Abstract
Purpose
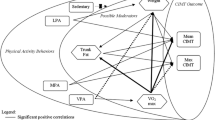
Physical activity (PA) and body fat percentage (%BF) are independently associated with arterial stiffness, but it has not been explored if there is an associative pathway among these variables. This study examined whether %BF mediates the relationship between PA or sedentary behavior levels with arterial stiffness.
Methods
Fifty adults (1:1 men:women; age 28 ± 11 year) had carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (CF-PWV) measured by applanation tonometry, %BF by bioelectrical impedance, and PA levels by accelerometry. Accelerometer data determined minutes per day spent in sedentary, light, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA), and Total PA.
Results
Pearson correlation indicated statistically significant associations among age, %BF, CF-PWV, MVPA, and Total PA (r = 0.34–0.65, p < 0.05). Sedentary and light PA were not associated with CF-PWV. Mediation analysis indicated significant total effects of MVPA (β = − 0.34, p = 0.044) and age (β = 0.65, p < 0.001) on CF-PWV. %BF mediated the relationship between Total PA and CF-PWV due to indirect effect of Total PA on %BF (β = − 0.34, p = 0.02) and %BF on CF-PWV (β = 0.44, p = 0.002), and partially mediated the relationship between age and CF-PWV (β = 0.54, p < 0.001). Total PA retained its significant effect on %BF (β = − 0.28, p = 0.04) and the effect of %BF on CF-PWV remained significant (β = 0.26, p = 0.03), despite age having a significant effect on both %BF (β = 0.31, p = 0.023) and CF-PWV (β = 0.54, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
%BF mediated the relationship between Total PA and arterial stiffness, even after accounting for age. Engagement in more Total PA may help to reduce %BF, resulting in decreased arterial stiffness.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, BKB, upon resonable request.
Abbreviations
- %BF:
-
Body fat percentage
- CF-PWV:
-
Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity
- MVPA:
-
Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity
- PA:
-
Physical activity
- Total PA:
-
Light and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity
References
Aguilar-Farías N, Brown WJ, Peeters GG (2014) ActiGraph GT3X+ cut-points for identifying sedentary behaviour in older adults in free-living environments. J Sci Med Sport 17(3):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2013.07.002
Ahmadi-Abhari S, Sabia S, Shipley MJ, Kivimäki M, Singh-Manoux A, Tabak A, McEniery C, Wilkinson IB, Brunner EJ (2017) Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and long-term changes in aortic stiffness: the Whitehall II study. J Am Heart Assoc 6(8):e005974. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.005974
Aminuddin A, Lazim MRMLM, Hamid AA, Hui CK, Mohd Yunus MH, Kumar J, Ugusman A (2020) The association between inflammation and pulse wave velocity in dyslipidemia: an evidence-based review. Mediators Inflamm 2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4732987
Arcaro G, Cretti A, Balzano S, Lechi A, Muggeo M, Bonora E, Bonadonna RC (2002) Insulin causes endothelial dysfunction in humans: sites and mechanisms. Circulation 105(5):576–582. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc0502.103333
Ashor AW, Lara J, Siervo M, Celis-Morales C, Mathers JC (2014) Effects of exercise modalities on arterial stiffness and wave reflection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 9(10):e110034. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110034
Ballenger BK, Hunter GR, Fisher G (2021) Vascular hemodynamics and blood pressure differences between young and older women. Clinical Hypertens 27(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40885-021-00181-3
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51(6):1173–1182
Bouchard C, Shephard RJ (1994) Physical activity, fitness, and health: the model and key concepts. In: Bouchard C, Shephard RJ, Stephens T (eds) Physical activity, fitness, and health: international proceedings and consensus stateemnt. Human Kinetics, pp 77–88
Bradbury KE, Guo W, Cairns BJ, Armstrong MEG, Key TJ (2017) Association between physical activity and body fat percentage, with adjustment for BMI: a large cross-sectional analysis of UK Biobank. BMJ Open 7(3):e011843. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011843
Choi L, Liu Z, Matthews CE, Buchowski MS (2011) Validation of accelerometer wear and nonwear time classification algorithm. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(2):357–364. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ed61a3
Covic A, Siriopol D (2015) Pulse wave velocity ratio: the new “gold standard” for measuring arterial stiffness. Hypertension 65(2):289–290. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04678
