Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate diagnostic accuracy of cystic lesions of the pancreas in order to determine if less aggressive surgical treatment might be safe and therefore warranted.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted in 232 patients with either observed or resected cystic lesions of the pancreas referred for evaluation and treatment to the University Medical Center Freiburg, Germany, between 2001 and 2011.
Results
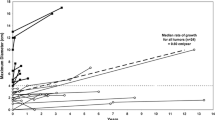
Most patients had MRI or CT for preoperative imaging (90.6 %). Preoperatively, benign pseudocysts (BPC) were diagnosed in 84 (36.2 %) patients and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) in 59 (25.2 %) patients, whereas serous cyst adenoma, mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN), solid pseudopapillary tumors (SPPTs), and neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) were less common. In 43 % of patients, the preoperative diagnosis concurred with the postoperative diagnosis. The preoperative diagnosis was accurate in BPC, less so in IPMN, and inaccurate in MCN, NET, and SPPT. However, prediction of tumor biology was accurate; only 11 % of the lesions regarded as benign turned out to be malignant after resection, and no patient without resection developed malignancy at a median follow-up of 8 months. Subsequently, 89 % of diagnosed benign tumors had indeed benign pathology.
Conclusions
The prediction of biology is often correct, whereas specific diagnosis is often wrong. A considerable amount of benign lesions are treated more aggressively than warranted if malignancy is suspected prior to surgery. Parenchyma-sparing techniques might be an option, but prospective multicenter studies need to follow. Experienced pancreatic radiologists can improve accuracy of preoperative biology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adsay NV (2008) Cystic neoplasia of the pancreas: pathology and biology. J Gastrointest Surg : Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 12:401–4. doi:10.1007/s11605-007-0348-z
Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Saokar A et al (2005) Cystic pancreatic lesions: a simple imaging-based classification system for guiding management. Radiographics : Rev Publ Radiol Soc North Am, Inc 25:1471–84. doi:10.1148/rg.256045161
Palmucci S, Cappello G, Trombatore C et al (2014) Cystic pancreatic neoplasms: diagnosis and management emphasizing their imaging features. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18:1259–68
Nagai E, Ueki T, Chijiiwa K et al (1995) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas associated with so-called “mucinous ductal ectasia”. Histochemical and immunohistochemical analysis of 29 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 19:576–89
Crippa S, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Salvia R et al (2010) Mucin-producing neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of distinguishing clinical and epidemiologic characteristics. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol : Off Clin Pract J Am Gastroenterol Assoc 8:213–9. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2009.10.001
Terris B, Ponsot P, Paye F et al (2000) Intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas confined to secondary ducts show less aggressive pathologic features as compared with those involving the main pancreatic duct. Am J Surg Pathol 24:1372–7
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V et al (2006) International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatol : Off J Int Assoc Pancreatol 6:17–32. doi:10.1159/000090023
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V et al (2012) International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatol : Off J Int Assoc Pancreatol 12:183–97. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2012.04.004
Hackert T, Fritz S, Klauss M et al (2015) Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: high cancer risk in duct diameter of 5 to 9 mm. Ann Surg 262:875–81. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000001462
Sahora K, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Dong F et al (2014) Not all mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms behave like main-duct lesions: implications of minimal involvement of the main pancreatic duct. Surgery 156:611–21. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2014.04.023
Yamao K, Ohashi K, Nakamura T et al (2000) The prognosis of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Hepato-Gastroenterology 47:1129–34
Bernard P, Scoazec JY, Joubert M et al (2002) Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas: predictive criteria of malignancy according to pathological examination of 53 cases. Arch Surg 137:1274–8
Salvia R, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Bassi C et al (2004) Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival following resection. Ann Surg 239:678–85, discussion 85–7
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL et al (2004) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an updated experience. Ann Surg 239:788–97, discussion 97–9
Yamao K, Yanagisawa A, Takahashi K et al (2011) Clinicopathological features and prognosis of mucinous cystic neoplasm with ovarian-type stroma: a multi-institutional study of the Japan pancreas society. Pancreas 40:67–71. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181f749d3
Del Chiaro M, Verbeke C, Salvia R et al (2013) European experts consensus statement on cystic tumours of the pancreas. Dig Liver Dis : Off J Italian Soc Gastroenterol Italian Assoc Study Liver 45:703–11. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2013.01.010
Galanis C, Zamani A, Cameron JL et al (2007) Resected serous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: a review of 158 patients with recommendations for treatment. J Gastrointest Surg : Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 11:820–6. doi:10.1007/s11605-007-0157-4
Bassi C, Salvia R, Molinari E et al (2003) Management of 100 consecutive cases of pancreatic serous cystadenoma: wait for symptoms and see at imaging or vice versa? World J Surg 27:319–23. doi:10.1007/s00268-002-6570-7
