Abstract
Introduction
Newly developed wearable fabric sensors (WFS) can increase the ease and accuracy of sweat sodium measurements by performing simultaneous sampling and analysis on the body during exercise.
Purpose
Determine the accuracy of a WFS for measurement of sodium concentration in sweat. METHODS: Subjects wore a WFS prototype and sweat collectors on their forearm during cycle ergometry. Subjects exercised at a moderate intensity (~ 65% heart rate reserve) for 30–60 min. Sweat samples were collected and analyzed using a commercial sweat sodium analyzer (SSA) every 10–15 min. WFS were adhered with an armband and connected to custom built electronics. Accuracy was determined by comparing predicted WFS concentration to the actual concentration from the commercial SSA and analyzed statistically using ANOVA and Bland−Altman plots.
Results
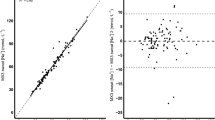
A total of 19 subjects completed the study. The average sweat sodium concentration was 59 mM ± 22 mM from a SSA compared with 54 mM ± 22 mM from the WFS. Overall, the average accuracy of the WFS was 88% in comparison to the SSA with p = 0.45. A line of best fit comparing predicted versus actual sweat sodium concentration had a slope of 0.99, intercept of – 4.46, and an r2 of 0.90. Bland−Altman analysis showed the average concentration difference between the WFS and the SSA was 5.35 mM, with 99% of data points between ± 1.96 times the standard deviation.
Conclusion
The WFS accurately predicted sweat sodium concentration during moderate intensity cycle ergometry. With the need for precise assessment of sodium loss, especially during long duration exercise, this novel analysis method can benefit athletes and coaches. Further research involving longer duration and more intense exercise is warranted.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WFS:
-
Wearable fabric sensor
- SSA:
-
Sweat sodium analyzer
- rc :
-
Lin’s concordance correlation coefficients
- MAPE:
-
Mean absolute percentage error
- % NRMSE:
-
Percent normalized root mean square error
- MAE:
-
Mean absolute error
- 95% CI:
-
95% Confidence interval
- %SD:
-
Percent standard deviation
- SE:
-
Standard error over the mean
References
Baker LB, Ungaro CT, Barnes KA, Nuccio RP, Reimel AJ, Stofan JR (2014) Validity and reliability of a field technique for sweat Na+ and K+ analysis during exercise in a hot-humid environment. Physiol Rep. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12007
Baker LB, De Chavez PJD, Ungaro CT, Sopena BC, Nuccio RP, Reimel AJ, Barnes KA (2019) Exercise intensity effects on total sweat electrolyte losses and regional vs. whole-body sweat {[}Na+], {[}Cl-], and {[}K+]. Eur J Appl Physiol 119(2):361–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-4048-z
Baker LB, Model JB, Barnes KA, Anderson ML, Lee SP, Lee KA, Brown SD, Reimel AJ, Roberts TJ, Nuccio RP, Bonsignore JL, Ungaro CT, Carter JM, Li W, Seib MS, Reeder JT, Aranyosi AJ, Rogers JA, Ghaffari R (2020) Skin-interfaced microfluidic system with personalized sweating rate and sweat chloride analytics for sports science applications. Sci Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abe3929
Brothers MC, Debrosse M, Grigsby CC, Naik RR, Hussain SM, Heikenfeld J, Kim SS (2019) Achievements and challenges for real-time sensing of analytes in sweat within wearable platforms. Acc Chem Res. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00555
Coppedè N, Giannetto M, Villani M, Lucchini V, Battista E, Careri M, Zappettini A (2020) Ion selective textile organic electrochemical transistor for wearable sweat monitoring. Org Electron 78:105579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2019.105579
Gokdemir Y, Karadag BT (2021) Sweat testing and recent advances. Front Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.649904
Hew-Butler T, Loi V, Pani A, Rosner MH (2017) Exercise-associated hyponatremia: 2017 update. Front Med. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00021
Huestis MA, Oyler JM, Cone EJ, Wstadik AT, Schoendorfer D, Joseph RE (1999) Sweat testing for cocaine, codeine and metabolites by gas chromatography - mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 733(1–2):247–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(99)00246-7
