Abstract
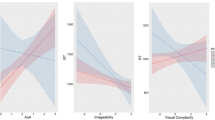
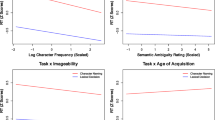
This study aimed to examine the locus of age of acquisition (AoA) and word frequency (WF) effects in Chinese spoken picture naming, using a picture–word interference task. We conducted four experiments manipulating the properties of picture names (AoA in Experiments 1 and 2, while controlling WF; and WF in Experiments 3 and 4, while controlling AoA), and the relations between distractors and targets (semantic or phonological relatedness). Both Experiments 1 and 2 demonstrated AoA effects in picture naming; pictures of early acquired concepts were named faster than those acquired later. There was an interaction between AoA and semantic relatedness, but not between AoA and phonological relatedness, suggesting localisation of AoA effects at the stage of lexical access in picture naming. Experiments 3 and 4 demonstrated WF effects: pictures of high-frequency concepts were named faster than those of low-frequency concepts. WF interacted with both phonological and semantic relatedness, suggesting localisation of WF effects at multiple levels of picture naming, including lexical access and phonological encoding. Our findings show that AoA and WF effects exist in Chinese spoken word production and may arise at related processes of lexical selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Baayen, R. H., Davidson, D. J., & Bates, D. M. (2008). Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. Journal of Memory and Language, 59, 390–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005
Balota, D. A., Cortese, M. J., Sergent-Marshall, S. D., Spieler, D. H., & Yap, M. J. (2004). Visual word recognition of single-syllable words. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 133(2), 283–316. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.133.2.283
Barry, C., Hirsh, K. W., Johnston, R. A., & Williams, C. L. (2001). Age of acquisition, word frequency, and the locus of repetition priming of picture naming. Journal of Memory and Language, 44(3), 350–375. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmla.2000.2743
Bates, D. (2005). Fitting linear mixed models in R. R News, 5(1), Article 5. http://modeloslineales.wdfiles.com/local–files/start/bates_2005.pdf. Accessed Aug 2021
Bonin, P., Fayol, M., & Chalard, M. (2001). Age of acquisition and word frequency in written picture naming. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 54(2), 469–489. https://doi.org/10.1080/713755968
Brown, G. D., & Watson, F. L. (1987). First in, first out: Word learning age and spoken word frequency as predictors of word familiarity and word naming latency. Memory and Cognition, 15(3), 208–216. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03197718
Brysbaert, M., & Ghyselinck, M. (2006). The effect of age of acquisition: Partly frequency related, partly frequency independent. Visual Cognition, 13(7/8), 992–1011. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280544000165
Brysbaert, M., Wijnendaele, I. V., & Deyne, S. D. (2000). Age-of-acquisition effects in semantic processing tasks. Acta Psychologica, 104(2), 215–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0001-6918(00)00021-4
Carroll, J. B., & White, M. N. (1973). Word frequency and age-of-acquisition as determiners of picture-naming latency. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 25(1), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/14640747308400325
Catling, J. C., Dent, K., & Williamson, S. (2008). Age of acquisition, not word frequency affects object recognition: Evidence from the effects of visual degradation. Acta Psychologica, 129(1), 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2008.05.005
Cattell, J. M. (1886). The time it takes to see and name objects. Mind, 11(41), 63–65. https://doi.org/10.2307/2247157
Chang, Y.-N., & Lee, C.-Y. (2020). Age of acquiaition effects on traditional Chinese naming and lexical decision. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 27(6), 1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-020-01787-8
Chang, Y.-N., Welbourne, S., & Lee, C.-Y. (2016). Exploring orthographic neighborhood size effects in a computational model of Chinese character naming. Cognitive Psychology, 91, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogpsych.2016.09.001
Chen, B., Dent, K., You, W., & Wu, G. (2009). Age of acquisition affects early orthographic processing during Chinese character recognition. Acta Psychologica, 130(3), 196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2008.12.004
Chen, B., & Peng, D. (2001). The time course of graphic, phonological and semantic information processing in Chinese character recognition. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 33(1), 1–6.
Chen, B., You, W., & Zhou, W. (2007a). Age of acquisition effects in reading Chinese: Evidence in favor of the semantic hypothesis. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 39(1), 9–17.
Chen, B., Zhou, H., Dunlap, S., & Perfetti, C. A. (2007b). Age of acquisition effects in reading Chinese: Evidence in favour of the arbitrary mapping hypothesis. British Journal of Psychology, 98(3), 499–516. https://doi.org/10.1348/000712606x165484
Chinese Linguistic Data Consortium. (2003). 现代汉语通用词表 [Chinese Lexicon] (CLDC-LAC-2003-001). Tsinghua University, State Key Laboratory of Intelligent Technology and Systems, and Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Automation.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Erlbaum.