del Pozo-Cruz J, García-Hermoso A, Alfonso-Rosa RM, Alvarez-Barbosa F, Owen N, Chastin S, del Pozo-Cruz B (2018) Replacing sedentary time: meta-analysis of objective-assessment studies. Am J Prev Med 55(3):395–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2018.04.042
Department of Health and Human Services. (2018). 2018 physical activity guidelines advisory committee scientific report
Engeli S, Sharma A (2000) Role of adipose tissue for cardiovascular-renal regulation in health and disease. Horm Metab Res 32(11/12):485–499. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-978675
Escobedo-de la Peña J, Ramírez-Hernández JA, Fernández-Ramos MT, González-Figueroa E, Champagne B (2020) Body fat percentage rather than body mass index related to the high occurrence of type 2 diabetes. Arch Med Res 51(6):564–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.05.010
Fernberg U, op’t Roodt J, Fernström M, Hurtig-Wennlof A (2019) Body composition is a strong predictor of local carotid stiffness in Swedish, young adults – the cross sectional Lifestyle, biomarkers, and atherosclerosis study. BMC Cardiovasc Disorders 19(1):205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-019-1180-6
Fernberg U, Fernström M, Hurtig-Wennlöf A (2021) Higher total physical activity is associated with lower arterial stiffness in Swedish, young adults: The cross-sectional lifestyle, biomarkers, and atherosclerosis study. Vasc Health Risk Manag 17:175–185. https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S283211
Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Williams K, Karter A, Mayer-Davis E, Tracy R, Haffner S (2001) The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int J Obes 25(10):1407–1415. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801792
Gando Y, Yamamoto K, Murakami H, Ohmori Y, Kawakami R, Sanada K, Higuchi M, Tabata I, Miyachi M (2010) Longer time spent in light physical activity is associated with reduced arterial stiffness in older adults. Hypertension 56(3):540–546. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.156331
Germano-Soares AH, Andrade-Lima A, Menêses AL, Correia MA, Parmenter BJ, Tassitano RM, Cucato GG, Ritti-Dias RM (2018) Association of time spent in physical activities and sedentary behaviors with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 269:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.01.009
Gorzelitz J, Peppard PE, Malecki K, Gennuso K, Nieto FJ, Cadmus-Bertram L (2018) Predictors of discordance in self-report versus device-measured physical activity measurement. Ann Epidemiol 28(7):427–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2018.03.016
Gram-Kampmann EM, Hansen CD, Hugger MB, Jensen JM, Brønd JC, Hermann AP, Krag A, Olsen MH, Beck-Nielsen H, Højlund K (2022) Effects of a 6-month, low-carbohydrate diet on glycaemic control, body composition, and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: An open-label randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 24(4):693–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14633
Gutin B, Yin Z, Humphries MC, Bassali R, Le N-A, Daniels S, Barbeau P (2005) Relations of body fatness and cardiovascular fitness to lipid profile in black and white adolescents. Pediatr Res 58(1):78–82. https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000163386.32348.90
Hawkins M, Gabriel KP, Cooper J, Storti KL, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Kriska A (2014) The impact of change in physical activity on change in arterial stiffness in overweight or obese sedentary young adults. Vasc Med 19(4):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X14536630
Hayes AF (2022) Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis, third edition: a regression-based approach, 3rd edn. The Guilford Pressl, New York
Healy GN, Clark BK, Winkler EAH, Gardiner PA, Brown WJ, Matthews CE (2011) Measurement of adults’ sedentary time in population-based studies. Am J Prev Med 41(2):216–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.005
Heffernan KS, Jae SY, Tomayko E, Ishaque MR, Fernhall B, Wilund KR (2009) Influence of arterial wave reflection on carotid blood pressure and intima-media thickness in older endurance trained men and women with pre-hypertension. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 29(3):193–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-097X.2009.00856.x
Herzig K-H, Ahola R, Leppäluoto J, Jokelainen J, Jämsä T, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S (2014) Light physical activity determined by a motion sensor decreases insulin resistance, improves lipid homeostasis and reduces visceral fat in high-risk subjects: PreDiabEx study RCT. Int J Obes 38(8):1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2013.224
