Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to detect potential differences in heart-rate variability (HRV) during a moderate-intensity intermittent exercise in the heat among physically active young (25.8 ± 1.9 years), middle-aged (43.5 ± 2.8 years), and older (62.9 ± 3.7 years) men.
Methods
Thirty-three participants (11/group) performed four successive bouts of 15-min cycling at a moderate fixed rate of metabolic heat production of ~ 400 W; each separated by a 15-min recovery with 1 h of final recovery in a hot and dry environment (35 °C, 20% relative humidity). Twelve HRV indices were computed that have been commonly described in the literature, and characterized various domains of the variability and complexity of heart rate.
Results
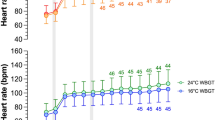
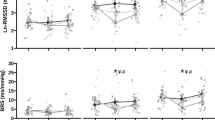
Cardiac autonomic regulation during intermittent exercise in the heat, as well as during pre-exercise rest and recovery was significantly affected by age, as changes were observed among the three different aged groups in five indices (p ≤ 0.05). Similarly, time influenced cardiac autonomic regulation as three indices showed changes across time (p ≤ 0.05) during intermittent exercise, whilst five indices displayed significant changes (p ≤ 0.05) during rest and recovery in the heat.
Conclusions
This study supports that moderate-intensity intermittent exercise in the heat is associated with significant cardiac autonomic dysregulation in older men, as compared to young and middle-aged men, yet it highlights the importance of developing preventative health strategies for heat-related illness in aged individuals.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CoV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- HF power:
-
High-frequency power
- HRV:
-
Heart-rate variability
- LF/HF ratio:
-
Low/high-frequency power ratio
- LF power:
-
Low-frequency power
References
Basagana X, Sartini C, Barrera-Gomez J, Dadvand P, Cunillera J, Ostro B, Sunyer J, Medina-Ramon M (2011) Heat waves and cause-specific mortality at all ages. Epidemiology 22(6):765–772. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e31823031c5
Basu R, Samet JM (2002) Relation between elevated ambient temperature and mortality: a review of the epidemiologic evidence. Epidemiol Rev 24(2):190–202
Beckers F, Verheyden B, Aubert AE (2006) Aging and nonlinear heart rate control in a healthy population. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290(6):H2560–2570. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00903.2005
Bradley B, Green GC, Batkin I, Seely AJ (2012) Feasibility of continuous multiorgan variability analysis in the intensive care unit. J Crit Care 27(2):218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2011.09.009
Brennan M, Palaniswami M, Kamen P (2001) New insights into the relationship between poincare plot geometry and linear measures of heart rate variability. In: Conference proceedings of the 23rd annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, vol 1, pp 526–29. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2001.1018984
Brenner IK, Thomas S, Shephard RJ (1997) Spectral analysis of heart rate variability during heat exposure and repeated exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 76(2):145–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050227
Carrillo AE, Flouris AD, Herry CL, Poirier MP, Boulay P, Dervis S, Friesen BJ, Malcolm J, Sigal RJ, Seely AJ, Kenny GP (2016) Heart rate variability during high heat stress: a comparison between young and older adults with and without Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 311(4):R669–R675. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00176.2016
Chen CH, Huang PW, Tang SC, Shieh JS, Lai DM, Wu AY, Jeng JS (2015) Complexity of heart rate variability can predict stroke-in-evolution in acute ischemic stroke patients. Sci Rep 5:17552. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17552
Conti S, Meli P, Minelli G, Solimini R, Toccaceli V, Vichi M, Beltrano C, Perini L (2005) Epidemiologic study of mortality during the Summer 2003 heat wave in Italy. Environ Res 98(3):390–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.10.009
Dinas PC, Koutedakis Y, Flouris AD (2011) Effects of active and passive tobacco cigarette smoking on heart rate variability. Int J Cardiol 163(2):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.10.140
DuBois D, DuBois EF (1916) A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Arch Intern Med 17:863–871
Eckberg DL, Drabinsky M, Braunwald E (1971) Defective cardiac parasympathetic control in patients with heart disease. N Engl J Med 285(16):877–883. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197110142851602
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A (2007) G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods 39(2):175–191
Flouris AD, Bravi A, Wright-Beatty HE, Green G, Seely AJ, Kenny GP (2014a) Heart rate variability during exertional heat stress: effects of heat production and treatment. Eur J Appl Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2804-7