Cuetos, F., Alvarez, B., González-Nosti, M., Méot, A., & Bonin, P. (2006). Determinants of lexical access in speech production: Role of word frequency and age of acquisition. Memory and Cognition, 34(5), 999–1010. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193247
Cuetos, F., Barbón, A., Urrutia, M., & Domínguez, A. (2009). Determining the time course of lexical frequency and age of acquisition using ERP. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(2), 285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.11.003
Damian, M. F., & Martin, R. C. (1999). Semantic and phonological codes interact in single word production. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 25(2), 345–361. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.25.2.345
Dang, M., Zhang, R., Wang, X., & Yang, J. (2019). The interaction between phonological and semantic processing in reading Chinese characters. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02748
Dell, G. S. (1990). Effects of frequency and vocabulary type on phonological speech errors. Language and Cognitive Processes, 5(4), 313–349. https://doi.org/10.1080/01690969008407066
Dell’Acqua, R., Sessa, P., Peressotti, F., Mulatti, C., Navarrete, E., & Grainger, J. (2010). ERP evidence for ultra-fast semantic processing in the picture–word interference paradigm. Frontiers in Psychology, 1, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2010.00177
Ellis, A. W., & Lambon Ralph, M. A. (2000). Age of acquisition effects in adult lexical processing reflect loss of plasticity in maturing systems: Insights from connectionist networks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 26(5), 1103–1123. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.26.5.1103
Glaser, W. R., & Düngelhoff, F.-J. (1984). The time course of picture–word interference. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 10(5), 640–654. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-1523.10.5.640
Hao, M., Liu, Y., Shu, H., & Cheng, C. (2003). The role of age of acquisition on picture naming in Chinese. Studies of Psychology and Behavior, 1(4), 268–273.
Indefrey, P. (2011). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components: A critical update. Frontiers in Psychology, 2, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00255
Indefrey, P., & Levelt, W. J. M. (2004). The spatial and temporal signatures of word production components. Cognition, 92(1–2), 101–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2002.06.001
Jeffreys, H. (1961). Theory of Probability (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
Jescheniak, J. D., & Levelt, W. J. M. (1994). Word frequency effects in speech production: Retrieval of syntactic information and of phonological form. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Language, Memory, and Cognition, 20, 824–843. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.20.4.824
Johnston, R. A., & Barry, C. (2006). Age of acquisition and lexical processing. Visual Cognition, 13(7/8), 789–845. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506280544000066
Juhasz, B. J. (2005). Age-of-acquisition effects in word and picture identification. Psychological Bulletin, 131(5), 684–712. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.131.5.684
Laganaro, M., & Perret, C. (2011). Comparing electrophysiological correlates of word production in immediate and delayed naming through the analysis of word age of acquisition effects. Brain Topography, 24(1), 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-010-0162-x
Laganaro, M., Valente, A., & Perret, C. (2012). Time course of word production in fast and slow speakers: A high density ERP topographic study. NeuroImage, 59(4), 3881–3888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.082
Levelt, W. J. M., Roelofs, A., & Meyer, A. S. (1999). A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 22(1), 1–75. https://doi.org/10.3115/992628.992631
Liu, Y., Hao, M., Li, P., & Shu, H. (2011). Timed picture naming norms for Mandarin Chinese. PLoS ONE, 6(1), e16505. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016505
Liu, Y., Hao, M., Shu, H., Tan, L., & Weekes, B. S. (2008). Age-of-acquisition effects on oral reading in Chinese. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 15(2), 344–350. https://doi.org/10.3758/pbr.15.2.344
Liu, Y., Shu, H., & Li, P. (2007). Word naming and psycholinguistic norms: Chinese. Behavior Research Methods, 39(2), 192–198. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03193147
Lou, H., Li, C., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Distinct effects of age of acquisition in Chinese object and action picture naming: An ERP study. Acta Psychologica Sinica, 51(2), 143–153.
Monsell, S. (1991). The nature and locus of word frequency effects in reading. In D. Besner & G. W. Humphreys (Eds.), Basic Processes in Reading: Visual Word Recognition (pp. 148–197). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.