Kyle UG, Gremion G, Genton L, Slosman DO, Golay A, Pichard C (2001) Physical activity and fat-free and fat mass by bioelectrical impedance in 3853 adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005768-200104000-00011
Lee M, Choh AC, Demerath EW, Towne B, Siervogel RM, Czerwinski SA (2012) Associations between trunk, leg and total body adiposity with arterial stiffness. Am J Hypertens 25(10):1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2012.92
Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A (2002) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105(9):1135–1143. https://doi.org/10.1161/hc0902.104353
Mac Ananey O, McLoughlin B, Leonard A, Maher L, Gaffney P, Boran G, Maher V (2015) Inverse relationship between physical activity, adiposity, and arterial stiffness in healthy middle-aged subjects. J Phys Act Health 12(12):1576–1581. https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2014-0395
Malden D, Lacey B, Emberson J, Karpe F, Allen N, Bennett D, Lewington S (2019) Body fat distribution and systolic blood pressure in 10,000 adults with whole-body imaging: UK biobank and Oxford biobank. Obesity 27(7):1200–1206. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22509
Mansoubi M, Pearson N, Biddle SJH, Clemes S (2014) The relationship between sedentary behaviour and physical activity in adults: a systematic review. Prev Med 69:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.08.028
Migueles JH, Cadenas-Sanchez C, Ekelund U, Delisle Nyström C, Mora-Gonzalez J, Löf M, Labayen I, Ruiz JR, Ortega FB (2017) Accelerometer data collection and processing criteria to assess physical activity and other outcomes: a systematic review and practical considerations. Sports Med 47(9):1821–1845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-017-0716-0
Mikael LDR, de Paiva AMG, Gomes MM, Sousa ALL, Jardim PCBV, Vitorino PV, Euzébio MB, Sousa WDM, Barroso WKS (2017) Vascular aging and arterial stiffness. Arq Bras Cardiol 109(3):253–258. https://doi.org/10.5935/abc.20170091
Mitchell GF, Parise H, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Keyes MJ, Vita JA, Vasan RS, Levy D (2004) Changes in arterial stiffness and wave reflection with advancing age in healthy men and women: the framingham heart study. Hypertension 43(6):1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000128420.01881.aa
Mott JW, Wang J, Thornton JC, Allison DB, Heymsfield SB, Pierson RN (1999) Relation between body fat and age in 4 ethnic groups. Am J Clin Nutr 69(5):1007–1013. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/69.5.1007
Mozos I, Malainer C, Horbańczuk J, Gug C, Stoian D, Luca CT, Atanasov AG (2017) Inflammatory markers for arterial stiffness in cardiovascular diseases. Front Immunol 8:1058. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01058
Mun J, Kim Y, Farnsworth JL, Suh S, Kang M (2018) Association between objectively measured sedentary behavior and a criterion measure of obesity among adults. Am J Human Biol 30(2):e23080. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.23080
Oda E (2018) LDL cholesterol was more strongly associated with percent body fat than body mass index and waist circumference in a health screening population. Obes Res Clin Pract 12(2):195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2017.05.005
O’Donovan C, Lithander FE, Raftery T, Gormley J, Mahmud A, Hussey J (2014) Inverse relationship between physical activity and arterial stiffness in adults with hypertension. J Phys Act Health 11(2):272–277. https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2012-0075
Pearson N, Biddle SJH (2011) Sedentary behavior and dietary intake in children, adolescents, and adults: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 41(2):178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.002
Pickett K, Yardley L, Kendrick T (2012) Physical activity and depression: a multiple mediation analysis. Ment Health Phys Act 5(2):125–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mhpa.2012.10.001
Rubin J, Nambi V, Chambless LE, Steffes MW, Juraschek SP, Coresh J, Sharrett AR, Selvin E (2012) Hyperglycemia and arterial stiffness: the atherosclerosis risk in the communities study. Atherosclerosis 225(1):246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.09.003
Same RV, Feldman DI, Shah N, Martin SS, Al Rifai M, Blaha MJ, Graham G, Ahmed HM (2016) Relationship between sedentary behavior and cardiovascular risk. Curr Cardiol Rep 18(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-015-0678-5
