Abstract
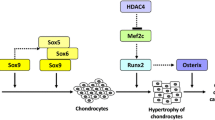
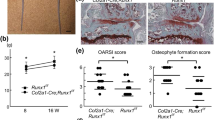
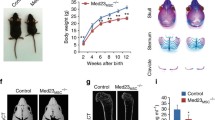
Runx2 is a transcription factor that is essential for osteoblast differentiation and chondrocyte maturation. Ihh, expressed in prehypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes, is required for the specification of Runx2+ osteoprogenitors in endochondral bone development. Runx2 induces Sp7, an essential transcription factor for osteoblast differentiation. Canonical Wnt signaling is also required for osteoblast differentiation. Runx2+ osteoprogenitors retain the capacity to differentiate into chondrocytes, and Sp7 and canonical Wnt signaling direct cells to osteoblasts, thereby inhibiting chondrocyte differentiation. The function of Runx2 after the commitment to osteoblasts remains controversial. Runx3 has a redundant function with Runx2 in chondrocyte maturation. Runx2 regulates the expression of Ihh, Col10a1, Spp1, Ibsp, Mmp13, and Vegfa in the respective layers in growth plates. Runx2 enhances chondrocyte proliferation through the induction of Ihh. Ihh induces Pthlh, which inhibits Runx2 and chondrocyte maturation, forming a negative feedback loop for chondrocyte maturation. Runx2 is one of the genes responsible for the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) because RUNX2 is up-regulated in chondrocytes in OA cartilage and a germline haplodeficiency or deletion of Runx2 in articular chondrocytes decelerates OA progression. Runx2 plays an important role in the bone metastasis of breast and prostate cancers by up-regulating Spp1, Ibsp, Mmp9, Mmp13, Vegfa, Tnfsf11, and Ihh expression and down-regulating Tnfrsf11b expression. Cbfb forms a heterodimer with Runx2 and is required for the efficient DNA binding of Runx2. Cbfb stabilizes Runx proteins at different levels among Runx family proteins by inhibiting their ubiquitination-mediated degradation. Cbfb plays more important roles in endochondral ossification than in intramembranous ossification.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhami MD, Rashid H, Chen H, Javed A (2014) Runx2 activity in committed osteoblasts is not essential for embryonic skeletogenesis. Connect Tissue Res 55 Suppl 1:102–106. https://doi.org/10.3109/03008207.2014.923873
Akech J, Wixted JJ, Bedard K, Van der Deen M, Hussain S, Guise TA, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Languino LR, Altieri DC (2010) Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients: mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. Oncogene 29(6):811–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.389
Akune T, Ohba S, Kamekura S, Yamaguchi M, Chung UI, Kubota N, Terauchi Y, Harada Y, Azuma Y, Nakamura K, Kadowaki T, Kawaguchi H (2004) PPARγ insufficiency enhances osteogenesis through osteoblast formation from bone marrow progenitors. J Clin Invest 113(6):846–855. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci19900
Amano K, Densmore MJ, Lanske B (2015) Conditional deletion of indian hedgehog in limb mesenchyme results in complete loss of growth plate formation but allows mature osteoblast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 30(12):2262–2272. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2582
Baek WY, Lee MA, Jung JW, Kim SY, Akiyama H, de Crombrugghe B, Kim JE (2009) Positive regulation of adult bone formation by osteoblast-specific transcription factor osterix. J Bone Miner Res 24(6):1055–1065. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.081248
Bauer O, Sharir A, Kimura A, Hantisteanu S, Takeda S, Groner Y (2015) Loss of osteoblast Runx3 produces severe congenital osteopenia. Mol Cell Biol 35(7):1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01106-14
Cao K, Wei L, Zhang Z, Guo L, Zhang C, Li Y, Sun C, Sun X, Wang S, Li P, Wei X (2014) Decreased histone deacetylase 4 is associated with human osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration by releasing histone deacetylase 4 inhibition of runt-related transcription factor-2 and increasing osteoarthritis-related genes: a novel mechanism of human osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther 16(6):491. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-014-0491-3
Castano-Betancourt MC, Evans DS, Ramos YF, Boer CG, Metrustry S, Liu Y, den Hollander W, van Rooij J, Kraus VB, Yau MS, Mitchell BD, Muir K, Hofman A, Doherty M, Doherty S, Zhang W, Kraaij R, Rivadeneira F, Barrett-Connor E, Maciewicz RA, Arden N, Nelissen RG, Kloppenburg M, Jordan JM, Nevitt MC, Slagboom EP, Hart DJ, Lafeber F, Styrkarsdottir U, Zeggini E, Evangelou E, Spector TD, Uitterlinden AG, Lane NE, Meulenbelt I, Valdes AM, van Meurs JB (2016) Novel genetic variants for cartilage thickness and hip osteoarthritis. PLoS Genet 12(10):e1006260. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006260
