fletcher P, Liddle PF, Frackowiak RSJ (1996) Functional topography: multidimensional scaling and functional connectivity in the brain. Cerebral cortex 6:156–164
Friston KJ, Kahan J, Biswal B, Razi A (2014) A DCM for resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 94:396–407. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.009
Fullana MA, Harrison BJ, Soriano-Mas C, Vervliet B, Cardoner N, Àvila-Parcet A, Radua J (2015) Neural signatures of human fear conditioning: an updated and extended meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Mol Psychiatry 21:500–508. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.88
Gao F, Edden RA, Li M, Puts NA, Wang H, Bai X, Zhao C, Wang X, Barker PB, Wang H, Bai X, Zhao C, Wang X, Barker PB (2013) Edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects an age-related decline in brain GABA levels. Neuroimage 78:75–82. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.012
Ghashghaei HT, Barbas H (2002) Pathways for emotion: interactions of prefrontal and anterior temporal pathways in the amygdala of the rhesus monkey. Neuroscience 115:1261–1279. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00446-3
Ghashghaei HT, Hilgetag CC, Barbas H (2007) Sequence of information processing for emotions based on the anatomic dialogue between prefrontal cortex and amygdala. Neuroimage 34:905–923. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.09.046
Giovagnoli AR, Del Pesce M, Mascheroni S, Simoncelli M, Laiacona M, Capitani E (1996) Trail making test: normative values from 287 normal adult controls. Ital J Neurol Sci 17:305–309. doi:10.1007/BF01997792
Gläscher J, Adolphs R (2003) Processing of the arousal of subliminal and supraliminal emotional stimuli by the human amygdala. J Neurosci 23:10274–10282
Greenberg T, Carlson JM, Cha J, Hajcak G, Mujica-Parodi LR (2013) Ventromedial prefrontal cortex reactivity is altered in generalized anxiety disorder during fear generalization. Depress Anxiety 30:242–250. doi:10.1002/da.22016
Groenink L, Joordens RJ, Hijzen TH, Dirks A, Olivier B (2000) Infusion of flesinoxan into the amygdala blocks the fear-potentiated startle. Neuroreport 11:2285–2288
Harris AD, Puts NA, Edden RA (2015) Tissue correction for GABA-edited MRS: considerations of voxel composition, tissue segmentation, and tissue relaxations. J Magn Reson Imaging 42:1431–1440. doi:10.1002/jmri.24903
Henry PG, Dautry C, Hantraye P, Bloch G (2001) Brain GABA editing without macromolecule contamination. Magn Reson Med 45:517–520
Horn DI, Yu C, Steiner J, Buchmann J, Kaufmann J, Osoba A, Eckert U, Zierhut KC, Schiltz K, He H, Biswal B, Bogerts B, Walter M (2010) Glutamatergic and resting-state functional connectivity correlates of severity in major depression—the role of pregenual anterior cingulate cortex and anterior insula. Front Syst Neurosci. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2010.00033
Horner MD, Teichner G, Kortte KB, Harvey RT (2002) Construct validity of the Babcock Story recall test. Appl Neuropsychol 9:114–116. doi:10.1207/S15324826AN0902_7
Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM (2012) FSL. Neuroimage 62:782–790. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
Johnstone T, van Reekum CM, Urry HL, Kalin NH, Davidson RJ (2007) Failure to regulate: counterproductive recruitment of top-down prefrontal-subcortical circuitry in major depression. J Neurosci 27:8877–8884. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2063-07.2007
Kapogiannis D, Reiter DA, Willette AA, Mattson MP (2013) Posteromedial cortex glutamate and GABA predict intrinsic functional connectivity of the default mode network. Neuroimage 64:112–119. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.029
Kim H, Somerville LH, Johnstone T, Alexander AL, Whalen PJ (2003) Inverse amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex responses to surprised faces. Neuroreport 14:2317–2322. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000101520.44335.20
Kim MJ, Loucks RA, Palmer AL, Brown AC, Solomon KM, Marchante AN, Whalen PJ (2011) The structural and functional connectivity of the amygdala: from normal emotion to pathological anxiety. Behav Brain Res 223:403–410. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.04.025
Kragel PA, LaBar KS (2016) Decoding the Nature of Emotion in the Brain. Trends Cogn Sci 20:444–455. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2016.03.011
Krettek JE, Price JL (1978) A description of the amygdaloid complex in the rat and cat with observations on intra-amygdaloid axonal connections. J Comp Neurol 178:255–280. doi:10.1002/cne.901780205
Li B, Daunizeau J, Stephan KE, Penny W, Hu D, Friston K (2011) Generalised filtering and stochastic DCM for fMRI. Neuroimage 58:442–457. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.01.085
Likhtik E, Pelletier JG, Paz R, Paré D (2005) Prefrontal control of the amygdala. J Neurosci 25:7429–7437. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2314-05.2005
Magni E, Binetti G, Bianchetti A, Rozzini R, Trabucchil M (1996a) Mini-Mental State Examination: a normative study in Italian elderly population. Eur J Neurol 3:198–202. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.1996.tb00423.x