Sasaki JE, John D, Freedson PS (2011) Validation and comparison of ActiGraph activity monitors. J Sci Med Sport 14(5):411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2011.04.003
Schiffrin E (2004) Vascular stiffening and arterial compliance: Implications for systolic blood pressure. Am J Hypertens 17(12):S39–S48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.08.019
Segers P, Rietzschel ER, Chirinos JA (2020) How to measure arterial stiffness in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40(5):1034–1043. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313132
Smith DL, Fernhall B (2022) Advanced cardiovascular exercise physiology, 2nd edn. Human Kinetics, Champaign
Strasser B, Arvandi M, Pasha EP, Haley AP, Stanforth P, Tanaka H (2015) Abdominal obesity is associated with arterial stiffness in middle-aged adults. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 25(5):495–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2015.01.002
Sun Z (2015) Aging, arterial stiffness, and hypertension. Hypertension 65:252–256. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03617
Tanaka H (2019) Antiaging effects of aerobic exercise on systemic arteries. Hypertension 74(2):237–243. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.13179
Thanassoulis G, Peloso GM, Pencina MJ, Hoffmann U, Fox CS, Cupples LA, Levy D, D’Agostino RB, Hwang S-J, O’Donnell CJ (2012) A genetic risk score is associated with incident cardiovascular disease and coronary artery calcium: The framingham heart study. Circ: Cardiovasc Genet 5(1):113–121. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.111.961342
Thorp AA, Owen N, Neuhaus M, Dunstan DW (2011) Sedentary behaviors and subsequent health outcomes in adults: a systematic review of longitudinal studies, 1996–2011. Am J Prev Med 41(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.004
Tourlouki E (2009) Dietary habits and cardiovascular disease risk in middle-aged and elderly populations: a review of evidence. Clin Interv Aging. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S5697
Vaitkevicius PV, Fleg JL, Engel JH, O’Connor FC, Wright JG, Lakatta LE, Yin FC, Lakatta EG (1993) Effects of age and aerobic capacity on arterial stiffness in healthy adults. Circulation 88(4):1456–1462. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.88.4.1456
van der Heijden-Spek JJ, Staessen JA, Fagard RH, Hoeks AP, Boudier HAS, Van Bortel LM (2000) Effect of age on brachial artery wall properties differs from the aorta and is gender dependent: a population study. Hypertension 35(2):637–642. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.35.2.637
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(13):1318–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.061
Wang L, Zhi F, Gao B, Ni J, Liu Y, Mo X, Huang J (2020) Association between lipid profiles and arterial stiffness: a secondary analysis based on a cross-sectional study. J Int Med Res 48(7):030006052093818. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060520938188
Westerterp KR (2017) Control of energy expenditure in humans. Eur J Clin Nutr 71(3):340–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2016.237
Wilckens KA, Erickson KI, Wheeler ME (2018) Physical activity and cognition: a mediating role of efficient sleep. Behav Sleep Med 16(6):569–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/15402002.2016.1253013
Wildman RP, Mackey RH, Bostom A, Thompson T, Sutton-Tyrrell K (2003) Measures of obesity are associated with vascular stiffness in young and older adults. Hypertension 42(4):468–473. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000090360.78539.CD
Wildman RP, Farhat GN, Patel AS, Mackey RH, Brockwell S, Thompson T, Sutton-Tyrrell K (2005) Weight change is associated with change in arterial stiffness among healthy young adults. Hypertension 45(2):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000152200.10578.5d
Zhao X, Lynch JG, Chen Q (2010) Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: myths and truths about mediation analysis. J Consum Res 37(2):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1086/651257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception or design of work, made critical revisions to the manuscript, approved the final version of the manuscript, and agree to be held accountable for all aspects of the work. We followed the ICMJE definitions of authorship for this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Michael I Lindinger.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ballenger, B.K., Carter, S.L., Norman, G. et al. Physical activity and arterial stiffness: is body fat a mediator?. Eur J Appl Physiol 124, 527–535 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05296-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-023-05296-z