Chen H, Ghori-Javed FY, Rashid H, Adhami MD, Serra R, Gutierrez SE, Javed A (2014a) Runx2 regulates endochondral ossification through control of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 29(12):2653–2665. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2287
Chen W, Ma J, Zhu G, Jules J, Wu M, McConnell M, Tian F, Paulson C, Zhou X, Wang L, Li YP (2014b) Cbfb deletion in mice recapitulates cleidocranial dysplasia and reveals multiple functions of Cbfb required for skeletal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(23):8482–8487. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1310617111
Chung UI, Schipani E, McMahon AP, Kronenberg HM (2001) Indian hedgehog couples chondrogenesis to osteogenesis in endochondral bone development. J Clin Invest 107(3):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci11706
Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y (2005) Wnt/β-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell 8(5):739–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.03.016
Engin F, Yao Z, Yang T, Zhou G, Bertin T, Jiang MM, Chen Y, Wang L, Zheng H, Sutton RE, Boyce BF, Lee B (2008) Dimorphic effects of Notch signaling in bone homeostasis. Nat Med 14(3):299–305. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1712
Enomoto H, Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iwamoto M, Nomura S, Himeno M, Kitamura Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T (2000) Cbfa1 is a positive regulatory factor in chondrocyte maturation. J Biol Chem 275(12):8695–8702
Enomoto H, Shiojiri S, Hoshi K, Furuichi T, Fukuyama R, Yoshida CA, Kanatani N, Nakamura R, Mizuno A, Zanma A, Yano K, Yasuda H, Higashio K, Takada K, Komori T (2003) Induction of osteoclast differentiation by Runx2 through receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin regulation and partial rescue of osteoclastogenesis in Runx2−/− mice by RANKL transgene. J Biol Chem 278(26):23971–23977. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302457200
Enomoto H, Furuichi T, Zanma A, Yamana K, Yoshida C, Sumitani S, Yamamoto H, Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Iwamoto M, Komori T (2004) Runx2 deficiency in chondrocytes causes adipogenic changes in vitro. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 3):417–425. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.00866
Fei T, Mengrui W, Lianfu D, Guochun Z, Junqing M, Bo G, Lin W, Yi-Ping L, Wei C (2014) Core binding factor β (Cbfβ) controls the balance of chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation by upregulating Indian hedgehog (Ihh) expression and inhibiting parathyroid hormone-related protein receptor (PPR) expression in postnatal cartilage and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 29(7):1564–1574. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2275
Ferrari N, McDonald L, Morris JS, Cameron ER, Blyth K (2013) RUNX2 in mammary gland development and breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 228(6):1137–1142. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24285
Fujiwara M, Tagashira S, Harada H, Ogawa S, Katsumata T, Nakatsuka M, Komori T, Takada H (1999) Isolation and characterization of the distal promoter region of mouse Cbfa1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1446(3):265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-4781(99)00113-X
Galindo M, Pratap J, Young DW, Hovhannisyan H, Im H-J, Choi J-Y, Lian JB, Stein JL, Stein GS, Van Wijnen AJ (2005) The bone-specific expression of Runx2 oscillates during the cell cycle to support a G1-related antiproliferative function in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 280(21):20274–20285. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413665200
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, Bhat RA, Bodine PV, Komm BS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2005) Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem 280(39):33132–33140. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M500608200
Geoffroy V, Kneissel M, Fournier B, Boyde A, Matthias P (2002) High bone resorption in adult aging transgenic mice overexpressing cbfa1/runx2 in cells of the osteoblastic lineage. Mol Cell Biol 22(17):6222–6233. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.17.6222-6233.2002
Ghali O, Chauveau C, Hardouin P, Broux O, Devedjian JC (2010) TNF-α’s effects on proliferation and apoptosis in human mesenchymal stem cells depend on RUNX2 expression. J Bone Miner Res 25(7):1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.52
