Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether orally administered vitamin C attenuates expected mental stress-induced reductions in brachial artery endothelial function as measured by flow-mediated dilation (FMD).
Methods
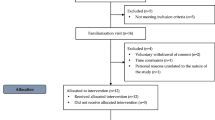
Fifteen men (21 ± 2 years) were given 1000 mg of vitamin C or placebo over two visits in a randomized, double-blinded, within-subject design. Acute mental stress was induced using the Trier Social Stress Test (TSST). Saliva samples for cortisol determination and FMD measures were obtained at baseline, pre-TSST, and 30 and 90-min post-TSST. An additional saliva sample was obtained immediately post-TSST. Cardiovascular stress reactivity was characterized by changes in heart rate (HR) and mean arterial pressure (MAP).
Results
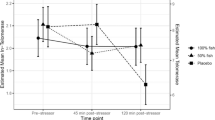
A significant stress response was elicited by the TSST in both conditions [MAP, HR, and salivary cortisol increased (p < 0.001)]. Overall FMD did not differ pre- vs. post-stress (time: p = 0.631) and there was no effect of vitamin C (condition: p = 0.792) (interaction between time and condition, p = 0.573). However, there was a correlation between cortisol reactivity and changes in FMD from pre- to post-stress in the placebo condition (r 2 = 0.66, p < 0.001) that was abolished in the vitamin C condition (r 2 = 0.02, p = 0.612).
Conclusion
Acute mental stress did not impair endothelial function, and vitamin C disrupted the relationship between cortisol reactivity and changes in FMD post-stress. This suggests that acute mental stress does not universally impair endothelial function and that reactive oxygen species signaling may influence the interaction between FMD and stress responses.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- absFMD:
-
Absolute FMD
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- BH4:
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- C:
-
Condition
- EDHF:
-
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunoassay
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- FMD:
-
Flow-mediated dilation
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- ONOO-:
-
Peroxynitrite
- PAR:
-
Physical activity recall
- RH:
-
Reactive hyperemia
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SR:
-
Shear rate
- TSST:
-
Trier Social Stress Test
- TxC:
-
Time by condition
References
Ashton T, Young IS, Peters JR, Jones E, Jackson SK, Davies B, Rowlands CC (1999) Electron spin resonance spectroscopy, exercise, and oxidative stress: an ascorbic acid intervention study. J Appl Physiol 87:2032–2036
Atkinson CL, Carter HH, Dawson EA, Naylor LH, Thijssen DH, Green DJ (2015) Impact of handgrip exercise intensity on brachial artery flow-mediated dilation. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:1705–1713
Brandes RP, Weissmann N, Schroder K (2014) Redox-mediated signal transduction by cardiovascular Nox NADPH oxidases. J Mol Cell Cardiol 73:70–79
Breton-Romero R, Lamas S (2013) Hydrogen peroxide signaling mediator in the activation of p38 MAPK in vascular endothelial cells. Methods Enzymol 528:49–59
Breton-Romero R, Gonzalez de OC, Romero N, Sanchez-Gomez FJ, de Alvaro C, Porras A, Rodriguez-Pascual F, Laranjinha J, Radi R, Lamas S (2012) Critical role of hydrogen peroxide signaling in the sequential activation of p38 MAPK and eNOS in laminar shear stress. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1093–1100
Broadley AJ, Korszun A, Abdelaal E, Moskvina V, Jones CJ, Nash GB, Ray C, Deanfield J, Frenneaux MP (2005) Inhibition of cortisol production with metyrapone prevents mental stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and baroreflex impairment. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:344–350
Burke TM, Wolin MS (1987) Hydrogen peroxide elicits pulmonary arterial relaxation and guanylate cyclase activation. Am J Physiol 252:H721–H732
Capettini LS, Cortes SF, Gomes MA, Silva GA, Pesquero JL, Lopes MJ, Teixeira MM, Lemos VS (2008) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase-derived hydrogen peroxide is a major endothelium-dependent relaxing factor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H2503–H2511
Chatterjee S, Fisher AB (2014) Mechanotransduction in the endothelium: role of membrane proteins and reactive oxygen species in sensing, transduction, and transmission of the signal with altered blood flow. Antioxid Redox Signal 20:899–913
Dickerson SS, Kemeny ME (2004) Acute stressors and cortisol responses: a theoretical integration and synthesis of laboratory research. Psychol Bull 130:355–391
