Abstract
Objective
The relationship between metalworking fluids (MWFs) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has not been previously explored. We aim to investigate the relationship between occupational exposure to MWFs and the prevalence of NAFLD and to determine the cumulative exposure threshold per day.
Methods
In 2020, 2079 employees were selected randomly from one computer numerical control machining factory in Wuxi for a questionnaire survey, and occupational health examinations were conducted at the affiliated branch of Wuxi Eighth People's Hospital. MWF samples were collected within the factory using the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) 5524 method. NAFLD was defined as having a hepatic steatosis index (HSI) ≥ 36 without significant alcohol consumption. The relationship between NAFLD and MWFs was analyzed using logistic regression, and the daily exposure threshold was calculated using R software.
Results
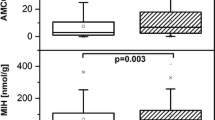
MWF exposure was found to be a risk factor for NAFLD in exposed workers compared to the non-exposed group. The OR for NAFLD in workers exposed to MWFs compared to controls was 1.42 (95% CI: 1.04–1.95). An increased risk of NAFLD was shown to be associated with an increasing dose. The daily exposure dose threshold to MWFs was found to be 6.54 mg/m3 (OR = 2.09, 95% CI: 1.24–3.52).
Conclusion
An association between occupational exposure to MWFs and NAFLD was found. As the concentration of exposure rose, the prevalence of NAFLD was also escalated.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to personal privacy and hospital requirements that employee medical examination data cannot be disclosed, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Humadi NH, Shvedova AA, Batteli L, Diotte N, Castranova V, Kommineni C (2000a) Dermal and systemic toxicity after application of semisynthetic metal-working fluids in B6C3F1 mice. J Toxicol Environ Health A 61:579–589
Al-Humadi NH, Patsy LB, Willard A, Schwegler-Berry D, Castranova V, Kommineni C (2000b) Effects of metal working fluids on B6C3F1 mouse skin. Toxicol Ind Health 16:203–210
Blair A, Stewart PA (1989) Correlation between different measures of occupational exposure to formaldehyde. Am J Epidemiol 131:510–514
Bonfanti-Azzolin G, Capelleti CP, Rodrigues KS, Abdallah SDR, Frielink AP, Rupphental G, Kuhn BB, Cattaneo R, Wolkmer P, Bortolotto JW, Parisi MM (2021) Accelerated apoptosis, oxidative stress, and cholinergic inflammation in blood of metalworkers. Toxicol Ind Health 37:752–762
Brans R, Schoenmaker M, Kiewert A, Skudlik C (2022) Occupational allergic contact dermatitis to dicylohexylamine in a metalworking fluid. Contact Dermatitis 87:205–207
Choi B (2020) Developing a job exposure matrix of work organization hazards in the united states: a review on methodological issues and research protocol. Saf Health Work 11:397–404
Choi YH, Lee JY, Moon KW (2023) Exposure to volatile organic compounds and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is associated with the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adolescents: Korea national environmental health survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 251:114508
Cohen H, White EM (2006) Metalworking fluid mist occupational exposure limits: a discussion of alternative methods. J Occup Environ Hyg 3:501–507
Colbeth HL, Chen KT, Picciotto S, Costello S, Eisen EA (2023) Metalworking fluids and cancer incidence in the united auto workers-general motors cohort. Am J Epidemiol 192:171–181
Colin R, Grzebyk M, Wild P, Hedelin G, Bourgkard E (2018) Bladder cancer and occupational exposure to metalworking fluid mist: a counter-matched case-control study in French steel-producing factories. Occup Environ Med 75:328–336
Costello S, Chen K, Picciotto S, Lutzker L, Eisen E (2020) Metalworking fluids and cancer mortality in a US autoworker cohort (1941–2015). Scand J Work Environ Health 46:525–532