Harada H, Tagashira S, Fujiwara M, Ogawa S, Katsumata T, Yamaguchi A, Komori T, Nakatsuka M (1999) Cbfa1 isoforms exert functional differences in osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 274(11):6972–6978. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.11.6972
Hassan MQ, Tare R, Lee SH, Mandeville M, Weiner B, Montecino M, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2007) HOXA10 controls osteoblastogenesis by directly activating bone regulatory and phenotypic genes. Mol Cell Biol 27(9):3337–3352. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.01544-06
Hess J, Porte D, Munz C, Angel P (2001) AP-1 and Cbfa/runt physically interact and regulate parathyroid hormone-dependent MMP13 expression in osteoblasts through a new osteoblast-specific element 2/AP-1 composite element. J Biol Chem 276(23):20029–20038. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010601200
Hill TP, Spater D, Taketo MM, Birchmeier W, Hartmann C (2005) Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Dev Cell 8(5):727–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.013
Hilton MJ, Tu X, Wu X, Bai S, Zhao H, Kobayashi T, Kronenberg HM, Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP, Kopan R, Long F (2008) Notch signaling maintains bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Med 14(3):306–314. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1716
Himeno M, Enomoto H, Liu W, Ishizeki K, Nomura S, Kitamura Y, Komori T (2002) Impaired vascular invasion of Cbfa1-deficient cartilage engrafted in the spleen. J Bone Miner Res 17(7):1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.7.1297
Hirata M, Kugimiya F, Fukai A, Saito T, Yano F, Ikeda T, Mabuchi A, Sapkota BR, Akune T, Nishida N, Yoshimura N, Nakagawa T, Tokunaga K, Nakamura K, Chung UI, Kawaguchi H (2012) C/EBPβ and RUNX2 cooperate to degrade cartilage with MMP-13 as the target and HIF-2α as the inducer in chondrocytes. Hum Mol Genet 21(5):1111–1123. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr540
Hu H, Hilton MJ, Tu X, Yu K, Ornitz DM, Long F (2005) Sequential roles of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling in osteoblast development. Development 132(1):49–60. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01564
Inada M, Yasui T, Nomura S, Miyake S, Deguchi K, Himeno M, Sato M, Yamagiwa H, Kimura T, Yasui N, Ochi T, Endo N, Kitamura Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T (1999) Maturational disturbance of chondrocytes in Cbfa1-deficient mice. Dev Dyn 214 (4):279–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199904)214:4<279::AID-AJA1>3.0.CO;2-W
Iwamoto M, Kitagaki J, Tamamura Y, Gentili C, Koyama E, Enomoto H, Komori T, Pacifici M, Enomoto-Iwamoto M (2003) Runx2 expression and action in chondrocytes are regulated by retinoid signaling and parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP). Osteoarthritis Cartilage 11(1):6–15. https://doi.org/10.1053/joca.2002.0860
Jeon MJ, Kim JA, Kwon SH, Kim SW, Park KS, Park SW, Kim SY, Shin CS (2003) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ inhibits the Runx2-mediated transcription of osteocalcin in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 278(26):23270–23277. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M211610200
Jiang Q, Qin X, Kawane T, Komori H, Matsuo Y, Taniuchi I, Ito K, Izumi SI, Komori T (2016) Cbfb2 isoform dominates more potent Cbfb1 and is required for skeletal development. J Bone Miner Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2814
Jimenez MJ, Balbin M, Lopez JM, Alvarez J, Komori T, Lopez-Otin C (1999) Collagenase 3 is a target of Cbfa1, a transcription factor of the runt gene family involved in bone formation. Mol Cell Biol 19(6):4431–4442. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.19.6.4431
Kamekura S, Kawasaki Y, Hoshi K, Shimoaka T, Chikuda H, Maruyama Z, Komori T, Sato S, Takeda S, Karsenty G, Nakamura K, Chung UI, Kawaguchi H (2006) Contribution of runt-related transcription factor 2 to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis in mice after induction of knee joint instability. Arthritis Rheum 54(8):2462–2470. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22041
Kanatani N, Fujita T, Fukuyama R, Liu W, Yoshida CA, Moriishi T, Yamana K, Miyazaki T, Toyosawa S, Komori T (2006) Cbfb regulates Runx2 function isoform-dependently in postnatal bone development. Dev Biol 296(1):48–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.03.039
Kawane T, Komori H, Liu W, Moriishi T, Miyazaki T, Mori M, Matsuo Y, Takada Y, Izumi S, Jiang Q, Nishimura R, Kawai Y, Komori T (2014) Dlx5 and Mef2 regulate a novel Runx2 enhancer for osteoblast-specific expression. J Bone Miner Res 29(9):1960–1969. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2240