Flouris AD, Dinas PC, Ioannou LG, Nybo L, Havenith G, Kenny GP, Kjellstrom T (2018a) Workers’ health and productivity under occupational heat strain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Plan Health 2(12):E521–E531
Flouris AD, Kenny GP (2017) Heat remains unaccounted for in thermal physiology and climate change research. J Res 6:221. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10554.2
Flouris AD, McGinn R, Poirier MP, Louie JC, Ioannou LG, Tsoutsoubi L, Sigal RJ, Boulay P, Hardcastle SG, Kenny GP (2018b) Screening criteria for increased susceptibility to heat stress during work or leisure in hot environments in healthy individuals aged 31–70 years. Temperature (Austin) 5(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1381800
Flouris AD, Poirier MP, Bravi A, Wright-Beatty HE, Herry C, Seely AJ, Kenny GP (2014b) Changes in heart rate variability during the induction and decay of heat acclimation. Eur J Appl Physiol 114(10):2119–2128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2935-5
Fouillet A, Rey G, Laurent F, Pavillon G, Bellec S, Guihenneuc-Jouyaux C, Clavel J, Jougla E, Hemon D (2006) Excess mortality related to the August 2003 heat wave in France. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-006-0089-4
Fouillet A, Rey G, Wagner V, Laaidi K, Empereur-Bissonnet P, Le Tertre A, Frayssinet P, Bessemoulin P, Laurent F, De Crouy-Chanel P, Jougla E, Hemon D (2008) Has the impact of heat waves on mortality changed in France since the European heat wave of summer 2003? A study of the 2006 heat wave. Int J Epidemiol 37(2):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dym253
Francesco B, Maria Grazia B, Emanuele G, Valentina F, Sara C, Chiara F, Riccardo M, Francesco F (2012) Linear and nonlinear heart rate variability indexes in clinical practice. Comput Math Methods Med 2012:219080. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/219080
Hjorth B (1970) EEG analysis based on time domain properties. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 29(3):306–310
Hjorth B (1973) The physical significance of time domain descriptors in EEG analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 34(3):321–325
Ho KK, Moody GB, Peng CK, Mietus JE, Larson MG, Levy D, Goldberger AL (1997) Predicting survival in heart failure case and control subjects by use of fully automated methods for deriving nonlinear and conventional indices of heart rate dynamics. Circulation 96(3):842–848
Ho YL, Lin C, Lin YH, Lo MT (2011) The prognostic value of non-linear analysis of heart rate variability in patients with congestive heart failure–a pilot study of multiscale entropy. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18699. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018699
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Jacob D, Taylor M, Bindi M, Brown S, Camilloni I, Diedhiou A, Djalante R, Ebi KL, Engelbrecht F, Guiot J, Hijioka Y, Mehrotra S, Payne A, Seneviratne SI, Thomas A, Warren R, Zhou G (2018) Impacts of 1.5 ºC global warming on natural and human systems. In: Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pörtner H-O et al (eds) Global warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC special report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Switzerland
Huikuri HV, Makikallio TH, Peng CK, Goldberger AL, Hintze U, Moller M (2000) Fractal correlation properties of R-R interval dynamics and mortality in patients with depressed left ventricular function after an acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 101(1):47–53
Ingall TJ, McLeod JG, O'Brien PC (1990) The effect of ageing on autonomic nervous system function. Aust N Z J Med 20(4):570–577
Jandackova VK, Scholes S, Britton A, Steptoe A (2016) Are changes in heart rate variability in middle-aged and older people normative or caused by pathological conditions? Findings from a large population-based longitudinal cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc 5(2):1. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.115.002365
Kaminsky LA, Arena R, Myers J (2015) Reference standards for cardiorespiratory fitness measured with cardiopulmonary exercise testing: data from the fitness registry and the importance of exercise national database. Mayo Clin Proc 90(11):1515–1523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.07.026
Kenney WL, Craighead DH, Alexander LM (2014) Heat waves, aging, and human cardiovascular health. Med Sci Sports Exerc 46(10):1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000000325
Kenny GP, Jay O (2013) Thermometry, calorimetry, and mean body temperature during heat stress. Compr Physiol 3(4):1689–1719. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c130011
Kenny GP, Larose J, Boulay P, Hardcastle SG, Sigal RJ, Miller S, Wright HE (2012) Older adults have a reduced capacity to dissipate heat during physical activity in the heat. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37(Sl):S19.
