Abstract
Purpose
Increased arterial stiffness is observed with ageing and in individuals with low cardiorespiratory fitness (\(\dot {V}\)O2peak), and associated with cardiovascular risk. Following an exercise bout, transient arterial stiffness reductions offer short-term benefit, but may depend on exercise intensity. This study assessed the effects of exercise intensity on post-exercise arterial stiffness in older adults with varying fitness levels.
Methods
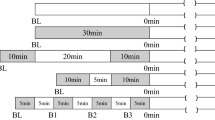
Fifty-one older adults (72 ± 5 years) were stratified into fitness tertiles (\(\dot {V}\)O2peak: low-, 22.3 ± 3.1; mid-, 27.5 ± 2.4 and high-fit 36.3 ± 6.5 mL kg−1 min−1). In a randomised order, participants underwent control (no-exercise), moderate-intensity continuous exercise (40% of peak power output; PPO), and higher-intensity interval exercise (70% of PPO) protocols. Pulse wave velocity (PWV), augmentation index (AIx75) and reflection magnitude (RM) were assessed at rest and during 90 min of recovery following each protocol.
Results
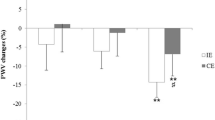
After control, delta PWV increased over time (P < 0.001) and delta RM was unchanged. After higher-intensity interval exercise, delta PWV (P < 0.001) and delta RM (P < 0.001) were lower to control in all fitness groups. After moderate-intensity continuous exercise, delta PWV was not different from control in low-fit adults (P = 0.057), but was lower in the mid- and higher-fit older adults. Post-exercise AIx75 was higher to control in all fitness groups (P = 0.001).
Conclusions
In older adults, PWV increases during seated rest and this response is attenuated after higher-intensity interval exercise, regardless of fitness level. This attenuation was also observed after moderate-intensity continuous exercise in adults with higher, but not lower fitness levels. Submaximal exercise reveals differences in the arterial stiffness responses between older adults with higher and lower cardiorespiratory fitness.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIx75:
-
Augmentation index corrected for heart rate
- cDBP:
-
Central diastolic blood pressure
- cPP:
-
Central pulse pressure
- cSBP:
-
Central systolic blood pressure
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- LMM:
-
Linear mixed model
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- Pb:
-
Backward pressure wave
- Pf:
-
Forward pressure wave
- PPO:
-
Peak power output
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- RM:
-
Reflection magnitude
- RPE:
-
Rate of perceived exertion
- \(\dot {V}\)O2peak :
-
Peak oxygen consumption
References
Akazawa N, Ra S-G, Sugawara J, Maeda S (2015) Influence of aerobic exercise training on post-exercise responses of aortic pulse pressure and augmentation pressure in postmenopausal women. Front Physiol 6:268. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00268
Binder J, Bailey KR, Seward JB, Squires RW, Kunihiro T, Hensrud DD, Kullo IJ (2006) Aortic augmentation index is inversely associated with cardiorespiratory fitness in men without known coronary heart disease. Am J Hypertens 19(10):1019–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.02.012
Bond B, Hind S, Williams CA, Barker AR (2015) The acute effect of exercise intensity on vascular function in adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47(12):2628–2635. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000715
Borg G (1998) Borg’s perceived exertion and pain scales. Human Kinetics, Champaign. ISBN-13: 978-0880116237
Bunsawat K, Ranadive SM, Lane-Cordova AD, Yan H, Kappus RM, Fernhall B, Baynard T (2017) The effect of acute maximal exercise on postexercise hemodynamics and central arterial stiffness in obese and normal-weight individuals. Physiol Rep 5(7):e13226. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13226
Butlin M, Qasem A, Avolio AP (2012) Estimation of central aortic pressure waveform features derived from the brachial cuff volume displacement waveform. Confer Proc Ann Int Confer IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Ann Confer 2012:2591–2594. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2012.6346494
Cecelja M, Chowienczyk P (2012) Role of arterial stiffness in cardiovascular disease. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis 1(4):cvd.2012.012016. https://doi.org/10.1258/cvd.2012.012016
Chirinos JA, Kips JG, Jacobs DR Jr, Brumback L, Duprez DA, Kronmal R, Bluemke DA, Townsend RR, Vermeersch S, Segers P (2012) Arterial wave reflections and incident cardiovascular events and heart failure: MESA (Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). J Am Coll Cardiol 60(21):2170–2177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.07.054