Kim IS, Otto F, Zabel B, Mundlos S (1999) Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by Cbfa1. Mech Dev 80(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(98)00210-X
Kobayashi H, Gao Y, Ueta C, Yamaguchi A, Komori T (2000) Multilineage differentiation of Cbfa1-deficient calvarial cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273(2):630–636. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.2981
Komori T (2006) Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by transcription factors. J Cell Biochem 99(5):1233–1239. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.20958
Komori T (2010a) Regulation of bone development and extracellular matrix protein genes by RUNX2. Cell Tissue Res 339(1):189–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0832-8
Komori T (2010b) Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by runx2. Adv Exp Med Biol 658:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1050-9_5
Komori T (2015) Animal models for osteoporosis. Eur J Pharmacol 759:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.028
Komori T (2017) Roles of Runx2 in skeletal development. Adv Exp Med Biol 962:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3233-2_6
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, Sato M, Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S, Kishimoto T (1997) Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 89(5):755–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80258-5
Kundu M, Javed A, Jeon JP, Horner A, Shum L, Eckhaus M, Muenke M, Lian JB, Yang Y, Nuckolls GH, Stein GS, Liu PP (2002) Cbfb interacts with Runx2 and has a critical role in bone development. Nat Genet 32(4):639–644. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1050
Lecka-Czernik B, Gubrij I, Moerman EJ, Kajkenova O, Lipschitz DA, Manolagas SC, Jilka RL (1999) Inhibition of Osf2/Cbfa1 expression and terminal osteoblast differentiation by PPARγ2. J Cell Biochem 74(3):357–371
Lee B, Thirunavukkarasu K, Zhou L, Pastore L, Baldini A, Hecht J, Geoffroy V, Ducy P, Karsenty G (1997) Missense mutations abolishing DNA binding of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor OSF2/CBFA1 in cleidocranial dysplasia. Nat Genet 16(3):307–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0797-307
Lee MH, Kim YJ, Yoon WJ, Kim JI, Kim BG, Hwang YS, Wozney JM, Chi XZ, Bae SC, Choi KY, Cho JY, Choi JY, Ryoo HM (2005) Dlx5 specifically regulates Runx2 type II expression by binding to homeodomain-response elements in the Runx2 distal promoter. J Biol Chem 280(42):35579–35587. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M502267200
Lengner CJ, Drissi H, Choi JY, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2002) Activation of the bone-related Runx2/Cbfa1 promoter in mesenchymal condensations and developing chondrocytes of the axial skeleton. Mech Dev 114(1–2):167–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(02)00050-3
Lenton K, James AW, Manu A, Brugmann SA, Birker D, Nelson ER, Leucht P, Helms JA, Longaker MT (2011) Indian hedgehog positively regulates calvarial ossification and modulates bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Genesis 49(10):784–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvg.20768
Li F, Lu Y, Ding M, Napierala D, Abbassi S, Chen Y, Duan X, Wang S, Lee B, Zheng Q (2011) Runx2 contributes to murine Col10a1 gene regulation through direct interaction with its cis-enhancer. J Bone Miner Res 26(12):2899–2910. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.504
Li H, Zhou RJ, Zhang GQ, Xu JP (2013) Clinical significance of RUNX2 expression in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer: a 5-year follow-up study. Tumour Biol 34(3):1807–1812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0720-4
Liao L, Zhang S, Gu J, Takarada T, Yoneda Y, Huang J, Zhao L, Oh CD, Li J, Wang B, Wang M, Chen D (2017) Deletion of Runx2 in articular chondrocytes decelerates the progression of DMM-induced osteoarthritis in adult mice. Sci Rep 7(1):2371. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02490-w
Lim M, Zhong C, Yang S, Bell AM, Cohen MB, Roy-Burman P (2010) Runx2 regulates survivin expression in prostate cancer cells. Lab Invest 90(2):222–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2009.128
Lim KE, Park NR, Che X, Han MS, Jeong JH, Kim SY, Park CY, Akiyama H, Kim JE, Ryoo HM, Stein JL, Lian JB, Stein GS, Choi JY (2015) Core binding factor β of osteoblasts maintains cortical bone mass via stabilization of Runx2 in mice. J Bone Miner Res 30(4):715–722. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2397