Dalbey WE, Biles RW (2003) Respiratory toxicology of mineral oils in laboratory animals. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 18:921–929
Dalbey WE, McKee RH, Goyak KO, Biles RW, Murray J, White R (2014) Acute, subchronic, and developmental toxicological properties of lubricating oil base stocks. Int J Toxicol 33:110S-S135
Estrada-Ortiz N, Starokozhko V, van Steenwijk H, van der Heide C, Permentier H, van Heemskerk L, Prins GH, Heegsma J, Faber KN, Bressers S, Steiblen G, de Groot A, Groome S, van Miert E, Groothuis G, de Graaf IAM (2022) Disruption of vitamin A homeostasis by the biocide tetrakis(hydroxymethyl) phosphonium sulphate in pregnant rabbits. J Appl Toxicol 42:1921–1936
Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ (2018) Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med 24:908–922
Gamer AO, Rossbacher R, Kaufmann W, van Ravenzwaay B (2008) The inhalation toxicity of di- and triethanolamine upon repeated exposure. Food Chem Toxicol 46:2173–2183
Gandomani EA, Mosaffa N, Zendehdel R, Kohneshahri MH, Vahabi M, Sabour S (2022) Release of Interleukin-1beta evaluation among mineral oil mist-exposed workers. Toxicol Ind Health 38:270–276
Huff M, da Silveira W, Starr Hazard E, Courtney SM, Renaud L, Hardiman G (2019) Systems analysis of the liver transcriptome in adult male zebrafish exposed to the non-ionic surfactant nonylphenol. Gen Comp Endocrinol 271:1–14
International Physical Activity Questionnaire Committee (2004) Guideline for data processing and analysis of the international physical activity questionnaire. Available from https://www.physio-pedia.com/images/c/c7/Quidelines_for_interpreting_the_IPAQ.pdf. Accessed 22 May 2023
Le MH, Yeo YH, Li X, Li J, Zou B, Wu Y, Ye Q, Huang DQ, Zhao C, Zhang J, Liu C, Chang N, Xing F, Yan S, Wan ZH, Tang NSY, Mayumi M, Liu X, Liu C, Rui F, Yang H, Yang Y, Jin R, Le RHX, Xu Y, Le DM, Barnett S, Stave CD, Cheung R, Zhu Q, Nguyen MH (2022) 2019 Global NAFLD prevalence: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 20(2809–17):e28
Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HJ, Lee CH, Yang JI, Kim W, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, Cho SH, Sung MW, Lee HS (2010) Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis 42:503–508
Lee I, Park H, Kim MJ, Kim S, Choi S, Park J, Cho YH, Hong S, Yoo J, Cheon GJ, Choi K, Park YJ, Moon MK (2022) Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and volatile organic compounds is associated with a risk of obesity and diabetes mellitus among Korean adults: Korean national environmental health survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017. Int J Hyg Environ Health 240:113886
Li J, Zou B, Yeo YH, Feng Y, Xie X, Lee DH, Fujii H, Wu Y, Kam LY, Ji F, Li X, Chien N, Wei M, Ogawa E, Zhao C, Wu X, Stave CD, Henry L, Barnett S, Takahashi H, Furusyo N, Eguchi Y, Hsu YC, Lee TY, Ren W, Qin C, Jun DW, Toyoda H, Wong VW, Cheung R, Zhu Q, Nguyen MH (2019) Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:389–398
Li J, Wang T, Liu P, Yang F, Wang X, Zheng W, Sun W (2021) Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD. Food Funct 12:3898–3918
Liao C, Kim UJ, Kannan K (2018) A review of environmental occurrence, fate, exposure, and toxicity of benzothiazoles. Environ Sci Technol 52:5007–5026
Mirer F (2003) Updated epidemiology of workers exposed to metalworking fluids provides sufficient evidence for carcinogenicity. Appl Occup Environ Hyg 18:902–912
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2021) National data-FY2021 data. Available from: https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01. Accessed 22 Sept 2023
National Toxicology Program, Public Health Service National Institutes of Health U. S. Department of Health, and Services Human (2004) NTP toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of triethanolamine (Cas No. 102–71–6) in B6C3F1 mice (dermal studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 5–163.
