Abstract
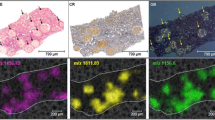
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is one of the most diffuse glomerulonephrites worldwide, and many issues still remain regarding our understanding of its pathogenesis. The disease is diagnosed by renal biopsy examination, but potential pitfalls still persist with regard to discriminating its primary origin and, as a result, determining patient outcome remains challenging. In this pilot study, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) was performed on renal biopsies obtained from patients with IgAN (n = 11) and other mesangioproliferative glomerulonephrites (MesPGN, n = 6) in order to enlighten proteomic alterations that may be associated with the progression of IgAN. Differences in the proteomic profiles of IgAN and MesPGN tissue could clearly be detected using this approach and, furthermore, 14 signals (AUC ≥ 0.8) were observed to have an altered intensity among the different CKD stages within the IgAN group. In particular, large increases in the intensity of these signals could be observed at CKD stages II and above. These signals primarily corresponded to proteins involved in either inflammatory and healing pathways and their increased intensity was localized within regions of tissue with large amounts of inflammatory cells or sclerosis. Despite much work in recent years, our molecular understanding of IgAN progression remains incomplete. This pilot study represents a promising starting point in the search for novel protein markers that can assist clinicians in better understanding the pathogenesis of IgAN and highlighting those patients who may progress to end-stage renal disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glassock RJ (2010) IgA nephropathy and Henoch-Schonlein nephritis. In: Floege J, Johnson RJ, Feehaly J (eds) Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 270–281
Tomino Y (2016) Pathogenesis and treatment in IgA nephropathy. Springer, Tokyo
KDIGO (2012) clinical practice guidelines for glomerulonephritis. Chapter 1: introduction. Kidney Int Suppl 2(2):156–162 http://www.kdigo.org/clinical_practice_guidelines/pdf/KDIGO-GN-Guideline.pdf
KDIGO (2012) clinical practice guidelines for glomerulonephritis. Chapter 2: general principles in the management of glomerular disease. Kidney Int Suppl 2(2):156–162 http://www.kdigo.org/clinical_practice_guidelines/pdf/KDIGO-GN-Guideline.pdf
Bartosik LP, Lajoie G, Sugar L, Cattran DC (2001) Predicting progression in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 38:728–735
Feehally J (2001) Predicting prognosis in IgA nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis 38(4):728–735
Floege J, Boor P, Moeller MJ (2018) Was ist gesichert in der Therapie der Glomerulonephritis? Internist (Berl) 59:1268–1278
Cook TH (2007) Interpretation of renal biopsies. in IgA nephropathy. In: Tomino Y (ed) IgA Nephropathy Today. Contrib Nephrol, vol 157. Karger, Basel, pp 44–49
Yeo SC, Cheung CK, Barratt J (2018) New insights into the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 33:763–777
Schena FP, Cox SN (2018) Biomarkers and precision medicine in IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 38:521–530
Coppo R (2016) Biomarkers and targeted new therapies for IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 32:725–731
Smith A, L'Imperio V, Ajello E, Ferrario F, Mosele N, Stella M, Galli M, Chinello C, Pieruzzi F, Spasovski G, Pagni F, Magni F (2017) The putative role of MALDI-MSI in the study of membranous nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta, Proteins Proteomics 1865:865–874
Vlahou A, Mischak H, Zoidakis J, Magni F (2018) Integration of omics approaches and system biology for clinical applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Krochmal M, Cisek K, Filip S, Markoska K, Orange C, Zoidakis J, Gakiopoulou C, Mischak H, Delles C, Vlahou A, Jankowski J (2017) Identification of novel molecular signatures of IgA nephropathy through an integrative -omics analysis. Sci Rep 7:9091
Mainini V, Pagni F, Ferrario F, Pieruzzi F, Grasso M, Stella A, Cattoretti G, Magni F (2014) MALDI imaging mass spectrometry in glomerulonephritis: feasibility study. Histopathology 64:901–906
