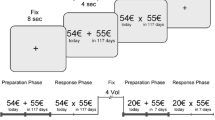
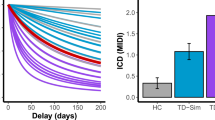
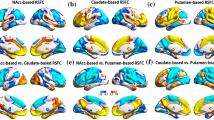
Abstract
The steepness of the delay discounting function shows considerable interindividual differences. Moreover, faster devaluation of future rewards has been consistently observed in pathological gamblers (PGs). Here, we asked whether variability in delay discounting is at least partially driven by differences in the anatomy of gray and white matter. For 40 healthy young subjects (study 1) as well as 15 PG and 15 age-matched healthy controls (HCs, study 2), the individual discounting parameter k was obtained. Based on 3D T1-weighted high-resolution magnetic resonance scans and diffusion tensor imaging, we performed voxel-based morphometry and tract-based spatial statistics, respectively, to examine the relation of gray matter volume (GMV) and white matter properties (as indicated by fractional anisotropy, FA) to k. Healthy groups from both studies showed a negative correlation between k and FA for the superior longitudinal fascicle and inferior longitudinal fascicle, whereas a positive correlation was found in the PG group for the inferior longitudinal fascicle and left inferior fronto-occipital fascicle. The latter also was significantly different between HC and PG in the group statistics (albeit on the right side), thus suggesting that this is a significant structure for the development of pathological gambling. GMV of the right frontal orbital cortex, left insular cortex and right lateral occipital cortex showed a positive correlation to k HC (studies 1 and 2) and PG, whereas a negative correlation was found for the left frontal pole in all three groups. Group comparison of GMV (study 2) revealed a decrease in PG for several cortical and subcortical areas.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSM IV:
-
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual IV
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- EPI:
-
Echo planar imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- FWHM:
-
Full width half maximum
- HC:
-
Healthy control
- KFG:
-
Kurzfragebogen zum Glücksspielverhalten (German gambling questionnaire)
- LDR:
-
Large delayed reward
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- PG:
-
Pathological gambler
- SIR:
-
Small immediate reward
- SOGS:
-
South Oaks Gambling Screen
- TBSS:
-
Tract-based spatial statistics
- VBM:
-
Voxel-based morphometry
References
Alessi SM, Petry NM (2003) Pathological gambling severity is associated with impulsivity in a delay discounting procedure. Behav Process 64:345–354
Amiez C, Joseph JP, Procyk E (2006) Reward encoding in the monkey anterior cingulate cortex. Cereb Cortex 16:1040–1055
Andersson JLR, Jenkinson M, Smith S (2007a) Non-linear optimisation. FMRIB technical report TR07JA1 from www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/techrep
Andersson JLR, Jenkinson M, Smith S (2007b) Non-linear registration, aka Spatial normalization. FMRIB technical report TR07JA2 from www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/techrep
Anokhin AP, Golosheykin S, Grant JD, Heath AC (2011) Heritability of delay discounting in adolescence: a longitudinal twin study. Behav Genet 41:175–183
Ashburner J, Friston K (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. NeuroImage 11:805–821
Ashtari M, Cervellione K, Cottone J, Ardekani B, Sevy S, Kumra S (2009) Diffusion abnormalities in adolescents and young adults with a history of heavy cannabis use. J Psychiat Res 43:189–204
Basser PJ, Jones DK (2002) Diffusion-tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis: a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:456–467
Beaulieu C (2002) The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system: a technical review. NMR Biomed 15:435–455
Brevers D, Cleeremans A, Verbruggen F, Bechara A, Kornreich C, Verbanck P, Noël X (2012) Impulsive action but not impulsive choice determines problem gambling severity. PLoS One 7:e50647
Camara E, Rodriguez-Fornells A, Münte TF (2010) Microstructural brain differences predict functional hemodynamic responses in a reward processing task. J Neurosci 30:11398–11402
Cho SS, Pellecchia G, Aminian K, Ray N, Segura B, Obeso I, Strafella AP (2013) Morphometric correlation of impulsivity in medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Topogr 26:479–487
Dixon MR, Marley J, Jacobs EA (2003) Delay discounting by pathological gamblers. J Appl Behav Anal 36:449–458