Friebe V, Keck T, Mattern D et al (2005) Serous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas: management of a rare entity. Pancreas 31:182–7
Butte JM, Brennan MF, Gonen M et al (2011) Solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas. Clinical features, surgical outcomes, and long-term survival in 45 consecutive patients from a single center. J Gastrointest Surg : Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 15:350–7. doi:10.1007/s11605-010-1337-1
Brun A, Agarwal N, Pitchumoni CS (2011) Fluid collections in and around the pancreas in acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 45:614–25. doi:10.1097/MCG.0b013e318213ef3e
Lerch MM, Stier A, Wahnschaffe U et al (2009) Pancreatic pseudocysts: observation, endoscopic drainage, or resection? Deutsches Arzteblatt Int 106:614–21. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2009.0614
Chronic Pancreatitis German Society of D, Metabolic D, Hoffmeister A et al (2012) S3-Consensus guidelines on definition, etiology, diagnosis and medical, endoscopic and surgical management of chronic pancreatitis German Society of Digestive and Metabolic Diseases (DGVS). Z Gastroenterol 50:1176–224. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1325479
Salvia R, Malleo G, Marchegiani G et al (2012) Pancreatic resections for cystic neoplasms: from the surgeon’s presumption to the pathologist’s reality. Surgery 152:S135–42. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.019
Zaruba P, Dvorakova T, Zavada F et al (2013) Is accurate preoperative assessment of pancreatic cystic lesions possible? Rozhledy v chirurgii : mesicnik Ceskoslovenske chirurgicke spolecnosti 92:708–14
Donahue TR, Hines OJ, Farrell JJ et al (2010) Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: results of 114 cases. Pancreas 39:1271–6. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181e1d6f4
Sauvanet A, Gaujoux S, Blanc B et al (2014) Parenchyma-sparing pancreatectomy for presumed noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg 260:364–71. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000000601
Fisher WE, Hodges SE, Yagnik V et al (2008) Accuracy of CT in predicting malignant potential of cystic pancreatic neoplasms. HPB : Off J Int Hepatol Pancreatol Biliary Assoc 10:483–90. doi:10.1080/13651820802291225
Brugge WR, Lewandrowski K, Lee-Lewandrowski E et al (2004) Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: a report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 126:1330–6
Khalid A, Zahid M, Finkelstein SD et al (2009) Pancreatic cyst fluid DNA analysis in evaluating pancreatic cysts: a report of the PANDA study. Gastrointest Endosc 69:1095–102. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2008.07.033
Valsangkar NP, Morales-Oyarvide V, Thayer SP et al (2012) 851 resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: a 33-year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Surgery 152:S4–12. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2012.05.033
Keck TW, U.F (2015) Recopanc Trial. Ann Surg
Nakamura M, Nakashima H (2013) Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy and pancreatoduodenectomy: is it worthwhile? A meta-analysis of laparoscopic pancreatectomy. J Hepatol-Biliary-Pancreat Sci 20:421–8. doi:10.1007/s00534-012-0578-7
Jin T, Altaf K, Xiong JJ et al (2012) A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing laparoscopic and open distal pancreatectomy. HPB : Off J Int Hepatol Pancreatol Biliary Assoc 14:711–24. doi:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00531.x
Hackert T, Hinz U, Fritz S et al (2011) Enucleation in pancreatic surgery: indications, technique, and outcome compared to standard pancreatic resections. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg / Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chirurgie 396:1197–203. doi:10.1007/s00423-011-0801-z
Tseng JF, Warshaw AL, Sahani DV et al (2005) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas: tumor growth rates and recommendations for treatment. Ann Surg 242:413–9, discussion 19–21
Khalid A, Brugge W (2007) ACG practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Am J Gastroenterol 102:2339–49. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01516.x
Ito T, Ishiguro H, Ohara H et al (2016) Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for chronic pancreatitis 2015. J Gastroenterol 51:85–92. doi:10.1007/s00535-015-1149-x
Sainani NI, Saokar A, Deshpande V et al (2009) Comparative performance of MDCT and MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in characterizing small pancreatic cysts. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:722–31. doi:10.2214/AJR.08.1253
Fritz S, Buchler MW, Werner J (2012) Surgical therapy of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Der Chirurg; Zeitschrift fur alle Gebiete der operativen Medizen 83:130–5. doi:10.1007/s00104-011-2184-7
Distler M, Kersting S, Niedergethmann M et al (2013) Pathohistological subtype predicts survival in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas. Ann Surg 258:324–30. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e318287ab73
Authors’ contributions
Kim C Honselmann: Analysis and interpretation of data and drafting of manuscript.
Tobias Krauss: Study conception and design and critical revision of manuscript.
Sebastian Geserick: Acquisition of data.
Ulrich F Wellner: Critical revision of manuscript and analysis of data.
Uwe Wittel: Critical revision of manuscript.
Ulrich T. Hopt: Critical revision of manuscript.
Tobias Keck: Critical revision of manuscript.
Dirk Bausch: Study conception and design and critical revision of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not funded.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Financial disclosures
The authors received no financial support.
Additional information
Kim C. Honselmann and Tobias Krauss contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Honselmann, K.C., Krauss, T., Geserick, S. et al. Cystic lesions of the pancreas—is radical surgery really warranted?. Langenbecks Arch Surg 401, 449–456 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1416-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-016-1416-1