Niosh (1988) Criteria for a recommended standard:occupational exposure metalworking fluids 98-102. DHHS Publication: National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
Niosh (2014) Metalworking fluids(MWF) all categories: method 5524 9–10. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
Nowak P, Kucharska K, Kaminski M (2019) Ecological and health effects of lubricant oils emitted into the environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(16):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16163002
Park D (2012) The occupational exposure limit for fluid aerosol generated in metalworking operations: limitations and recommendations. Saf Health Work 3:1–10
Peng W, Li K, Yan AF, Shi Z, Zhang J, Cheskin LJ, Hussain A, Wang Y (2022) Prevalence, management, and associated factors of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes in tibetan population compared with China overall. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(14):8787. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148787
Peng J, Du LL, Ma QL (2023) Serum glycolipids mediate the relationship of urinary bisphenols with NAFLD: analysis of a population-based, cross-sectional study. Environ Health 21:124
Pineiro-Carrero VM, Pineiro EO (2004) Liver. Pediatrics 113:1097–1106
Regencia ZJ, Dalmacion GV, Ligsay AD, Baja ES (2021) Short-term cumulative exposure to ambient traffic-related black carbon and blood pressure: MMDA traffic enforcers health study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(22):12122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182212122
Riazi K, Azhari H, Charette JH, Underwood FE, King JA, Afshar EE, Swain MG, Congly SE, Kaplan GG, Shaheen AA (2022) The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:851–861
Sarin SK, Kumar M, Eslam M, George J, Al Mahtab M, Akbar SMF, Jia J, Tian Q, Aggarwal R, Muljono DH, Omata M, Ooka Y, Han KH, Lee HW, Jafri W, Butt AS, Chong CH, Lim SG, Pwu RF, Chen DS (2020) Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: a lancet gastroenterology & hepatology commission. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 5:167–228
Seen S (2021) Chronic liver disease and oxidative stress-a narrative review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:1021–1035
Shrestha D, Picciotto S, LaValley MP, Liu S, Hammond SK, Weiner DE, Eisen EA, Applebaum KM (2022) End-stage renal disease and metalworking fluid exposure. Occup Environ Med 79:24–31
Stout MD, Kissling GE, Suarez FA, Malarkey DE, Herbert RA, Bucher JR (2008) Influence of Helicobacter hepaticus infection on the chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity of triethanolamine in B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Pathol 36:783–794
Ullah R, Rauf N, Nabi G, Ullah H, Shen Y, Zhou YD, Fu J (2019) Role of nutrition in the pathogenesis and prevention of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: recent updates. Int J Biol Sci 15:265–276
World Health Organization (2019) Classification of diabetes mellitus, Geneva
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J, Bugianesi E (2018) Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:11–20
Younossi Z, Tacke F, Arrese M, Chander Sharma B, Mostafa I, Bugianesi E, Wai-Sun Wong V, Yilmaz Y, George J, Fan J, Vos MB (2019) Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 69:2672–2682
Zhou J, Zhou F, Wang W, Zhang XJ, Ji YX, Zhang P, She ZG, Zhu L, Cai J, Li H (2020) Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China. Hepatology 71:1851–1864
Acknowledgements
The authors are appreciative of the help provided by the Wuxi Eighth People's Hospital Physical Examination Center.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China [Grant No. BK20211331].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL and WC contributed to the study’s conception and design. JX designed the questionnaire and communicated with the company and hospital. JW, LS, and LZ surveyed to collect data. LL and BW did the job of data entry and sorted it. WC, GL, and LZ analyzed the data. YL and WC wrote the first draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All subjects gave their signed informed consent after reading the research-related information. The study was approved by the Ethics Committees of Nantong University (2013-L073).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, W., Li, G., Zhou, L. et al. Relationship between exposure to metalworking fluids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 97, 57–64 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-023-02025-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-023-02025-z