Dixon MR, Jacobs EA, Sanders S (2006) Contextual control of delay discounting by pathological gamblers. J Appl Behav Anal 39:413–422
Frederick S, Loewenstein G, O’Donoghue T (2002) Time discounting and time preference: a critical review. J Economic Lit 40:351–401
Frederick S, Loewenstein G, O’Donoghue T (2003) Time discounting and time preference: A critical review. In: Loewenstein G, Read D, Baumeister R (eds) Time and decision: economic and psychological perspectives on intertemporal choice. Sage, New York, pp 13–86
Good C, Johnsrude I, Ashburner J, Henson R, Friston K, Frackowiak R (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. NeuroImage 14:21–36
Grant JE, Potenza MN (2004) Pathological gambling: a clinical guide to treatment. American Psychiatric Publishing Inc, Washington, DC
Jacobus J, McQueeny T, Bava S, Schweinsburg B, Frank L, Yang T, Tapert S (2009) White matter integrity in adolescents with histories of marijuana use and binge drinking. Neurotox Teratol 31:349–355
Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5:143–156
Jenkinson M, Bannister PR, Brady JM, Smith SM (2002) Improved optimisation for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage 17:825–841
Joutsa J, Saunavaara J, Parkkola R, Niemelä S, Kaasinen V (2011) Extensive abnormality of brain white matter integrity in pathological gambling. Psychiatry Res 194:340–346
Kalenscher T, Pennartz CMA (2008) Is a bird in the hand worth two in the future? The neuroeconomics of intertemporal decision-making. Prog Neurobiol 84:284–315
Kalenscher T, Windmann S, Diekamp B, Rose J, Güntürkün O, Colombo M (2005) Single units in the pigeon brain integrate reward amount and time-to-reward in an impulsive choice task. Curr Biol 15:594–602
Kirby KN, Petry NM, Bickel WK (1999) Heroin addicts have higher discount rates for delayed rewards than non-drug-using controls. J Exp Psychol Gen 128:78–87
Koehler S, Hasselmann E, Wüstenberg T, Heinz A, Romanczuk-Seiferth N (2013) Higher volume of ventral striatum and right prefrontal cortex in pathological gambling. Brain Struct Funct [Epub ahead of print]
Kräplin A, Dshemuchadse M, Behrendt S, Scherbaum S, Goschke T, Bühringer G (2014) Dysfunctional decision-making in pathological gambling: pattern specificity and the role of impulsivity. Psychiatry Res 215:675–682
Kuhnen CM, Knutson B (2005a) The neural basis of financial risk taking. Neuron 47:763–770
Kuhnen CM, Knutson B (2005b) The neural basis of financial risk taking. Neuron 47(5):763–770
Lane S, Steinberg J, Ma L, Hasan K, Kramer L, Zuniga E, Narayana P, Moeller F (2010) Diffusion tensor imaging and decision making in cocaine dependence. PloS One 5:e11591
Lesieur HR, Blume SB (1987) The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): a new instrument for the identification of Pathological gamblers. Am J Psychiat 144:1184–1188
Lim KO, Wozniak JR, Mueller BA, Franc DT, Specker SM, Rodriguez CP, Silverman AB, Rotrosen JP (2008) Brain macrostructural and microstructural abnormalities in cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 92:164–172
Marco-Pallares J, Mohammadi B, Samii A, Münte TF (2010) Brain activations reflect individual discount rates in intertemporal choice. Brain Res 1320:123–129
Mazur JE (1984) Tests of an equivalence rule for fixed and variable reinforcer delays. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 10:426–436
McClure SM, Laibson DI, Loewenstein G, Cohen JD (2004) Separate neural systems value immediate and delayed monetary rewards. Science 306:503–507
Miedl SF, Fehr T, Meyer G, Herrmann M (2010) Neurobiological correlates of problem gambling in a quasi-realistic blackjack scenario as revealed by fMRI. Psychiatry Res 181:165–173
Miedl SF, Peters J, Büchel C (2012) Altered neural reward representations in pathological gamblers revealed by delay and probability discounting. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69:177–186
Milenkova M, Mohammadi B, Kollewe K, Schrader C, Fellbrich A, Wittfoth M, Dengler R, Münte TF (2011) Intertemporal choice in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:2004–2010
Mitchell SH (1999) Measures of impulsivity in cigarette smokers and non-smokers. Psychopharmacology 146:455–464
Mitchell JM, Fields HL, D’Esposito M, Boettiger CA (2005) Impulsive responding in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:2158–2169
Papadakis NG, Xing D, Huang CL, Hall LD, Carpenter TA (1999) A comparative study of acquisition schemes for diffusion tensor imaging using MRI. J Magn Reson 137:67–82
