Abstract
Purpose
To develop and validate a deep learning system for diabetic retinopathy (DR) grading based on fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) images.
Methods
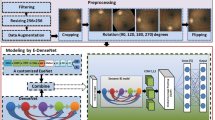
A total of 11,214 FFA images from 705 patients were collected to form the internal dataset. Three convolutional neural networks, namely VGG16, RestNet50, and DenseNet, were trained using a nine-square grid input, and heat maps were generated. Subsequently, a comparison between human graders and the algorithm was performed. Lastly, the best model was tested on two external datasets (Xian dataset and Ningbo dataset).
Results
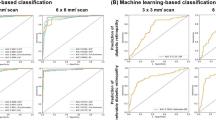
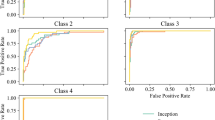
VGG16 performed the best, with a maximum accuracy of 94.17%, and had an AUC of 0.972, 0.922, and 0.994 for levels 1, 2, and 3, respectively. For Xian dataset, our model reached the accuracy of 82.47% and AUC of 0.910, 0.888, and 0.976 for levels 1, 2, and 3. As for Ningbo dataset, the network performed with the accuracy of 88.89% and AUC of 0.972, 0.756, and 0.945 for levels 1, 2, and 3.
Conclusions
A deep learning system for DR staging was trained based on FFA images and evaluated through human–machine comparisons as well as external dataset testing. The proposed system will help clinical practitioners to diagnose and treat DR patients, and lay a foundation for future applications of other ophthalmic or general diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material and code availability
The datasets presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Cheung N, Mitchell P, Wong TY (2010) Diabetic retinopathy. The Lancet 376(9735):124–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(09)62124-3
Yau JWY, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, Chen SJ, Dekker JM, Fletcher A, Grauslund J, Haffner S, Hamman RF, Ikram MK, Kayama T, Klein BEK, Klein R, Krishnaiah S, Mayurasakorn K, O’Hare JP, Orchard TJ, Porta M, Rema M, Roy MS, Sharma T, Shaw J, Taylor H, Tielsch JM, Varma R, Wang JJ, Wang NL, West S, Xu L, Yasuda M, Zhang XZ, Mitchell P, Wong TY, Meta-EYE Study (2012) Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35(3):556–564. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1909
Lu JY, Ma XJ, Zhou J, Zhang L, Mo YF, Ying LW, Lu W, Zhu W, Bao YQ, Vigersky RA, Jia WP (2018) Association of time in range, as assessed by continuous glucose monitoring, with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 41(11):2370–2376. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-1131
Lee R, Wong TY, Sabanayagam C (2015) Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and related vision loss. Eye Vis 2:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40662-015-0026-2
Stitt AW, Curtis TM, Chen M, Medina RJ, McKay GJ, Jenkins A, Gardiner TA, Lyons TJ, Hammes HP, Simo R, Lois N (2016) The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res 51:156–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.08.001
Li X, Hu X, Yu L, Zhu L, Fu CW, Heng PA (2020) CANet: cross-disease attention network for joint diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema grading. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):1483–1493. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2019.2951844
Cole ED, Novais EA, Louzada RN, Waheed NK (2016) Contemporary retinal imaging techniques in diabetic retinopathy: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 44(4):289–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/ceo.12711
Wong TY, Cheung CM, Larsen M, Sharma S, Simo R (2016) Diabetic retinopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16012. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.12
Porwal P, Pachade S, Kokare M, Deshmukh G, Son J, Bae W, Liu L, Wang J, Liu X, Gao L, Wu T, Xiao J, Wang F, Yin B, Wang Y, Danala G, He L, Choi YH, Lee YC, Jung SH, Li Z, Sui X, Wu J, Li X, Zhou T, Toth J, Baran A, Kori A, Chennamsetty SS, Safwan M, Alex V, Lyu X, Cheng L, Chu Q, Li P, Ji X, Zhang S, Shen Y, Dai L, Saha O, Sathish R, Melo T, Araujo T, Harangi B, Sheng B, Fang R, Sheet D, Hajdu A, Zheng Y, Mendonca AM, Zhang S, Campilho A, Zheng B, Shen D, Giancardo L, Quellec G, Meriaudeau F (2020) IDRiD: diabetic retinopathy - segmentation and grading challenge. Med Image Anal 59:101561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.101561
Williams GA, Scott IU, Haller JA, Maguire AM, Marcus D, McDonald HR (2004) Single-field fundus photography for diabetic retinopathy screening. Ophthalmology 111(5):1055–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2004.02.004
Kwan CC, Fawzi AA (2019) Imaging and biomarkers in diabetic macular edema and diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diabetes Rep 19(10):95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1226-2
Pan X, Jin K, Cao J, Liu Z, Wu J, You K, Lu Y, Xu Y, Su Z, Jiang J, Yao K, Ye J (2020) Multi-label classification of retinal lesions in diabetic retinopathy for automatic analysis of fundus fluorescein angiography based on deep learning. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 258(4):779–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-019-04575-w