Makovac E, Meeten F, Watson DR, Herman A, Garfinkel SN, D Critchley H, Ottaviani C (2016) Alterations in amygdala-prefrontal functional connectivity account for excessive worry and autonomic dysregulation in generalized anxiety disorder. Biol Psychiatry 80:786–795. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.10.013
Mandal MK, Tandon SC, Asthana HS (1991) Right brain damage impairs recognition of negative emotions. Cortex 27:247–253
Markowitsch HJ (1998) Differential contribution of right and left amygdala to affective information processing. Behavioral. Neurology 11:233–244
McDonald AJ (1998) Cortical pathways to the mammalian amygdala. Prog Neurobiol 55:257–332. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(98)00003-3
McKlveen JM, Morano RL, Fitzgerald M, Zoubovsky S, Cassella SN, Scheimann JR, Ghosal S, Mahbod P, Packard BA, Myers B, Baccei ML, Herman JP (2016) Chronic stress increases prefrontal inhibition: a mechanism for stress-induced prefrontal dysfunction. Biol Psychiatry 80(10):754–764. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.03.2101
Mochcovitch MD, da Rocha Freire RC, Garcia RF, Nardi AE (2014) A systematic review of fMRI studies in generalized anxiety disorder: evaluating its neural and cognitive basis. J Affect Disord 167:336–342. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2014.06.041
Moscarello JM, LeDoux JE (2013) Active avoidance learning requires prefrontal suppression of amygdala-mediated defensive reactions. J Neurosci 33:3815–3823. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2596-12.2013
Mullins PG, McGonigle DJ, O’Gorman RL, Puts NA, Vidyasagar R, Evans CJ, Edden RA (2014) Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA. Neuroimage 86:43–52. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.12.004
Muthukumaraswamy SD, Evans CJ, Edden RA, Wise RG, Singh KD (2012) Individual variability in the shape and amplitude of the BOLD-HRF correlates with endogenous GABAergic inhibition. Hum Brain Mapp 33:455–465. doi:10.1002/hbm.21223
Near J, Edden R, Evans CJ, Paquin R, Harris A, Jezzard P (2015) Frequency and phase drift correction of magnetic resonance spectroscopy data by spectral registration in the time domain. Magn Reson Med 73:44–50. doi:10.1002/mrm.25094
Northoff G, Walter M, Schulte RF, Beck J, Dydak U, Henning A, Boeker H, Grimm S, Boesiger P (2007) GABA concentrations in the human ACC predict negative BOLD responses in fMRI. Nat Neurosci 10:1515–1517. doi:10.1038/nn2001
Nuss P (2015) Anxiety disorders and GABA neurotransmission: a disturbance of modulation. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:165–175. doi:10.2147/NDT.S58841
Ochsner KN, Knierim K, Ludlow DH, Hanelin J, Ramachandran T, Glover G, Mackey SC (2004) Reflecting upon feelings: an fMRI study of neural systems supporting the attribution of emotion to self and other. J Cogn Neurosci 16:1746–1772. doi:10.1162/0898929042947829
Oppenheimer DM (2008) The secret life of fluency. Trends Cogn Sci 12:237–241. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2008.02.014
Palomero-Gallagher N, Mohlberg H, Zilles K, Vogt B (2008) Cytology and receptor architecture of human anterior cingulate cortex. J Comp Neurol 508:906–926. doi:10.1002/cne.21684
Palomero-Gallagher N, Zilles K, Schleicher A, Vogt BA (2013) Cyto- and receptor architecture of area 32 in human and macaque brains. J Comp Neurol 521:3272–3286. doi:10.1002/cne.23346
Phillips ML, Ladouceur CD, Drevets WC (2008) A neural model of voluntary and automatic emotion regulation: implications for understanding the pathophysiology and neurodevelopment of bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry 13:833–857. doi:10.1038/mp.2008.65
Power JD, Barnes KA, Snyder AZ, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2012) Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 59:2142–2154. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.018
Quirk GJ, Gehlert DR (2003) Inhibition of the amygdala: key to pathological states? Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:263–272. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07087.x
Rae CD (2014) A guide to the metabolic pathways and function of metabolites observed in human brain 1 H magnetic resonance spectra. Neurochem Res 39:1–36. doi:10.1007/s11064-013-1199-5
Razi A, Kahan J, Rees G, Friston KJ (2015) Construct validation of a DCM for resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 106:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.11.027
Robinson OJ, Charney DR, Overstreet C, Vytal K, Grillon C (2012) The adaptive threat bias in anxiety: amygdala-dorsomedial prefrontal cortex coupling and aversive amplification. Neuroimage 60:523–529. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011
Rothman DL, Behar KL, Prichard JW, Petroff OA (1997) Homocarnosine and the measurement of neuronal pH in patients with epilepsy. Magn Reson Med 38:924–929. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910380611
Roy AK, Shehzad Z, Margulies DS, Kelly AM, Uddin LQ, Gotimer K, Biswal BB, Castellanos FX, Milham MP (2009) Functional connectivity of the human amygdala using resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 45:614–626. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.030
Rule RR, Shimamura AP, Knight RT (2002) Orbitofrontal cortex and dynamic filtering of emotional stimuli. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2:264–270. doi:10.3758/CABN.2.3.264