Monaghan, J., & Ellis, A. W. (2002). What exactly interacts with spelling–sound consistency in word naming? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 28(1), 183–206. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.28.1.183
Monaghan, P., & Ellis, A. W. (2010). Modeling reading development: Cumulative, incremental learning in a computational model of word naming. Journal of Memory and Language, 63(4), 506–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2010.08.003
Morey, R. D., Rouder, J. N., & Jamil, T. (2015). BayesFactor: Computation of Bayes factors for common designs. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/BayesFactor/BayesFactor.pdf. Accessed Aug 2021
Morrison, C. M., & Ellis, A. W. (1995). Roles of word frequency and age of acquisition in word naming and lexical decision. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and Cognition, 21(1), 116–133. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.21.1.116
Morrison, C. M., Ellis, A. W., & Quinlan, P. T. (1992). Age of acquisition, not word frequency, affects object naming, not object recognition. Memory and Cognition, 20(6), 705–714. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03202720
Navarrete, E., Basagni, B., Alario, F.-X., & Costa, A. (2006). Does word frequency affect lexical selection in speech production? The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 59(10), 1681–1690. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470210600750558
Oldfield, R. C., & Wingfield, A. (1965). Response latencies in naming objects. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 17(4), 273–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470216508416445
Perret, C., & Bonin, P. (2018). Which variables should be controlled for to investigate picture naming in adults? A Bayesian meta-analysis. Behavior Research Methods, 51, 2533–2545. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-018-1100-1
Perret, C., Bonin, P., & Laganaro, M. (2014). Exploring the multiple-level hypothesis of AoA effects in spoken and written object naming using a topographic ERP analysis. Brain and Language, 135, 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2014.04.006
Perret, C., & Laganaro, M. (2012). Comparison of electrophysiological correlates of writing and speaking: A topographic ERP analysis. Brain Topography, 25(1), 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-011-0200-3
Qu, Q., Zhang, Q., & Damian, M. F. (2016). Tracking the time course of lexical access in orthographic production: An event-related potential study of word frequency effects in written picture naming. Brain and Language, 159, 118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2016.06.008
R Development Core Team. (2013). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. http://www.R-project.org. Accessed Aug 2021
Schriefers, H., Meyer, A. S., & Levelt, W. J. (1990). Exploring the time course of lexical access in language production: Picture–word interference studies. Journal of Memory and Language, 29(1), 86–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-596x(90)90011-n
Starreveld, P. A., & La Heij, W. (1995). Semantic interference, orthographic facilitation, and their interaction in naming tasks. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 21(3), 686–698. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.21.3.686
Starreveld, P. A., & La Heij, W. (1996). Time-course analysis of semantic and orthographic context effects in picture naming. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 22(4), 896–918. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.22.4.896
Sternberg, S. (1969). The discovery of processing stages: Extensions of Donders’method. Acta Psychologica, 30, 276–315.
Steyvers, M., & Tenenbaum, J. B. (2005). The large-scale structure of semantic networks: Statistical analyses and a model of semantic growth. Cognitive Science, 29(1), 41–78. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15516709cog2901_3
Strijkers, K., Costa, A., & Thierry, G. (2010). Tracking lexical access in speech production: Electrophysiological correlates of word frequency and cognate effects. Cerebral Cortex, 20(4), 912–928. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp153
Strijkers, K., Holcomb, P. J., & Costa, A. (2011). Conscious intention to speak proactively facilitates lexical access during overt object naming. Journal of Memory and Language, 65(4), 345–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2011.06.002
Sze, W. P., Yap, M. J., & Rickard Liow, S. J. (2015). The role of lexical variables in the visual recognition of Chinese characters: A megastudy analysis. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 68(8), 1541–1570. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2014.985234
You, W., Chen, B., & Dunlap, S. (2009). Frequency trajectory effects in Chinese character recognition: Evidence for the arbitrary mapping hypothesis. Cognition, 110(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2008.08.004
Zhang, Z., Ding, G., & Chen, B. (2011). Age-of-acquisition effects of Chinese character: Test of phonological completeness hypothesis. Psychological Development and Education, 27(6), 577–583.
Zhu, X., Damian, M. F., & Zhang, Q. (2015). Seriality of semantic and phonological processes during overt speech in Mandarin as revealed by event-related brain potentials. Brain and Language, 144, 16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandl.2015.03.007
Zhu, X., Zhang, Q., & Damian, M. F. (2016). Additivity of semantic and phonological effects: Evidence from speech production in Mandarin. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 69(11), 2285–2304. https://doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2015.1129427
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 32171055), and the foundation of Humanities and Social Sciences, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (Grant no. 21YJA190011) to Qingfang Zhang. This work was also supported by Major Innovation & Planning Interdisciplinary Platform for the "Double-First Class" Initiative, Renmin University of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
The current study was approved by the Independent Ethics Committee of the Department of Psychology, Renmin University of China, Beijing.
Consent to participate
Written consent was obtained from each participant before the administration of the experiment.
Consent for publication
This manuscript has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhou, Y. & Lou, H. The dissociation between age of acquisition and word frequency effects in Chinese spoken picture naming. Psychological Research 86, 1918–1929 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-021-01616-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-021-01616-0