Climie RED, Srikanth V, Keith LJ, Davies JE, Sharman JE (2015) Exercise excess pressure and exercise-induced albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 308(9):H1136–H1142. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00739.2014
Coutinho T, Borlaug BA, Pellikka PA, Turner ST, Kullo IJ (2013) Sex differences in arterial stiffness and ventricular-arterial interactions. J Am Coll Cardiol 61(1):96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.997
Davies JE, Baksi J, Francis DP, Hadjiloizou N, Whinnett ZI, Manisty CH, Aguado-Sierra J, Foale RA, Malik IS, Tyberg JV, Parker KH, Mayet J, Hughes AD (2010) The arterial reservoir pressure increases with aging and is the major determinant of the aortic augmentation index. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298(2):H580-586. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00875.2009
Denham J, Brown NJ, Tomaszewski M, Williams B, O’Brien BJ, Charchar FJ (2016) Aortic augmentation index in endurance athletes: a role for cardiorespiratory fitness. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(8):1537–1544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3407-x
DeSouza CA, Shapiro LF, Clevenger CM, Dinenno FA, Monahan KD, Tanaka H, Seals DR (2000) Regular aerobic exercise prevents and restores age-related declines in endothelium-dependent vasodilation in healthy men. Circulation 102(12):1351–1357
Di Francescomarino S, Sciartilli A, Di Valerio V, Di Baldassarre A, Gallina S (2009) The effect of physical exercise on endothelial function. Sports Med (Auckland NZ) 39(10):797–812. https://doi.org/10.2165/11317750-000000000-00000
Doonan RJ, Mutter A, Egiziano G, Gomez YH, Daskalopoulou SS (2013) Differences in arterial stiffness at rest and after acute exercise between young men and women. Hypertens Res 36(3):226–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2012.158
Fok H, Jiang B, Clapp B, Chowienczyk P (2012) Regulation of vascular tone and pulse wave velocity in human muscular conduit arteries. Selective effects of nitric oxide donors to dilate muscular arteries relative to resistance vessels. Hypertension 60 (5):1220–1225. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.112.198788
Francois ME, Little JP (2015) Effectiveness and safety of high-intensity interval training in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Spectr 28(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.2337/diaspect.28.1.39
Fujie S, Sato K, Miyamoto-Mikami E, Hasegawa N, Fujita S, Sanada K, Hamaoka T, Iemitsu M (2014) Reduction of arterial stiffness by exercise training is associated with increasing plasma apelin level in middle-aged and older adults. PLoS One 9 (4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093545
Fujie S, Hasegawa N, Sato K, Fujita S, Sanada K, Hamaoka T, Iemitsu M (2015) Aerobic exercise training-induced changes in serum adropin level are associated with reduced arterial stiffness in middle-aged and older adults. Am J Physiol 309(10):H1642–H1647. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00338.2015
Gando Y, Kawano H, Yamamoto K, Sanada K, Tanimoto M, Oh T, Ohmori Y, Miyatani M, Usui C, Takahashi E, Tabata I, Higuchi M, Miyachi M (2010) Age and cardiorespiratory fitness are associated with arterial stiffening and left ventricular remodelling. J Hum Hypertens 24(3):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2009.57
Gando Y, Murakami H, Kawakami R, Yamamoto K, Kawano H, Tanaka N, Sawada SS, Miyatake N, Miyachi M (2016) Cardiorespiratory fitness suppresses age-related arterial stiffening in healthy adults: a 2-year longitudinal observational study. J Clin Hypertens 18(4):292–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12753
Gkaliagkousi E, Gavriilaki E, Nikolaidou B, Triantafyllou G, Douma S (2014) Exercise-induced pulse wave velocity changes in untreated patients with essential hypertension: the effect of an angiotensin receptor antagonist. J Clin Hypertens 16(7):482–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12340
Goodman JM, Burr JF, Banks L, Thomas SG (2016) The acute risks of exercise in apparently healthy adults and relevance for prevention of cardiovascular events. Can J Cardiol 32(4):523–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2016.01.019
Green DJ, Smith KJ (2017) Effects of exercise on vascular function, structure, and health in humans. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Med. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a029819
Hanssen H, Nussbaumer M, Moor C, Cordes M, Schindler C, Schmidt-Trucksäss A (2015) Acute effects of interval versus continuous endurance training on pulse wave reflection in healthy young men. Atherosclerosis 238(2):399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.12.038