Liu W, Toyosawa S, Furuichi T, Kanatani N, Yoshida C, Liu Y, Himeno M, Narai S, Yamaguchi A, Komori T (2001) Overexpression of Cbfa1 in osteoblasts inhibits osteoblast maturation and causes osteopenia with multiple fractures. J Cell Biol 155(1):157–166. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200105052
Long F, Chung UI, Ohba S, McMahon J, Kronenberg HM, McMahon AP (2004) Ihh signaling is directly required for the osteoblast lineage in the endochondral skeleton. Development 131(6):1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01006
Lucero CM, Vega OA, Osorio MM, Tapia JC, Antonelli M, Stein GS, Van Wijnen AJ, Galindo MA (2013) The cancer-related transcription factor Runx2 modulates cell proliferation in human osteosarcoma cell lines. J Cell Physiol 228(4):714–723. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24218
Maeno T, Moriishi T, Yoshida CA, Komori H, Kanatani N, Izumi S, Takaoka K, Komori T (2011) Early onset of Runx2 expression caused craniosynostosis, ectopic bone formation, and limb defects. Bone 49(4):673–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2011.07.023
Maruyama Z, Yoshida CA, Furuichi T, Amizuka N, Ito M, Fukuyama R, Miyazaki T, Kitaura H, Nakamura K, Fujita T, Kanatani N, Moriishi T, Yamana K, Liu W, Kawaguchi H, Komori T (2007) Runx2 determines bone maturity and turnover rate in postnatal bone development and is involved in bone loss in estrogen deficiency. Dev Dyn 236(7):1876–1890. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.21187
McDonald L, Ferrari N, Terry A, Bell M, Mohammed ZM, Orange C, Jenkins A, Muller WJ, Gusterson BA, Neil JC, Edwards J, Morris JS, Cameron ER, Blyth K (2014) RUNX2 correlates with subtype-specific breast cancer in a human tissue microarray, and ectopic expression of Runx2 perturbs differentiation in the mouse mammary gland. Dis Model Mech 7(5):525–534. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.015040
Miller J, Horner A, Stacy T, Lowrey C, Lian JB, Stein G, Nuckolls GH, Speck NA (2002) The core-binding factor β subunit is required for bone formation and hematopoietic maturation. Nat Genet 32(4):645–649. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1049
Moriishi T, Fukuyama R, Ito M, Miyazaki T, Maeno T, Kawai Y, Komori H, Komori T (2012) Osteocyte network; a negative regulatory system for bone mass augmented by the induction of rankl in osteoblasts and sost in osteocytes at unloading. PLoS One 7(6):e40143. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040143
Mundlos S, Otto F, Mundlos C, Mulliken JB, Aylsworth AS, Albright S, Lindhout D, Cole WG, Henn W, Knoll JH, Owen MJ, Mertelsmann R, Zabel BU, Olsen BR (1997) Mutations involving the transcription factor CBFA1 cause cleidocranial dysplasia. Cell 89(5):773–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80260-3
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Behringer RR, de Crombrugghe B (2002) The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell 108(1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00622-5
Nishimura R, Wakabayashi M, Hata K, Matsubara T, Honma S, Wakisaka S, Kiyonari H, Shioi G, Yamaguchi A, Tsumaki N, Akiyama H, Yoneda T (2012) Osterix regulates calcification and degradation of chondrogenic matrices through matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) expression in association with transcription factor Runx2 during endochondral ossification. J Biol Chem 287(40):33179–33190. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.337063
Nishio Y, Dong Y, Paris M, O’Keefe RJ, Schwarz EM, Drissi H (2006) Runx2-mediated regulation of the zinc finger Osterix/Sp7 gene. Gene 372:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.022
Ogawa E, Inuzuka M, Maruyama M, Satake M, Naito-Fujimoto M, Ito Y, Shigesada K (1993) Molecular cloning and characterization of PEBP2β, the heterodimeric partner of a novel Drosophila runt-related DNA binding protein PEBP2α. Virology 194(1):314–331. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1993.1262
Okura H, Sato S, Kishikawa S, Kaneto S, Nakashima T, Yoshida N, Takayanagi H, Kiyono H (2014) Runx2-I isoform contributes to fetal bone formation even in the absence of specific N-terminal amino acids. PLoS One 9(9):e108294. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108294
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A, Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen BR, Selby PB, Owen MJ (1997) Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell 89(5):765–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80259-7