Kenny GP, Poirier MP, Metsios GS, Boulay P, Dervis S, Friesen BJ, Malcolm J, Sigal RJ, Seely AJ, Flouris AD (2017) Hyperthermia and cardiovascular strain during an extreme heat exposure in young versus older adults. Temperature (Austin) 4(1):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2016.1230171
La Rovere MT, Bigger JT, Jr., Marcus FI, Mortara A, Schwartz PJ (1998) Baroreflex sensitivity and heart-rate variability in prediction of total cardiac mortality after myocardial infarction. ATRAMI (Autonomic Tone and Reflexes After Myocardial Infarction) Investigators. Lancet 351 (9101):478–484
La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Hohnloser SH, Marcus FI, Mortara A, Nohara R, Bigger JT Jr, Camm AJ, Schwartz PJ, Tone AIA, Reflexes After Myocardial I (2001) Baroreflex sensitivity and heart rate variability in the identification of patients at risk for life-threatening arrhythmias: implications for clinical trials. Circulation 103(16):2072–2077
La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Raczak G (2008) Baroreflex sensitivity: measurement and clinical implications. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol 13(2):191–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1542-474X.2008.00219.x
Larose J, Wright HE, Sigal RJ, Boulay P, Hardcastle S, Kenny GP (2013a) Do older females store more heat than younger females during exercise in the heat? Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31829d24cc
Larose J, Wright HE, Stapleton J, Sigal RJ, Boulay P, Hardcastle S, Kenny GP (2013b) Whole body heat loss is reduced in older males during short bouts of intermittent exercise. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 305(6):R619–629. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00157.2013
Leicht AS, Flouris AD, Kaltsatou A, Seely AJ, Herry CL, Wright Beatty HE, Kenny GP (2018) Age alters cardiac autonomic modulations during and following exercise-induced heat stress in females. Temperature (Austin) 5(2):184–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2018.1432918
Linares C, Diaz J (2008) Impact of high temperatures on hospital admissions: comparative analysis with previous studies about mortality (Madrid). Eur J Public Health 18(3):317–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckm108
Liu HF, Yang YZ, Dai ZH, Yu ZH (2003) The largest Lyapunov exponent of chaotic dynamical system in scale space and its application. Chaos 13(3):839–844. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1596556
Liu W, Lian Z, Liu Y (2008) Heart rate variability at different thermal comfort levels. Eur J Appl Physiol 103(3):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0718-6
Mastrangelo G, Fedeli U, Visentin C, Milan G, Fadda E, Spolaore P (2007) Pattern and determinants of hospitalization during heat waves: an ecologic study. BMC Public Health 7:200. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-7-200
Michelozzi P, Accetta G, De Sario M, D'Ippoliti D, Marino C, Baccini M, Biggeri A, Anderson HR, Katsouyanni K, Ballester F, Bisanti L, Cadum E, Forsberg B, Forastiere F, Goodman PG, Hojs A, Kirchmayer U, Medina S, Paldy A, Schindler C, Sunyer J, Perucci CA, Group PC (2009) High temperature and hospitalizations for cardiovascular and respiratory causes in 12 European cities. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179(5):383–389. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200802-217OC
Mortara A, La Rovere MT, Pinna GD, Prpa A, Maestri R, Febo O, Pozzoli M, Opasich C, Tavazzi L (1997) Arterial baroreflex modulation of heart rate in chronic heart failure: clinical and hemodynamic correlates and prognostic implications. Circulation 96(10):3450–3458
Nybo L, Kjellstrom T, Bogataj LK, Flouris AD (2017) Global heating: Attention is not enough; we need acute and appropriate actions. Temperature (Austin) 4(3):199–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2017.1338930
Peng CK, Havlin S, Stanley HE, Goldberger AL (1995) Quantification of scaling exponents and crossover phenomena in nonstationary heartbeat time series. Chaos (Woodbury, NY) 5(1):82–87. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.166141
Rey G, Jougla E, Fouillet A, Pavillon G, Bessemoulin P, Frayssinet P, Clavel J, Hemon D (2007) The impact of major heat waves on all-cause and cause-specific mortality in France from 1971 to 2003. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 80(7):615–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-007-0173-4