L'Imperio V, Smith A, Ajello E, Piga I, Stella M, Denti V, Tettamanti S, Sinico RA, Pieruzzi F, Garozzo M, Vischini G, Nebuloni M, Pagni F, Magni M (2018) MALDI-MSI pilot study highlights glomerular deposits of macrophage migration inhibitory factor as a possible indicator of response to therapy in membranous nephropathy. Proteomics Clin Appl https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/prca.201800019. Accessed October 2019
De Sio G, Smith A, Galli M, Grancini M, Chinello C, Bono F, Pagni F, Magni F (2015) A MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging method applicable to different formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissues. Mol Byosyst 11:1507–1514
Smith A, L’imperio V, Denti V, Mazza M, Ivanova M, Stella M, Piga I, Chinello C, Ajello E, Pieruzzi F, Pagni F, Magni F (2018) High spatial resolution MALDI-MS imaging in the study of membranous nephropathy. Proteomics Clin Appl https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/prca.201800016. Accessed October 2019
Trimarchi H, Barrat J, Cattran DC, Cook HT, Coppo R, Haas M, Liu ZH, Roberts IS, Yuzawa Y, Zhang H, Feehaly J (2017) IgA nephropathy Oxford Classification update. Kidney Int 91:1014–1021
Sethi S, D’Agati VD, Nast CC, Fogo AB, De Vriese AS, Markowitz GS, Glassock RJ, Fervenza FC, Seshan SV, Rule A, Racusen LC, Radhakrishan J, Winearls CG, Appel GB, Bajema IM, Chang A, Colvin RB, Cook TH, Hariharan S, Herrera Hernandez LP, Kambham N, Mengel M, Nath KA, Rennke HG, Ronco P, Rovin BH, Haas M (2017) A proposal for standardized grading of chronic changes in native kidney specimen. Kidney Int 91:787–789
McDonnel LA, Walch A, Stoeckli M, Corthals GL (2014) MsiMass list: a public database of identifications for protein MALDI MS imaging. J Proteome Res 13:1138–1142
Colvin R (2011) Diagnostic pathology. Kidney diseases. Amyrsys, Manitoba
Barbour SJ, Espino-Hernandez G, Reich HN, Coppo R, Roberts IS, Feehally J, Herzenberg AM, Cattran DC (2016) VALIGA; Oxford derivation and North American validation The MEST score provides earlier risk prediction in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 89:167–175
Levey AS, De Jong PE, Coresh J, El Nahas M, Astor BC, Matsushita K, Gansevoort RT, Kasiske BL, Eckardt KU (2011) The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: a KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int 80:17–28
Gutierrez E (2019) IgA Nephropathy: is a new approach beyond proteinuria necessary? Pediatr Nephrol 34:921–924
Ivanova M (2012) Immunohistochemical markers of interstitial fibrosis in primary proliferative glomerulonephritis, Abstracts of the international scientific & practical conference, dedicated to the World Health Day. Ukr Sci Med Youth J 1:228
Li H, Han J, Pan J, Liu T, Parker CE, Borchers CH (2017) Current trends in quantitative proteomics – an update. J Mass Spectrom 52:319–341
Schena FP, Serino G, Sallustio F, Falchi M, Cox SN (2018) Omics studies for comprehensive understanding of immunoglobulin A nephropathy: state-of-the-art and future directions. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33:2101–2112
Prikryl P, Vojtova L, Maixnerova D, Vokurka M, Neprasova M, Zima T, Tesar V (2017) Proteomic approach for identification of IgA nephropathy-related biomarkers in urine. Physiol Res 66:621–632
Smith A, L'Imperio V, De Sio G, Ferrario F, Scalia C, Dell'Antonio G, Pieruzzi F, Pontillo C, Filip S, Markoska K, Granata A, Spasovski G, Jankowski J, Capasso G, Pagni F, Magni F (2016) α-1-antitrypsin detected by MALDI imaging in the study of glomerulonephritis: its relevance in chronic kidney disease progression. Proteomics 16:1759–1766
Ivanova M, Dyadyk O, Smith A, Santorelli L, Stella M, Galli M, Chinello C, Magni F (2017) Proteomics and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ ionization mass spectrometry imaging as a modern diagnostic tool in kidney diseases. Pochki 6:25–30
Minz RW, Bakshi A, Chhabra S, Joshi K, Sakhuja V (2010) Role of myofibroblasts and collagen type IV in patients of IgA nephropathy as markers of renal dysfunction. Indian J Nephrol 20:34–39