Russchen FT (1982) Amygdalopetal projections in the cat. I. Cortical afferent connections. A study with retrograde and anterograde tracing techniques. J Comp Neurol 206:159–179
Sergerie K, Chochol C, Armony JL (2008) The role of the amygdala in emotional processing: a quantitative meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:811–830. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2007.12.002
Sesack SR, Deutch AY, Roth RH, Bunney BS (1989) Topographical organization of the efferent projections of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tract-tracing study with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 290:213–242
Shin MS, Park SY, Park SR, Seol SH, Kwon JS (2006) Clinical and empirical applications of the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test. Nat Protoc 1:892–899. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.115
Sladky R, Höflich A, Küblböck M, Kraus C, Baldinger P, Moser E, Lanzenberger R, Windischberger C (2015) Disrupted effective connectivity between the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex in social anxiety disorder during emotion discrimination revealed by dynamic causal modeling for fMRI. Cereb Cortex 25:895–903. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht279
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23:S208–S219. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
Somerville LH, Wagner DD, Wig GS, Moran JM, Whalen PJ, Kelley WM (2013) Interactions between transient and sustained neural signals support the generation and regulation of anxious emotion. Cereb Cortex 23:49–60. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr373
Spielberger CD (1983) Manual for the state–trait anxiety inventory STAI (Form Y). Mind Garden, Palo Alto
Stagg CJ, Bachtiar V, Amadi U, Gudberg CA, Ilie AS, Sampaio-Baptista C, O'Shea J, Woolrich M, Smith SM, Filippini N, Near J, Johansen-Berg H (2014) Local GABA concentration is related to network-level resting functional connectivity. eLife 3:e01465. doi:10.7554/eLife.01465
Taylor JM, Whalen PJ (2015) Neuroimaging and anxiety: the neural substrates of pathological and non-pathological anxiety. Curr Psychiatry Rep 17:49. doi:10.1007/s11920-015-0586-9
Urry HL, van Reekum CM, Johnstone T, Kalin NH, Thurow ME, Schaefer HS, Jackson CA, Frye CJ, Greischar LL, Alexander AL, Davidson RJ (2006) Amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex are inversely coupled during regulation of negative affect and predict the diurnal pattern of cortisol secretion among older adults. J Neurosci 26:4415–4425. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3215-05.2006
Wechsler D (1939) The measurement of adult intelligence. Williams & Wilkins Co, Baltimore
Wright CI, Martis B, Schwartz CE, Shin LM, Fischer HH, McMullin K et al (2003) Novelty responses and differential effects of order in the amygdala, substantia innominata, and inferior temporal cortex. Neuroimage 18:660–669
Zald DH, Donndelinger MJ, Pardo JV (1998) Elucidating dynamic brain interactions with across-subjects correlational analyses of positron emission tomographic data: the functional connectivity of the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex during olfactory tasks. J Cereb Blood Flow 18:896–905
Acknowledgements
The work has been supported by the Italian Ministry of Health (Grant No. GR-2010-2313418) and the Wellcome Trust (Grant No. 101253/A/13/Z). This study applies tools developed under NIH R01 EB016089 and P41 EB015909; RAEE also receives salary support from these grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In the original publication of this article, the family name co-author has been published incorrectly; this error has now been corrected.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1446-7.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
429_2017_1399_MOESM1_ESM.tiff
Supplementary figure 1. Representative GANNET-edited MR spectra showing the GABA peak (in red). Abbreviations: GABA=γ-Aminobutyric acid (3.02 ppm); mPFC=medial prefrontal cortex (TIFF 12 KB)
429_2017_1399_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Supplementary figure 2. Scatterplots displaying the relationship a GABA+/tCr content and effective connectivity. The strength of the effective connectivity is reported in Hz. FDR p values are reported for each correlation. Abbreviations: The wordings “mPFC-mPFC” and “AMG-AMG” refer to the intrinsic connectivity within mPFC and amygdala, respectively. RAMG=right amygdala; LAMG=left amygdala; mPFC=medial prefrontal cortex (TIFF 185 KB)
429_2017_1399_MOESM3_ESM.tiff
Supplementary figure 3. Scatterplots displaying the relationship among effective connectivity and STAI-Y1. The strength of the effective connectivity is reported in Hz. FDR p values are reported for each correlation. Abbreviations: The wordings “mPFC-mPFC” and “AMG-AMG” refer to the intrinsic connectivity within mPFC and amygdala, respectively. RAMG=right amygdala; LAMG=left amygdala; mPFC=medial prefrontal cortex (TIFF 61 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delli Pizzi, S., Chiacchiaretta, P., Mantini, D. et al. GABA content within medial prefrontal cortex predicts the variability of fronto-limbic effective connectivity. Brain Struct Funct 222, 3217–3229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1399-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1399-x