Rosenstein MT, Collins JJ (1993) A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Physica D 65(1):117–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(93)90009-P
Sassi R, Cerutti S, Lombardi F, Malik M, Huikuri HV, Peng CK, Schmidt G, Yamamoto Y (2015) Advances in heart rate variability signal analysis: joint position statement by the e-Cardiology ESC Working Group and the European Heart Rhythm Association co-endorsed by the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace 17(9):1341–1353. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euv015
Seely AJ, Macklem P (2012) Fractal variability: an emergent property of complex dissipative systems. Chaos 22(1):013108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3675622
Seely AJ, Macklem PT (2004) Complex systems and the technology of variability analysis. Crit Care 8(6):R367–384. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc2948
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27(3):379–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x
Siri WE (1993) Body composition from fluid spaces and density: analysis of methods. 1961. Nutrition 9(5):480–491 (discussion 480, 492)
Stapleton JM, Larose J, Simpson C, Flouris AD, Sigal RJ, Kenny GP (2014) Do older adults experience greater thermal strain during heat waves? Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39(3):292–298. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2013-0317
Stapleton JM, Poirier MP, Flouris AD, Boulay P, Sigal RJ, Malcolm J, Kenny GP (2015) At what level of heat load are age-related impairments in the ability to dissipate heat evident in females? PLoS ONE 10(3):e0119079. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119079
Tang SC, Jen HI, Lin YH, Hung CS, Jou WJ, Huang PW, Shieh JS, Ho YL, Lai DM, Wu AY, Jeng JS, Chen MF (2015) Complexity of heart rate variability predicts outcome in intensive care unit admitted patients with acute stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86(1):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-308389
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 93(5):1043–1065
Taylor JA, Carr DL, Myers CW, Eckberg DL (1998) Mechanisms underlying very-low-frequency RR-interval oscillations in humans. Circulation 98(6):547–555
Tsuji H, Larson MG, Venditti FJ Jr, Manders ES, Evans JC, Feldman CL, Levy D (1996) Impact of reduced heart rate variability on risk for cardiac events The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 94(11):2850–2855
United Nations (2013) World population ageing 2013. ST/ESA/SER.A/348. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division
World Health Organisation-Europe (2008) Heat-health action plans: guidance. World Health Organisation, Copenhagen, Denmark
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of the participants who volunteered for this study.
Funding
This study was in part supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Grant number: 286363 and 399434) and the Government of Ontario (Grant number: 16-R-036) (all funds held by Dr. Glen P. Kenny). The funding agencies had no role in the design, conduct or interpretation of results. G. P. Kenny is supported by a University of Ottawa Research Chair Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GPK and ADF conceptualized and designed the research; SRN, HWB, and GPK performed experiments; AK and CH analysed data; all authors interpreted experimental results; ADF and AK prepared figures; ADF and AK drafted manuscript; all authors edited and revised manuscript; all authors approved the final version. All measurements were performed in the Human and Environmental Physiology Research Unit, University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors, except A.S. and C.H., have no competing interests to declare. A.S. is a patent holder, Director and shareholder of Therapeutic Monitoring Systems (TMS) Inc., focused on commercialization of variability-derived clinical decision support tools developed in OHRI's Dynamical Analysis Laboratory. C.H. is a patent holder related to variability monitoring and physiological waveform analysis.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by George Havenith.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaltsatou, A., Flouris, A.D., Herry, C.L. et al. Age differences in cardiac autonomic regulation during intermittent exercise in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol 120, 453–465 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04290-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04290-8