Jaffal D, Daniels S, Tang HY, Ghadimi H, Monty CN (2021) Electroconductive nylon-6/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite for sodium sensing applications. Composites Part C: Open Access, In Press 4:100116
Kim J, Sempionatto JR, Imani S, Hartel MC, Barfidokht A, Tang G, Campbell AS, Mercier PP, Wang J (2018) Simultaneous monitoring of sweat and interstitial fluid using a single wearable biosensor platform. Adv Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201800880
Lee YK, Jang K-I, Ma Y, Koh A, Chen H, Jung HN, Kim Y, Kwak JW, Wang L, Xue Y, Yang Y, Tian W, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Feng X, Huang Y, Rogers JA (2017) Chemical sensing systems that utilize soft electronics on thin elastomeric substrates with open cellular designs. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201605476
Liu C, Xu T, Wang D, Zhang X (2020) The role of sampling in wearable sweat sensors. Talanta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120801
Maughan RJ, Shirreffs SM (2008) Development of individual hydration strategies for athletes. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 18(5):457–472. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.18.5.457
Mena-Bravo A, Luque de Castro MD (2014) Sweat: a sample with limited present applications and promising future in metabolomics. J Pharm Biomed Anal 90:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2013.10.048
Schazmann B, Morris D, Slater C, Beirne S, Fay C, Reuveny R, Moyna N, Diamond D (2010) A wearable electrochemical sensor for the real-time measurement of sweat sodium concentration. Anal Methods 2(4):342–348. https://doi.org/10.1039/b9ay00184k
Surapongchai J, Saengsirisuwan V, Rollo I, Randell RK, Nithitsuttibuta K, Sainiyom P, Leow CHW, Lee JKW (2021) Hydration status, fluid intake, sweat rate, and sweat sodium concentration in recreational tropical native runners. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041374
Wang S, Bai Y, Yang X, Liu L, Li L, Lu Q, Li T, Zhang T (2020) Highly stretchable potentiometric ion sensor based on surface strain redistributed fiber for sweat monitoring. Talanta 214:120869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120869
Wujcik EK, Blasdel NJ, Trowbridge D, Monty CN (2013) Ion sensor for the quantification of sodium in sweat samples. IEEE Sens J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2013.2257168
Xu T, Shi W, Huang J, Song Y, Zhang F, Xu L-P, Zhang X, Wang S (2017) Superwettable microchips as a platform toward microgravity biosensing. ACS Nano 11(1):621–626. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b06896
Yu Y, Prassas I, Muytjens CMJ, Diamandis EP (2017) Proteomic and peptidomic analysis of human sweat with emphasis on proteolysis. J Proteom 155:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2017.01.005
Zhao C, Li X, Wu Q, Liu X (2021) A thread-based wearable sweat nanobiosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 188:113270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113270
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dunia Jaffal for providing the electrospun mats used in this work.
Funding
This article is funded by National Science Foundation, 1843539, Chelsea Monty.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Sensor preparation was performed by SD, HG, MPN, MSF, and KD. Data collection and analysis were performed by RO, MPN, ZC, RE, VS, and CNM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KD and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation [grant number 1843539] and the Ohio Third Frontier Technology Validation and Startup Fund [grant number 20-0004]. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The University of Akron and all subjects provided written informed consent (IRB Number 20180408).
Additional information
Communicated by Michael I Lindinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dyshko, K., Nicodemus, M.P., Otterstetter, R. et al. Evaluation of a wearable fabric-based sensor for accurate sodium determination in sweat during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 124, 1347–1353 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05364-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05364-4