Stribos EGD, Nielsen SH, Brix S, Karsdal MA, Seelen MA, van Goor H, Bakker SJL, Olinga P, Mutsaers HAM, Genovese F (2017) Non-invasive quantification of collagen turnover in renal transplant recipients. PLoS ONE 12(4):e0175898. http://sci-hub.tw/10.1371/journal.pone.0175898
Djudjaj S, Papasotiriou M, Bülow RD, Wagnerova A, Lindenmeyer MT, Cohen CD, Strnad P, Goumenos DS, Floege J, Boor P (2018) Keratins are novel markers of renal epithelial cell injury. Kidney Int 89:792–808
Lindemeyer MT, Rastaldi MP, Ikehata M et al (2008) Proteinuria and hyperglycemia Induce endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:2225–2236
Yao J, Kez WX, Peng F, Li B, Wu R (2014) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells are associated with disease progression in patients with IgA nephropathy. Mol Med Rep 10:39–44
Monestier M, Fasy TM, Novick KE, Losman MJ, Rigal D, Wong GY, Terzidis-Trabelsi H, Pilatte Y, Rostoker G (1994) Histone-reactive IgA antibodies in adult IgA nephropathy and other primary glomerulonephritis. Nephron 68:25–31
Kumar SV, Kulkarni OP, Mulay SR et al (2015) Neutrophil extracellular trap-related extracellular histones cause vascular necrosis in severe GN. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:2399–2413
Van Dam LS, Rabelink TJ, van Kooten C, Teng YKO (2018) Clinical implications of excessive neutrophil extracellular trap formation in renal autoimmune diseases. Kidney Int Rep 19:196–211
Malek V, Sharma N, Gaikwad AB (2019) Histone acetylation regulates natriuretic peptides and neprilysin gene expressions in diabetic cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. Curr Mol Pharmacol 12:61–71
Hadden MJ, Advani A (2019) Histone deacetylase inhibitors and diabetic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 19. http://sci-hub.tw/10.3390/ijms19092630
Feng Z, Tang L, Wu L, Cui S, Hong Q, Cai G, Wu D, Fu B, Wei R, Chen X (2014) Na+/H+ exchanger-1 reduces podocyte injury caused by endoplasmic reticulum stress via autophagy activation. Lab Investig 94:439–454
Wilson PC, Kashgarian M, Moeckel G (2018) Interstitial inflammation and interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy predict renal survival in lupus nephritis. Clin Kidney J 11:207–218
Bruchfeld A, Wendt M, Miller EJ (2016) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in clinical kidney disease. Front Immunol 7:8. http://sci-hub.tw/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00008
Boor P (2018) MIF in kidney diseases. Der Pathol 40:25–30. http://sci-hub.tw/10.1007/s00292-018-0548-1
Djudjaj S, Lue H, Rong S, Papasotiriou M, Klinkhammer BM, Zok S, Klaener O, Braun GS, Lindenmeyer MT, Cohen CD, Bucala R, Tittel AP, Kurts C, Moeller MJ, Floege J, Ostendorf T, Bernhagen J, Boor P (2016) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor mediates proliferative GN via CD74. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:1650–1664
Smith A, Piga I, Galli M, Stella M, Denti V, Del Puppo M, Magni F (2017) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry imaging in the study of gastric cancer: a mini review. Int J Mol Sci 18:2588. http://sci-hub.tw/10.3390/ijms18122588
Galli M, Pagni F, De Sio G, Smith A, Chinello C, Stella M, L’imperio V, Manzoni M, Garancini M, Massimini D, Mosele N, Mauri G, Zoppis I, Magni F (2017) Proteomic profiles of thyroid tumors by mass spectrometry-imaging on tissue microarrays. Biochim Biophys Acta, Proteins Proteomics 1865:817–827
Funding
The research leading to these results has received funding from the MIUR: FIRB 2007 (RBRN07BMCT_11), FAR 2014–2018, and in part by Fondazione Gigi & Pupa Ferrari Onlus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The appropriate Ethical Committee approved the collection of these specimens, and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanova, M., Dyadyk, O., Ivanov, D. et al. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging to uncover protein alterations associated with the progression of IgA nephropathy. Virchows Arch 476, 903–914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-019-02705-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-019-02705-7