Dietz NM, Rivera JM, Eggener SE, Fix RT, Warner DO, Joyner MJ (1994) Nitric oxide contributes to the rise in forearm blood flow during mental stress in humans. J Physiol 480(Pt 2):361–368
Drummond GR, Cai H, Davis ME, Ramasamy S, Harrison DG (2000) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression by hydrogen peroxide. Circ Res 86:347–354
Forstermann U (2006) Janus-faced role of endothelial NO synthase in vascular disease: uncoupling of oxygen reduction from NO synthesis and its pharmacological reversal. Biol Chem 387:1521–1533
Forstermann U, Munzel T (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation 113:1708–1714
Garde AH, Hansen AM (2005) Long-term stability of salivary cortisol. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 65:433–436
Ghiadoni L, Donald AE, Cropley M, Mullen MJ, Oakley G, Taylor M, O’Connor G, Betteridge J, Klein N, Steptoe A, Deanfield JE (2000) Mental stress induces transient endothelial dysfunction in humans. Circulation 102:2473–2478
Gokce N, Keaney JF Jr, Frei B, Holbrook M, Olesiak M, Zachariah BJ, Leeuwenburgh C, Heinecke JW, Vita JA (1999) Long-term ascorbic acid administration reverses endothelial vasomotor dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 99:3234–3240
Iuchi T, Akaike M, Mitsui T, Ohshima Y, Shintani Y, Azuma H, Matsumoto T (2003) Glucocorticoid excess induces superoxide production in vascular endothelial cells and elicits vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circ Res 92:81–87
Jazuli F, Pyke KE (2011) The impact of baseline artery diameter on flow-mediated vasodilation: a comparison of brachial and radial artery responses to matched levels of shear stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301:H1667–H1677
Johnson BD, Mather KJ, Newcomer SC, Mickleborough TD, Wallace JP (2012) Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation following exercise with augmented oscillatory and retrograde shear rate. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 10:34
Kirschbaum C, Pirke KM, Hellhammer DH (1993) The ‘Trier Social Stress Test’—a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology 28:76–81
Kugiyama K, Motoyama T, Hirashima O, Ohgushi M, Soejima H, Misumi K, Kawano H, Miyao Y, Yoshimura M, Ogawa H, Matsumura T, Sugiyama S, Yasue H (1998) Vitamin C attenuates abnormal vasomotor reactivity in spasm coronary arteries in patients with coronary spastic angina. J Am Coll Cardiol 32:103–109
Laursen JB, Somers M, Kurz S, McCann L, Warnholtz A, Freeman BA, Tarpey M, Fukai T, Harrison DG (2001) Endothelial regulation of vasomotion in apoE-deficient mice: implications for interactions between peroxynitrite and tetrahydrobiopterin. Circulation 103:1282–1288
Levine GN, Frei B, Koulouris SN, Gerhard MD, Keaney JF Jr, Vita JA (1996a) Ascorbic acid reverses endothelial vasomotor dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 93:1107–1113
Levine M, Conry-Cantilena C, Wang Y, Welch RW, Washko PW, Dhariwal KR, Park JB, Lazarev A, Graumlich JF, King J, Cantilena LR (1996b) Vitamin C pharmacokinetics in healthy volunteers: evidence for a recommended dietary allowance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3704–3709
Milstien S, Katusic Z (1999) Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin by peroxynitrite: implications for vascular endothelial function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 263:681–684
Morimoto K, Morikawa M, Kimura H, Ishii N, Takamata A, Hara Y, Uji M, Yoshida K (2008) Mental stress induces sustained elevation of blood pressure and lipid peroxidation in postmenopausal women. Life Sci 82:99–107
Padayatty SJ, Sun H, Wang Y, Riordan HD, Hewitt SM, Katz A, Wesley RA, Levine M (2004) Vitamin C pharmacokinetics: implications for oral and intravenous use. Ann Intern Med 140:533–537
Poitras VJ, Pyke KE (2013) The impact of acute mental stress on vascular endothelial function: evidence, mechanisms and importance. Int J Psychophysiol 88:124–135
Poitras VJ, Slattery DJ, Levac BM, Fergus S, Gurd BJ, Pyke KE (2014) The combined influence of fat consumption and repeated mental stress on brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation: a preliminary study. Exp Physiol 99:715–728
Poll EM, Kreitschmann-Andermahr I, Langejuergen Y, Stanzel S, Gilsbach JM, Gressner A, Yagmur E (2007) Saliva collection method affects predictability of serum cortisol. Clin Chim Acta 382:15–19
Pyke KE, Jazuli F (2011) Impact of repeated increases in shear stress via reactive hyperemia and handgrip exercise: no evidence of systematic changes in brachial artery FMD. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300:H1078–H1089
