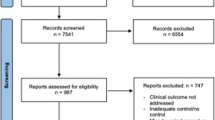
Abstract
Background-objective
The outcomes of split liver transplantation between recipients of deceased donor split liver transplant (SLT) or live donor liver transplants (LDLT) have never been compared in meta-analysis. It is important to understand graft and recipient survival between recipients of these grafts.
Methods
Databases were searched for relevant articles over the previous 20 years (MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library and Google Scholar). Meta-analyses were performed using both fixed- and random-effects models. Patient survival and graft survival were obtained using the inverse variance hazard ratio method.
Results
There were differences in the characteristics of the donors and recipients. Donors of the SLT were younger compared to LDLT cohort [mean difference (MD) = − 11.12 years (− 15.41 to − 6.84), p < 0.001] whilst recipients of LDLT were younger [MD = − 2.06 years (− 1.12 to − 3.01), p < 0.001]. Significantly fewer men received grafts after SLT, 45%, compared to those receiving LDLT, 55%, [OR = 0.66 (0.55 to 0.80), p < 0.001]. There were no significant differences detected in postoperative complications, graft and patient 1-, 3- and 5-year survival between the SLT and LDLT cohorts.
Conclusions
There is no apparent difference in overall survival, graft survival or complications between recipients of SLT or LDLT. However, characteristics of the donor and recipients differed suggesting the need for adequate risk-adjusted assessment of outcomes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bismuth H, Houssin D (1984) Reduced-size orthotopic liver graft in hepatic transplantation in children. Surgery 95:367–370
Pichlmayr R, Ringe B, Gubernatis G, Hauss J, Bunzendahl H (1988) Transplantation of a donor liver to 2 recipients (splitting transplantation) a new method in the further development of segmental liver transplantation. Langenbecks Arch Chir 373:127–130
Strong RW, Lynch SV, Ong TH, Matsunami H, Koido Y, Balderson GA (1990) Successful liver transplantation from a living donor to her son. N Engl J Med 322:1505–1507
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Higgins JPT, Green S, ends. (2006) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions Chichester, UK: John Willey& Son Ltd. The Cochrane library Issue 4
Hozo SP, Diulbegovic B, Hozo I (2005) Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 5:13
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected with simple graphical test. BMJ (Clin Res Ed) 315(7109):629–634
Giacomoni A, De Carlis L, Lauterio A, Slim AO, Aseni P, Sammartino I et al (2005) Right hemiliver transplant: results from living and cadaveric donors. Transplant Proc 37:1167–1169
Sebagh M, Yilmaz F, Karam V, Falissard B, Ichai P, Roche B et al (2006) Cadaveric full-size liver transplantation and the graft alternatives in adults: a comparative study from a single Centre. J Hepatol 44:118–125
Humar A, Beissel J, Crotteau S, Kandaswamy R, Lake J, Payne W (2008) Whole liver versus split liver versus living donor in the adult recipient: an analysis of outcomes by graft type. Transplantation 85:1420–1424
Saidi RF, Jabbour N, Li YF, Shah SA, Bozorgzadeh A (2011) Outcomes in partial liver transplantation: deceased donor split-liver vs live donor liver transplantation. HPB(Oxford) 13:797–801
Clavien PA, Petrowsky H, DeOliveira ML, Graf R (2007) Strategies for safer liver surgery and partial liver transplantation. N Engl J Med 356:1545–1559
Washburn K, Halff G, Mieles L, Goldstein R, Goss JA (2005) Split-liver transplantation: results of statewide usage of the right trisegmental graft. Am J Transplant 5:1652–1659
Wan P, Li Q, Zhang J, Xia Q (2015) Right lobe split liver transplantation versus whole liver transplantation in adult recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Transpl 21:928–943
Azoulay D, Castaing D, Adam R, Savier E, Delvart V, Karam V, Yan Ming B, Dannaoui M, Krissat J, Bismuth H (2001) Split-transplantation for two adult recipients: feasibility and long-term outcomes. Ann Surg 233:565–574
Toso C, Ris F, Mentha G, Oberholzer J, Morel P, Majno P (2002) Potential impact of in situ liver splitting on the number of available grafts. Transplantation 74:222–226
Goosen K, Tenckhoff S, Probst P, Grummich K, Mihaljevic AL, Büchler MW, Diener MK (2018) Optimal literature search for systematic review in surgery. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 403:119–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavriilidis, P., Azoulay, D., Sutcliffe, R.P. et al. Split versus living-related adult liver transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 404, 285–292 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-019-01771-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-019-01771-4