Heffernan KS, Collier SR, Kelly EE, Jae SY, Fernhall B (2007a) Arterial stiffness and baroreflex sensitivity following bouts of aerobic and resistance exercise. Int J Sports Med 28(3):197–203. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-924290
Heffernan KS, Jae SY, Echols GH, Lepine NR, Fernhall B (2007b) Arterial stiffness and wave reflection following exercise in resistance-trained men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39(5):842–848. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e318031b03c
Hickson SS, Nichols WW, McDonnell BJ, Cockcroft JR, Wilkinson IB, McEniery CM (2016) Influence of the central-to-peripheral arterial stiffness gradient on the timing and amplitude of wave reflections. Hypertens Res 39(10):723–729. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2016.64
Hughes AD, Park C, Davies J, Francis D, Mc GTSA., Mayet J, Parker KH (2013) Limitations of augmentation index in the assessment of wave reflection in normotensive healthy individuals. PLoS One 8(3):e59371. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059371
Hull JH, Ansley L, Bolton CE, Sharman JE, Knight RK, Cockcroft JR, Shale DJ, Garrod R (2011) The effect of exercise on large artery haemodynamics in cystic fibrosis. J Cystic Fibrosis 10(2):121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcf.2010.12.001
Hwang MH, Yoo JK, Kim HK, Hwang CL, Mackay K, Hemstreet O, Nichols WW, Christou DD (2014) Validity and reliability of aortic pulse wave velocity and augmentation index determined by the new cuff-based SphygmoCor Xcel. J Hum Hypertens 28(8):475–481. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.144
Jablonski KL, Donato AJ, Fleenor BS, Nowlan MJ, Walker AE, Kaplon RE, Ballak DB, Seals DR (2015) Reduced large elastic artery stiffness with regular aerobic exercise in middle-aged and older adults: potential role of suppressed nuclear factor kappa B signalling. J Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000000742
Jae SY, Heffernan KS, Fernhall B, Oh YS, Park WH, Lee M-K, Choi Y-H (2010) Association between cardiorespiratory fitness and arterial stiffness in men with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 90(3):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.08.025
Keith LJ, Rattigan S, Keske MA, Jose M, Sharman JE (2013) Exercise aortic stiffness: reproducibility and relation to end-organ damage in men. J Hum Hypertens 27(8):516–522. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.5
Kim H-K, Hwang C-L, Yoo J-K, Hwang M-H, Lim J, Handberg EM, Nichols WW, Christou DD (2016) All-extremity aerobic exercise training improves carotid artery compliance in older adults. FASEB J 30 (1 Supplement):lb604. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001229
Kingwell BA, Berry KL, Cameron JD, Jennings CL, Dart AM (1997) Arterial compliance increases after moderate-intensity cycling. Am J Physiol 273(542–5):H2186–H2191
Kiviniemi AM, Hautala AJ, Karjalainen JJ, Piira OP, Lepojarvi S, Ukkola O, Huikuri HV, Tulppo MP (2014) Acute post-exercise change in blood pressure and exercise training response in patients with coronary artery disease. Front Physiol 5:526. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00526
Lane AD, Ranadive SM, Yan H, Kappus RM, Cook MD, Sun P, Woods JA, Wilund K, Fernhall B (2013) Effect of sex on wasted left ventricular effort following maximal exercise. Int J Sports Med 34(9):770–776. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1329990
Li Y, Cordes M, Recio-Rodriguez JI, Garcia-Ortiz L, Hanssen H, Schmidt-Trucksass A (2014) Diurnal variation of arterial stiffness in healthy individuals of different ages and patients with heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Investig 74(2):155–162. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365513.2013.864787
Lim J, Pearman ME, Park W, Alkatan M, Machin DR, Tanaka H (2016) Impact of blood pressure perturbations on arterial stiffness. Am J Physiol 309(12):R1540-R1545. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00368.2015
London GM, Pannier B (2010) Arterial functions: how to interpret the complex physiology. Nephrol Dialysis Transpl. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfq614
Luttrell MJ, Halliwill JR (2015) Recovery from exercise: vulnerable state, window of opportunity, or crystal ball? Front Physiol 6:204. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00204
Mahmud A, Feely J (2008) β-Blockers reduce aortic stiffness in hypertension but nebivolol, not atenolol, reduces wave reflection. Am J Hypertens 21(6):663–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2008.156