Pyke KE, Hartnett JA, Tschakovsky ME (2008) Are the dynamic response characteristics of brachial artery flow mediated dilation sensitive to the magnitude of increase in shear stimulus? J Appl Physiol 105:282–292
Ray R, Murdoch CE, Wang M, Santos CX, Zhang M, Alom-Ruiz S, Anilkumar N, Ouattara A, Cave AC, Walker SJ, Grieve DJ, Charles RL, Eaton P, Brewer AC, Shah AM (2011) Endothelial Nox4 NADPH oxidase enhances vasodilatation and reduces blood pressure in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:1368–1376
Richardson RS, Donato AJ, Uberoi A, Wray DW, Lawrenson L, Nishiyama S, Bailey DM (2007) Exercise-induced brachial artery vasodilation: role of free radicals. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H1516–H1522
Rozanski A, Blumenthal JA, Kaplan J (1999) Impact of psychological factors on the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and implications for therapy. Circulation 99:2192–2217
Sales AR, Fernandes IA, Rocha NG, Costa LS, Rocha HN, Mattos JD, Vianna LC, Silva BM, Nobrega AC (2014) Aerobic exercise acutely prevents the endothelial dysfunction induced by mental stress among subjects with metabolic syndrome: the role of shear rate. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306:H963–H971
Sivonova M, Zitnanova I, Hlincikova L, Skodacek I, Trebaticka J, Durackova Z (2004) Oxidative stress in university students during examinations. Stress 7:183–188
Spieker LE, Hurlimann D, Ruschitzka F, Corti R, Enseleit F, Shaw S, Hayoz D, Deanfield JE, Luscher TF, Noll G (2002) Mental stress induces prolonged endothelial dysfunction via endothelin-A receptors. Circulation 105:2817–2820
Szijgyarto IC, King TJ, Ku J, Poitras VJ, Gurd BJ, Pyke KE (2013) The impact of acute mental stress on brachial artery flow-mediated dilation differs when shear stress is elevated by reactive hyperemia versus handgrip exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 38:498–506
Thomas SR, Chen K, Keaney JF Jr (2002) Hydrogen peroxide activates endothelial nitric-oxide synthase through coordinated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation via a phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277:6017–6024
Ting HH, Timimi FK, Boles KS, Creager SJ, Ganz P, Creager MA (1996) Vitamin C improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 97:22–28
Tinken TM, Thijssen DH, Hopkins N, Black MA, Dawson EA, Minson CT, Newcomer SC, Laughlin MH, Cable NT, Green DJ (2009) Impact of shear rate modulation on vascular function in humans. Hypertension 54:278–285
Tousoulis D, Davies G, Toutouzas P (1999) Vitamin C increases nitric oxide availability in coronary atherosclerosis. Ann Intern Med 131:156–157
Weitzman ED, Fukushima D, Nogeire C, Roffwarg H, Gallagher TF, Hellman L (1971) Twenty-four hour pattern of the episodic secretion of cortisol in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 33:14–22
Wever RM, van Dam T, van Rijn HJ, de Groot F, Rabelink TJ (1997) Tetrahydrobiopterin regulates superoxide and nitric oxide generation by recombinant endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237:340–344
Wolin MS, Burke TM (1987) Hydrogen peroxide elicits activation of bovine pulmonary arterial soluble guanylate cyclase by a mechanism associated with its metabolism by catalase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 143:20–25
Woodman RJ, Playford DA, Watts GF, Cheetham C, Reed C, Taylor RR, Puddey IB, Beilin LJ, Burke V, Mori TA, Green D (2001) Improved analysis of brachial artery ultrasound using a novel edge-detection software system. J Appl Physiol 91:929–937
Zheng JS, Yang XQ, Lookingland KJ, Fink GD, Hesslinger C, Kapatos G, Kovesdi I, Chen AF (2003) Gene transfer of human guanosine 5′-triphosphate cyclohydrolase I restores vascular tetrahydrobiopterin level and endothelial function in low renin hypertension. Circulation 108:1238–1245
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery Grant to K. E. Pyke. Meghan D. Plotnick was funded by an NSERC Canadian Graduate Scholarship-Master’s Program. The authors would like to acknowledge Brittany Edgett, Dr. Kathryn Wynne-Edwards, and Dr. Trisha Scribbans for their help in the analysis of salivary cortisol samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo Pagani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plotnick, M.D., D’Urzo, K.A., Gurd, B.J. et al. The influence of vitamin C on the interaction between acute mental stress and endothelial function. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 1657–1668 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3655-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3655-4