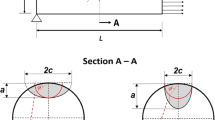
Abstract
A method is developed to evaluate the stress intensity factors (SIFs) for semi-elliptical circumferential cracks located at the inner wall of a pipe under arbitrary welding residual stress distribution. To accomplish this, at first, the three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) is performed employing singular elements along the crack front. Next, the weight function (WF) is incorporated in conjunction with the finite element results to predict the SIFs of semi-elliptical circumferential cracks in pipes. Then, the presented WF is extended to estimate the SIFs of fully circumferential cracks in pipes. Moreover, a closed-form formulation of SIFs is presented as a function of arbitrary loading condition and crack geometry. Finally, the closed-form relation has been used to predict the stress intensity factors of circumferential cracks under highly nonlinear residual stress fields. Comparison of the results and those in the literature shows an acceptable agreement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, X.B., Smith, R.A.: Fatigue growth prediction of internal surface cracks in pressure vessels. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 120, 17–23 (1998)
Grebner, H., Strathmeier, U.: Stress intensity factors for circumferential semielliptical surface cracks in a pipe under thermal loading. Eng. Fract. Mech. 22, 1–7 (1985)
Chen, X., You, Y.: Weight functions for multiple axial cracks in a coated hollow cylinder. Arch. Appl. Mech. (2014). doi:10.1007/s00419-014-0973-4
Xian-Ming, K., Si-Tao, Z., Zhen-Yuan, C.: Studies on stress intensity factor of surface cracks in a cylinder under remote tension loads. Eng. Fract. Mech. 33, 105–111 (1989)
Poette, C., Albaladejo, S.: Stress intensity factors and influence functions for circumferential surface cracks in pipes. Eng. Fract. Mech. 39, 641–650 (1991)
Wallbrink, C.D., Peng, D., Jones, R.: Assessment of partly circumferential cracks in pipes. Int. J. Fract. 133, 167–181 (2005)
Zahoor, A.: Closed form expressions for fracture mechanics analysis of cracked pipes. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 107, 203–205 (1985)
Bergman, M.: Stress intensity factors for circumferential surface cracks in pipes. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 18, 1155–1172 (1995)
Kumar, V., German, M.D., Schumacher, B.I.: Analysis of elastic surface cracks in cylinders using the line-spring model and shell finite element method. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 107(4), 403–411 (1985)
El Hakimi, A., Le Grognec, P., Hariri, S.: Numerical and analytical study of severity of cracks in cylindrical and spherical shells. Eng. Fract. Mech. 75, 1027–1044 (2008)
Kamaya, M., Nishioka, T.: Analysis of surface crack in cylinder by finite element alternating method. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 127(2), 165–172 (2005)
Alipour, K., Nabavi, S.M., Rahimi, F.: Local thermal stress intensity factors for an axial semi-elliptical crack in a hollow cylinder using the finite element method. Strength Fract. Complex. 8, 167–178 (2014)
Kamaya, M.: A combination rule for circumferential surface cracks on pipe under tension based on limit load analysis. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 133(2), 021205-1-7 (2011)
API 579–1/ASME FFS-1: Fitness-for-service, 2nd edn. American Petroleum Institute, Washington DC (2007)
Miyazaki, K., Mochizuki, M.: The effects of residual stress distribution and component geometry on the stress intensity factor of surface cracks. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 133(2), 011701-1-7 (2011)
Scarth, D.A., Xu, S.X.: Universal weight function consistent method to fit polynomial stress distribution for calculation of stress intensity factor. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 134(6), 061204-1-11 (2012)
Li, Y., Hasegawa, K., Xu, S.X., Scarth, D.A.: Weight function method with segment-wise polynomial interpolation to calculate stress intensity factors for complicated stress distributions. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 136(2), 021202-1-10 (2014)
Oh, C.Y., Kim, Y.J., Oh, Y.J., Kim, J.S., Song, T.K., Kim, Y.B.: Evaluation of stress intensity factors due to welding residual stresses for circumferential cracked pipes. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 105, 36–48 (2013)
Katsuyama, J., Tobita, T., Itoh, H., Onizawa, K.: Effect of welding conditions on residual stress and stress corrosion cracking behavior at butt-welding joints of stainless steel pipes. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 134(2), 021403-1-9 (2012)