McClean CM, Clegg M, Shafat A, Murphy MH, Trinick T, Duly E, McLaughlin J, Fogarty M, Davison GW (2011) The impact of acute moderate intensity exercise on arterial regional stiffness, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidant status in healthy males. Res Sports Med 19(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/15438627.2011.534963
McEniery CM, Hall IR, Qasem A, Wilkinson IB, Cockcroft JR (2005) Normal vascular aging: differential effects on wave reflection and aortic pulse wave velocity: the Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial (ACCT). J Am Coll Cardiol 46(9):1753–1760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2005.07.037
Millasseau SC, Stewart AD, Patel SJ, Redwood SR, Chowienczyk PJ (2005) Evaluation of carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity: influence of timing algorithm and heart rate. Hypertension 45(2):222–226. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000154229.97341.d2
Millen AM, Woodiwiss AJ, Norton GR (2016) Post-exercise effects on aortic wave reflection derived from wave separation analysis in young- to middle-aged pre-hypertensives and hypertensives. Eur J Appl Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3391-1
Mitchell GF, Parise H, Benjamin EJ, Larson MG, Keyes MJ, Vita JA, Vasan RS, Levy D (2004) Changes in arterial stiffness and wave reflection with advancing age in healthy men and women: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 43(6):1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000128420.01881.aa
Mitchell GF, Hwang S-J, Vasan RS, Larson MG, Pencina MJ, Hamburg NM, Vita JA, Levy D, Benjamin EJ (2010) Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: the Framingham Heart study. Circulation 121(4):505–511. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.886655
Moore SM, Berrones AJ, Clasey JL, Abel MG, Fleenor BS (2016) Arterial hemodynamics are impaired at rest and following acute exercise in overweight young men. Vasc Med (United Kingdom) 21(6):497–505. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X16666692
Munir S, Jiang B, Guilcher A, Brett S, Redwood S, Marber M, Chowienczyk P (2008) Exercise reduces arterial pressure augmentation through vasodilation of muscular arteries in humans. Am J Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.01171.2007
Mutter AF, Cooke AB, Saleh O, Gomez YH, Daskalopoulou SS (2017) A systematic review on the effect of acute aerobic exercise on arterial stiffness reveals a differential response in the upper and lower arterial segments. Hypertens Res 40(2):146–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2016.111
Nichols WW (2005) Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms. Am J Hypertens 18(1 Pt 2):3s–10s. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.10.009
Nichols WW, Singh BM (2002) Augmentation index as a measure of peripheral vascular disease state. Curr Opin Cardiol 17(5):543–551
Nichols W, O’Rourke M, Vlachopoulos C (2011) McDonald’s blood flow in arteries, sixth edition: theoretical, experimental and clinical principles. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Pialoux V, Brown AD, Leigh R, Friedenreich CM, Poulin MJ (2009) Effect of cardiorespiratory fitness on vascular regulation and oxidative stress in postmenopausal women. Hypertension 54(5):1014–1020. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.109.138917
Poveda JJ, Berrazueta JR, Ochoteco A, Montalban C, Garcia-Unzueta MT, Fernandez C, Pena N, Amado JA (1998) Age-related responses of vasoactive factors during acute exercise. Hormone Metabol Res 30 (11):668–672. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-978955
Radhakrishnan J, Swaminathan N, Pereira NM, Henderson K, Brodie DA (2016) Acute changes in arterial stiffness following exercise in people with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metabol Syndr. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2016.08.013
Ramos JS, Ramos MV, Dalleck LC, Borrani F, Walker KB, Fassett RG, Sharman JE, Coombes JS (2016) Fitness is independently associated with central hemodynamics in metabolic syndrome. Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000916
Romero SA, Minson CT, Halliwill JR (2017) The cardiovascular system after exercise. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda, Md: 1985) 122(4):925–932. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00802.2016
Rothman KJ (1990) No adjustments are needed for multiple comparisons. Epidemiology (Cambridge Mass) 1(1):43–46
Santana HA, Moreira SR, Asano RY, Sales MM, Cordova C, Campbell CS, Espindola FS, Sposito AC, Nobrega OT, Simoes HG (2013) Exercise intensity modulates nitric oxide and blood pressure responses in hypertensive older women. Aging Clin Exp Res 25(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0017-x
Schultz M, La Gerche A, Sharman J (2017) Blood pressure response to exercise and cardiovascular disease. Curr Hypertens Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-017-0787-1