Owens TW, Rogers RL, Best SA, Ledger A, Mooney AM, Ferguson A, Shore P, Swarbrick A, Ormandy CJ, Simpson PT, Carroll JS, Visvader JE, Naylor MJ (2014) Runx2 is a novel regulator of mammary epithelial cell fate in development and breast cancer. Cancer Res 74(18):5277–5286. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-14-0053
Park MH, Shin HI, Choi JY, Nam SH, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Ryoo HM (2001) Differential expression patterns of Runx2 isoforms in cranial suture morphogenesis. J Bone Miner Res 16(5):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.5.885
Porte D, Tuckermann J, Becker M, Baumann B, Teurich S, Higgins T, Owen MJ, Schorpp-Kistner M, Angel P (1999) Both AP-1 and Cbfa1-like factors are required for the induction of interstitial collagenase by parathyroid hormone. Oncogene 18(3):667–678. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202333
Pratap J, Galindo M, Zaidi SK, Vradii D, Bhat BM, Robinson JA, Choi J-Y, Komori T, Stein JL, Lian JB (2003) Cell growth regulatory role of Runx2 during proliferative expansion of preosteoblasts. Cancer Res 63(17):5357–5362
Pratap J, Lian JB, Javed A, Barnes GL, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS (2006) Regulatory roles of Runx2 in metastatic tumor and cancer cell interactions with bone. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25(4):589–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-006-9032-0
Pratap J, Wixted JJ, Gaur T, Zaidi SK, Dobson J, Gokul KD, Hussain S, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB (2008) Runx2 transcriptional activation of Indian Hedgehog and a downstream bone metastatic pathway in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 68(19):7795–7802. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-1078
Pratap J, Imbalzano KM, Underwood JM, Cohet N, Gokul K, Akech J, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Imbalzano AN, Nickerson JA (2009) Ectopic runx2 expression in mammary epithelial cells disrupts formation of normal acini structure: implications for breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 69(17):6807–6814. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1471
Qiao M, Shapiro P, Fosbrink M, Rus H, Kumar R, Passaniti A (2006) Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the RUNX2 transcription factor by cdc2 regulates endothelial cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 281(11):7118–7128. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M508162200
Qin X, Jiang Q, Matsuo Y, Kawane T, Komori H, Moriishi T, Taniuchi I, Ito K, Kawai Y, Rokutanda S, Izumi S, Komori T (2015) Cbfb regulates bone development by stabilizing Runx family proteins. J Bone Miner Res 30(4):706–714. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2379
Razzaque MS, Soegiarto DW, Chang D, Long F, Lanske B (2005) Conditional deletion of Indian hedgehog from collagen type 2α1-expressing cells results in abnormal endochondral bone formation. J Pathol 207(4):453–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1870
Rodda SJ, McMahon AP (2006) Distinct roles for Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling in specification, differentiation and maintenance of osteoblast progenitors. Development 133(16):3231–3244. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02480
Sancisi V, Borettini G, Maramotti S, Ragazzi M, Tamagnini I, Nicoli D, Piana S, Ciarrocchi A (2012) Runx2 isoform I controls a panel of proinvasive genes driving aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(10):E2006-2015. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1903
Sancisi V, Gandolfi G, Ambrosetti DC, Ciarrocchi A (2015) Histone deacetylase inhibitors repress tumoral expression of the proinvasive factor RUNX2. Cancer Res 75(9):1868–1882. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-14-2087
Sancisi V, Manzotti G, Gugnoni M, Rossi T, Gandolfi G, Gobbi G, Torricelli F, Catellani F, Faria do Valle I, Remondini D, Castellani G, Ragazzi M, Piana S, Ciarrocchi A (2017) RUNX2 expression in thyroid and breast cancer requires the cooperation of three non-redundant enhancers under the control of BRD4 and c-JUN. Nucleic Acids Res 45(19):11249–11267. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx802
Sasaki K, Yagi H, Bronson RT, Tominaga K, Matsunashi T, Deguchi K, Tani Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T (1996) Absence of fetal liver hematopoiesis in mice deficient in transcriptional coactivator core binding factor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(22):12359–12363
Sase T, Suzuki T, Miura K, Shiiba K, Sato I, Nakamura Y, Takagi K, Onodera Y, Miki Y, Watanabe M, Ishida K, Ohnuma S, Sasaki H, Sato R, Karasawa H, Shibata C, Unno M, Sasaki I, Sasano H (2012) Runt-related transcription factor 2 in human colon carcinoma: a potent prognostic factor associated with estrogen receptor. Int J Cancer 131(10):2284–2293. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27525