Huh, N.S.: Elastic t stress estimates for circumferential surface-cracked cylinders. Fatigue Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 29, 57–69 (2006)
Kim, Y.J., Kim, J.S., Lee, Y.Z., Kim, Y.J.: Non-linear fracture mechanics analyses of part circumferential surface cracked pipes. Int. J. Fract. 116, 347–375 (2002)
Cho, D.H., Woo, S.W., Chang, Y.S., Choi, J.B., Kim, Y.J., Jhung, M.J., Choi, Y.H.: Enhancement of j estimation for typical nuclear pipes with a circumferential surface crack under tensile load. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 24(3), 681–686 (2010)
Cho, D.H., Seo, H.B., Kim, Y.J., Chang, Y.S., Jhung, M.J., Choi, Y.H.: Advances in j-integral estimation of circumferentially surface cracked pipes. Fatigue Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 34, 667–681 (2011)
Mettu, S.R., Forman, R.G.: Analysis of circumferential cracks in circular cylinders using the weight-function method. In: Chona R (ed.) Fracture mechanics, twenty-third symposium, ASTM STP 1189, pp. 417–440. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia (1993)
Varfolomeyev, I.V., Petersilge, M., Busch, M.: Stress intensity factors for internal circumferential cracks in thin- and thick-walled cylinders. Eng. Fract. Mech. 60, 491–500 (1998)
Nabavi, S.M., Ghajar, R.: Analysis of thermal stress intensity factors for cracked cylinders using weight function method. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48, 1811–1823 (2010)
Ghajar, R., Nabavi, S.M.: Closed-form thermal stress intensity factors for an internal circumferential crack in a thick-walled cylinder. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 33(8), 504–512 (2010)
Nabavi, S.M., Kamyab, M.: Determination of transient thermal stress intensity factors for circumferential cracks in cylinders. In: Proceedings of the 20th ISME Mechanical Engineering Conference, Shiraz University, Shiraz, paper no. 2219, 15–17 May (2012)
ABAQUS: User’s manual, version 6.12, Dassault Systèmes Inc., USA (2012)
Bueckner, H.F.: A novel principle for the computation of stress intensity factors. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 50(9), 529–546 (1970)
Rice, J.R.: Some remarks on elastic crack-tip stress fields. Int. J. Solids Struct. 8, 751–758 (1972)
Peteoski, H.J., Achenbach, J.D.: Computation of the weight function from a stress intensity factor. Eng. Fract. Mech. 10, 257–266 (1978)
Shen, G., Glinka, G.: Weight function for a surface semi-elliptical crack in a finite thickness plate. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 15, 247–255 (1991)
Nabavi, S.M., Azad, R.: The effect of term numbers of a weight function on the accuracy of stress intensity factors in a cracked cylinder. In: Proceedings of the 20th ISME Mechanical Engineering Conference, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran, paper no. 1919, 15–17 May (2012)
Fett, T., Mattheck, C., Munz, D.: On the calculation of crack opening displacement from the stress intensity factor. Eng. Fract. Mech. 27, 697–715 (1987)
Newman, Jr, Raju, I.S.: Stress intensity factor equations for cracks in three-dimensional finite bodies. Technical Report No. 85793, NASA Langley Research Center, USA (1984)
Spiegel, M.R.: Mathematical Handbook of Formulas and Tables. Mc-Graw Hill, New York (1968)
Laham, S.: Stress Intensity Factors and Limit Load Handbooks. British Energy Generation Ltd., The United Kingdom (1999)
Mochizuki, M., Hattori, T., Nakakado, K.: Residual stress reduction and fatigue strength improvement by controlling welding pass sequences. ASME J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 122(1), 108–112 (2000)
Mochizuki, M., Hayashi, M., Hattori, T.: Residual stress distribution depending on welding sequence in multi-pass welded joints with x-shaped groove. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 122(1), 27–32 (2000)
Dong, P., Burst, F.: Welding residual stresses and effects on fracture in pressure vessels and piping components: a millennium review and beyond. ASME J. Press. Vessel. Technol. 122(3), 329–338 (2000)
ASME section IX: ASME boiler and pressure vessel code (BPVC) (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zareei, A., Nabavi, S.M. Weight function for circumferential semi-elliptical cracks in cylinders due to residual stress fields induced by welding. Arch Appl Mech 86, 1219–1230 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1087-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1087-3