Shim CY, Yang WI, Park S, Kang MK, Ko YG, Choi D, Jang Y, Chung N, Ha JW (2011) Overweight and its association with aortic pressure wave reflection after exercise. Am J Hypertens 24(10):1136–1142. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2011.121
Siasos G, Athanasiou D, Terzis G, Stasinaki A, Oikonomou E, Tsitkanou S, Kolokytha T, Spengos K, Papavassiliou AG, Tousoulis D (2016) Acute effects of different types of aerobic exercise on endothelial function and arterial stiffness. Eur J Prev Cardiol. https://doi.org/10.1177/2047487316647185
Thijssen DH, Carter SE, Green DJ (2016) Arterial structure and function in vascular ageing: are you as old as your arteries? J Physiol 594(8):2275–2284. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp270597
Tordi N, Mourot L, Colin E, Regnard J (2010) Intermittent versus constant aerobic exercise: effects on arterial stiffness. Eur J Appl Physiol 108(4):801–809
Tsao CW, Pencina KM, Massaro JM, Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vasan RS, Hoffmann U, O’Donnell CJ, Mitchell GF (2014) Cross-sectional relations of arterial stiffness, pressure pulsatility, wave reflection, and arterial calcification. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.114.303916
Vaitkevicius PV, Fleg JL, Engel JH, O’Connor FC, Wright JG, Lakatta LE, Yin FC, Lakatta EG (1993) Effects of age and aerobic capacity on arterial stiffness in healthy adults. Circulation 88(4 Pt 1):1456–1462
Van Bortel LM, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Chowienczyk P, Cruickshank JK, De Backer T, Filipovsky J, Huybrechts S, Mattace-Raso FU, Protogerou AD, Schillaci G, Segers P, Vermeersch S, Weber T (2012) Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens 30(3):445–448. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32834fa8b0
van de Velde L, Eeftinck Schattenkerk DW, Venema P, Best HJ, van den Bogaard B, Stok WJ, Westerhof BE, van den Born BJH (2017) Myocardial preload alters central pressure augmentation through changes in the forward wave. J Hypertens. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000001583
Wang JJ, O’Brien AB, Shrive NG, Parker KH, Tyberg JV (2003) Time-domain representation of ventricular-arterial coupling as a windkessel and wave system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284(4):H1358-1368. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00175.2002
Wang H, Zhang T, Zhu W, Wu H, Yan S (2014) Acute effects of continuous and interval low-intensity exercise on arterial stiffness in healthy young men. Eur J Appl Physiol 114(7):1385–1392
Westerhof BE, Guelen I, Westerhof N, Karemaker JM, Avolio A (2006) Quantification of wave reflection in the human aorta from pressure alone: a proof of principle. Hypertension 48(4):595–601. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000238330.08894.17
Wilkinson IB, MacCallum H, Flint L, Cockcroft JR, Newby DE, Webb DJ (2000) The influence of heart rate on augmentation index and central arterial pressure in humans. J Physiol 525(Pt 1):263–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00263.x
Wilkinson IB, McEniery CM, Schillaci G, Boutouyrie P, Segers P, Donald A, Chowienczyk PJ (2010) ARTERY Society guidelines for validation of non-invasive haemodynamic measurement devices: Part 1, arterial pulse wave velocity. Artery Res 4(2):34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artres.2010.03.001
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by grants from the National Health and Medical Research Council (1000967, 1022752, 1079369) and The Townsville Hospital. Professor Jonathan Golledge’s work is supported by fellowships from the NHMRC (1117061) and the Queensland Government (Senior Clinical Research Fellowship). Support for this work was also provided through the Inflammation and Healing Research Cluster at the University of the Sunshine Coast.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the manuscript. Below is the short description of the manuscript contribution made by each listed author: Conceived and designed the experiment: MP, MW, TB, CA. Performed the experiment: MP, MW, TB. Analysed the data: MP, TB, CA. Wrote/reviewed the paper: MP, TB, MW, MN, KG, AL, JG, CA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Keith Phillip George.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perissiou, M., Bailey, T.G., Windsor, M. et al. Effects of exercise intensity and cardiorespiratory fitness on the acute response of arterial stiffness to exercise in older adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 1673–1688 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3900-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3900-5