Sato M, Morii E, Komori T, Kawahata H, Sugimoto M, Terai K, Shimizu H, Yasui T, Ogihara H, Yasui N, Ochi T, Kitamura Y, Ito Y, Nomura S (1998) Transcriptional regulation of osteopontin gene in vivo by PEBP2αA/CBFA1 and ETS1 in the skeletal tissues. Oncogene 17(12):1517–1525. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202064
Selvamurugan N, Pulumati MR, Tyson DR, Partridge NC (2000) Parathyroid hormone regulation of the rat collagenase-3 promoter by protein kinase A-dependent transactivation of core binding factor α1. J Biol Chem 275(7):5037–5042. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.7.5037
Simpson F, Kerr MC, Wicking C (2009) Trafficking, development and hedgehog. Mech Dev 126(5–6):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mod.2009.01.007
St-Jacques B, Hammerschmidt M, McMahon AP (1999) Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev 13(16):2072–2086
Takahashi A, de Andres MC, Hashimoto K, Itoi E, Otero M, Goldring MB, Oreffo ROC (2017) DNA methylation of the RUNX2 P1 promoter mediates MMP13 transcription in chondrocytes. Sci Rep 7(1):7771. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08418-8
Takarada T, Hinoi E, Nakazato R, Ochi H, Xu C, Tsuchikane A, Takeda S, Karsenty G, Abe T, Kiyonari H, Yoneda Y (2013) An analysis of skeletal development in osteoblast-specific and chondrocyte-specific runt-related transcription factor-2 (Runx2) knockout mice. J Bone Miner Res 28(10):2064–2069. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1945
Takeda S, Bonnamy JP, Owen MJ, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2001) Continuous expression of Cbfa1 in nonhypertrophic chondrocytes uncovers its ability to induce hypertrophic chondrocyte differentiation and partially rescues Cbfa1-deficient mice. Genes Dev 15(4):467–481. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.845101
Terauchi K, Kobayashi H, Yatabe K, Yui N, Fujiya H, Niki H, Musha H, Yudoh K (2016) The NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1 regulates the expression of osteogenic transcriptional activator runt-related transcription Factor 2 (Runx2) and production of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-13 in chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci 17(7):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071019
Tetsunaga T, Nishida K, Furumatsu T, Naruse K, Hirohata S, Yoshida A, Saito T, Ozaki T (2011) Regulation of mechanical stress-induced MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 expression by RUNX-2 transcriptional factor in SW1353 chondrocyte-like cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 19(2):222–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2010.11.004
Thirunavukkarasu K, Pei Y, Wei T (2007) Characterization of the human ADAMTS-5 (aggrecanase-2) gene promoter. Mol Biol Rep 34(4):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-006-9037-3
Thomas DM, Johnson SA, Sims NA, Trivett MK, Slavin JL, Rubin BP, Waring P, McArthur GA, Walkley CR, Holloway AJ (2004) Terminal osteoblast differentiation, mediated by runx2 and p27KIP1, is disrupted in osteosarcoma. J Cell Biol 167(5):925–934. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200409187
Ueta C, Iwamoto M, Kanatani N, Yoshida C, Liu Y, Enomoto-Iwamoto M, Ohmori T, Enomoto H, Nakata K, Takada K, Kurisu K, Komori T (2001) Skeletal malformations caused by overexpression of Cbfa1 or its dominant negative form in chondrocytes. J Cell Biol 153(1):87–100. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.153.1.87
Van Der Deen M, Akech J, Wang T, FitzGerald TJ, Altieri DC, Languino LR, Lian JB, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS (2010) The cancer-related Runx2 protein enhances cell growth and responses to androgen and TGFβ in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 109(4):828–837. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22463
Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, Segre GV, Kronenberg HM, Tabin CJ (1996) Regulation of rate of cartilage differentiation by Indian hedgehog and PTH-related protein. Science 273(5275):613–622. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.273.5275.613
Wang Q, Stacy T, Miller JD, Lewis AF, Gu TL, Huang X, Bushweller JH, Bories JC, Alt FW, Ryan G, Liu PP, Wynshaw-Boris A, Binder M, Marin-Padilla M, Sharpe AH, Speck NA (1996) The CBFβ subunit is essential for CBFα2 (AML1) function in vivo. Cell 87(4):697–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81389-6