Peper JS, Mandl RCW, Braams BR, de Water E, Heijboer AC, Koolschijn PCMP, Crone EA (2013) Delay discounting and frontostriatal fiber tracts: a combined DTI and MTR study on impulsive choices in healthy young adults. Cerebral Cortex 23:1695–1702
Peters J, Büchel C (2011) The neural mechanisms of inter-temporal decision-making: understanding variability. Trends Cogn Sci 15:227–239
Petry J (1996) Psychotherapie der Glücksspielsucht. Beltz, Weinheim
Petry NM (2001a) Delay discounting of money and alcohol in actively using alcoholics, currently abstinent alcoholics, and controls. Psychopharmacology 154:243–250
Petry NM (2001b) Pathological gamblers, with and without substance use disorders, discount delayed rewards at high rates. J Abnorm Psychol 110:482–487
Pfefferbaum A, Rosenbloom M, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV (2009) Degradation of association and projection white matter systems in alcoholism detected with quantitative fiber tracking. Biol Psychiat 65:680–690
Preuschoff K, Quartz SR, Bossaerts P (2008) Human insula activation reflects risk prediction errors as well as risk. J Neurosci 28:2745–2752
Reynolds B, Richards JB, Horn K, Karraker K (2004) Delay discounting and probability discounting as related to cigarette smoking status in adults. Behav Processes 65:35–42
Rolls ET (2004) The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cogn 55:11–29
Rueckert D, Sonoda LI, Hayes C, Hill DL, Leach MO, Hawkes DJ (1999) Nonrigid registration using free-form deformations: application to breast MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18:712–721
Sarubbo S, De Benedictis A, Maldonado IL, Basso G, Duffau H (2013) Frontal terminations for the inferior fronto-occipital fascicle: anatomical dissection, DTI study and functional considerations on a multi-component bundle. Brain Struct Funct 218:21–37
Skare S, Hedehus M, Moseley ME, Li TQ (2000) Condition number as a measure of noise performance of diffusion tensor data acquisition schemes with MRI. J Magn Reson 147:340–352
Smith S (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155
Smith S, Nichols T (2009) Threshold-free cluster enhancement: addressing problems of smoothing, threshold dependence and localisation in cluster inference. NeuroImage 44:83–98
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Johansen-Berg H, Rueckert D, Nichols TE, Mackay CE, Watkins KE, Ciccarelli O, Cader MZ, Matthews PM, Behrens TE (2006) Tract-based spatial statistics: voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 31:1487–1505
Waxman SG, Bennett MV (1972) Relative conduction velocities of small myelinated and non-myelinated fibres in the central nervous system. Nat New Biol 238:217–219
Weng CB, Qian RB, Fu XM, Lin B, Han XP, Niu CS, Wang YH (2013) Gray matter and white matter abnormalities in online game addiction. Eur J Radiol 82:1308–1312
Wiehler A, Peters J (2014) Reward-based decision making in pathological gambling: the roles of risk and delay. Neurosci Res. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2014.09.008
Wittchen H-U, Zaudig M, Fydrich T (1997) Strukturiertes Klinisches Interview für DSM-IV. Hogrefe, Göttingen
Xu J, DeVito EE, Worhunsky PD, Carroll KM, Rounsaville BJ, Potenza MN (2010) White matter integrity is associated with treatment outcome measures in cocaine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:1541–1549
Xue G, Lu Z, Levin IP, Bechara A (2010) The impact of prior risk experiences on subsequent risky decision-making: the role of the insula. NeuroImage 50:709–716
Yeh PH, Simpson K, Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Meyerhoff DJ (2009) Tract-Based Spatial Statistics (TBSS) of diffusion tensor imaging data in alcohol dependence: abnormalities of the motivational neurocircuitry. Psychiatry Res 173:22–30
Yip SW, Lacadie C, Xu J, Worhunsky PD, Fulbright RK, Constable RT, Potenza MN (2013) Reduced genual corpus callosal white matter integrity in pathological gambling and its relationship to alcohol abuse or dependence. World J Biol Psychiatry 14:129–138
Zhang Y, Brady M, Smith S (2001) Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:45–57
Acknowledgments
TFM and MH are supported by grants of the DFG and BMBF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B. Mohammadi and A. Hammer.contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, B., Hammer, A., Miedl, S.F. et al. Intertemporal choice behavior is constrained by brain structure in healthy participants and pathological gamblers. Brain Struct Funct 221, 3157–3170 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1093-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-015-1093-9