Wang X, Manner PA, Horner A, Shum L, Tuan RS, Nuckolls GH (2004) Regulation of MMP-13 expression by RUNX2 and FGF2 in osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 12(12):963–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2004.08.008
Wang X, Li L, Wu Y, Zhang R, Zhang M, Liao D, Wang G, Qin G, Xu RH, Kang T (2016) CBX4 suppresses metastasis via recruitment of HDAC3 to the Runx2 promoter in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res 76(24):7277–7289. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-16-2100
Wu M, Li C, Zhu G, Wang Y, Jules J, Lu Y, McConnell M, Wang YJ, Shao JZ, Li YP, Chen W (2014a) Deletion of core-binding factor β (Cbfb) in mesenchymal progenitor cells provides new insights into Cbfb/Runxs complex function in cartilage and bone development. Bone 65:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2014.04.031
Wu M, Li YP, Zhu G, Lu Y, Wang Y, Jules J, McConnell M, Serra R, Shao JZ, Chen W (2014b) Chondrocyte-specific knockout of Cbfb reveals the indispensable function of Cbfb in chondrocyte maturation, growth plate development and trabecular bone formation in mice. Int J Biol Sci 10(8):861–872. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.8521
Xiao ZS, Hjelmeland AB, Quarles LD (2004) Selective deficiency of the “bone-related” Runx2-II unexpectedly preserves osteoblast-mediated skeletogenesis. J Biol Chem 279(19):20307–20313. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401109200
Xiao Z, Awad HA, Liu S, Mahlios J, Zhang S, Guilak F, Mayo MS, Quarles LD (2005) Selective Runx2-II deficiency leads to low-turnover osteopenia in adult mice. Dev Biol 283(2):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.04.028
Yoshida CA, Furuichi T, Fujita T, Fukuyama R, Kanatani N, Kobayashi S, Satake M, Takada K, Komori T (2002) Core-binding factor β interacts with Runx2 and is required for skeletal development. Nat Genet 32(4):633–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1015
Yoshida CA, Yamamoto H, Fujita T, Furuichi T, Ito K, Inoue K, Yamana K, Zanma A, Takada K, Ito Y, Komori T (2004) Runx2 and Runx3 are essential for chondrocyte maturation, and Runx2 regulates limb growth through induction of Indian hedgehog. Genes Dev 18(8):952–963. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1174704
Yoshida CA, Komori H, Maruyama Z, Miyazaki T, Kawasaki K, Furuichi T, Fukuyama R, Mori M, Yamana K, Nakamura K, Liu W, Toyosawa S, Moriishi T, Kawaguchi H, Takada K, Komori T (2012) SP7 inhibits osteoblast differentiation at a late stage in mice. PLoS One 7(3):e32364. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0032364
Zambotti A, Makhluf H, Shen J, Ducy P (2002) Characterization of an osteoblast-specific enhancer element in the CBFA1 gene. J Biol Chem 277(44):41497–41506. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204271200
Zeggini E, Panoutsopoulou K, Southam L, Rayner NW, Day-Williams AG, Lopes MC, Boraska V, Esko T, Evangelou E, Hoffman A, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Ingvarsson T, Jonsdottir I, Jonnson H, Kerkhof HJ, Kloppenburg M, Bos SD, Mangino M, Metrustry S, Slagboom PE, Thorleifsson G, Raine EV, Ratnayake M, Ricketts M, Beazley C, Blackburn H, Bumpstead S, Elliott KS, Hunt SE, Potter SC, Shin SY, Yadav VK, Zhai G, Sherburn K, Dixon K, Arden E, Aslam N, Battley PK, Carluke I, Doherty S, Gordon A, Joseph J, Keen R, Koller NC, Mitchell S, O’Neill F, Paling E, Reed MR, Rivadeneira F, Swift D, Walker K, Watkins B, Wheeler M, Birrell F, Ioannidis JP, Meulenbelt I, Metspalu A, Rai A, Salter D, Stefansson K, Stykarsdottir U, Uitterlinden AG, van Meurs JB, Chapman K, Deloukas P, Ollier WE, Wallis GA, Arden N, Carr A, Doherty M, McCaskie A, Willkinson JM, Ralston SH, Valdes AM, Spector TD, Loughlin J (2012) Identification of new susceptibility loci for osteoarthritis (arcOGEN): a genome-wide association study. Lancet 380(9844):815–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60681-3
Zelzer E, Glotzer DJ, Hartmann C, Thomas D, Fukai N, Soker S, Olsen BR (2001) Tissue specific regulation of VEGF expression during bone development requires Cbfa1/Runx2. Mech Dev 106(1–2):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(01)00428-2
Zhang Y, Hassan MQ, Xie RL, Hawse JR, Spelsberg TC, Montecino M, Stein JL, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, Stein GS (2009) Co-stimulation of the bone-related Runx2 P1 promoter in mesenchymal cells by SP1 and ETS transcription factors at polymorphic purine-rich DNA sequences (Y-repeats). J Biol Chem 284(5):3125–3135. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M807466200
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to TK (Grant number: 26221310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.