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521(7553):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Shin HC, Roth HR, Gao M, Lu L, Xu Z, Nogues I, Yao J, Mollura D, Summers RM (2016) Deep convolutional neural networks for computer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics and transfer Learning. IEEE T Med Imaging 35(5):1285–1298. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2528162
Ting DSW, Peng L, Varadarajan AV, Keane PA, Burlina PM, Chiang MF, Schmetterer L, Pasquale LR, Bressler NM, Webster DR, Abramoff M, Wong TY (2019) Deep learning in ophthalmology: the technical and clinical considerations. Prog Retin Eye Res 72:100759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2019.04.003
De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, Nikolov S, Tomasev N, Blackwell S, Askham H, Glorot X, O’Donoghue B, Visentin D, van den Driessche G, Lakshminarayanan B, Meyer C, Mackinder F, Bouton S, Ayoub K, Chopra R, King D, Karthikesalingam A, Hughes CO, Raine R, Hughes J, Sim DA, Egan C, Tufail A, Montgomery H, Hassabis D, Rees G, Back T, Khaw PT, Suleyman M, Cornebise J, Keane PA, Ronneberger O (2018) Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med 24(9):1342–1350. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0107-6
Verbraak FD, Abramoff MD, Bausch GCF, Klaver C, Nijpels G, Schlingemann RO, van der Heijden AA (2019) Diagnostic accuracy of a device for the automated detection of diabetic retinopathy in a primary care setting. Diabetes Care 42(4):651–656. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-0148
Schmidt-Erfurth U, Sadeghipour A, Gerendas BS, Waldstein SM, Bogunovic H (2018) Artificial intelligence in retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 67:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.07.004
Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, Stumpe MC, Wu D, Narayanaswamy A, Venugopalan S, Widner K, Madams T, Cuadros J, Kim R, Raman R, Nelson PC, Mega JL, Webster DR (2016) Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA 316(22):2402–2410. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.17216
Sayres R, Taly A, Rahimy E, Katy B, David C, Naama H, Jonathan K, Arunachalam N, Rastegar Zahra Wu, Shawn DX, Scott B, Anthony J, Michael S, Jesse S, Sood Arjun B, Corrado Greg S, Lily P, Webster Dale R (2019) Using a deep learning algorithm and integrated gradients explanation to assist grading for diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 126(4):552–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.11.016
Rasta SH, Nikfarjam S, Javadzadeh A (2015) Detection of retinal capillary nonperfusion in fundus fluorescein angiogram of diabetic retinopathy. Bioimpacts 5(4):183–190. https://doi.org/10.15171/bi.2015.27
Hemalakshmi GR, Santhi D, Mani VRS, Hemalakshmi GR, Santhi D, Mani V, Geetha A, Prakash NB (2020) Deep residual network based on image priors for single image super resolution in FFA images. CMES 125(1):125–143. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2020.011331
Jin K, Pan X, You K, Wu J, Liu Z, Cao J, Lou L, Xu Y, Su Z, Yao K, Ye J (2020) Automatic detection of non-perfusion areas in diabetic macular edema from fundus fluorescein angiography for decision making using deep learning. Sci Rep 10(1):15138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71622-6
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL, Klein RE, Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL, Klein RE, Lee PP, Agardh CD, Davis M, Dills D, Kampik A, Pararajasegaram R, Verdaguer JT (2003) Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 110(9):1677–1682. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(03)00475-5
Krause J, Gulshan V, Rahimy E, Karth P, Widner K, Corrado GS, Peng L, Webster DR (2018) Grader variability and the importance of reference standards for evaluating machine learning models for diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 125(8):1264–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.01.034
Son J, Shin JY, Kim HD, Jung KH, Park KH, Park SJ (2020) Development and validation of deep learning models for screening multiple abnormal findings in retinal fundus images. Ophthalmology 127(1):85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.05.029
Liu TYA (2019) Smartphone-based, artificial intelligence-enabled diabetic retinopathy screening. JAMA Ophthalmol 137(10):1188–1189. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2019.2883
Abramoff MD, Lou Y, Erginay A, Clarida W, Amelon R, Folk JC, Niemeijer M (2016) Improved automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on a publicly available dataset through integration of deep learning. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(13):5200–5206. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.16-19964
de la Torre J, Valls A, Puig D (2020) A deep learning interpretable classifier for diabetic retinopathy disease grading. Neurocomputing 396:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.07.102
Asiri N, Hussain M, Al Adel F, Alzaidi N (2019) Deep learning based computer-aided diagnosis systems for diabetic retinopathy: a survey. Artif Intell Med 99:20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.009
Gulshan V, Rajan RP, Widner K, Wu D, Wubbels P, Rhodes T, Whitehouse K, Coram M, Corrado G, Ramasamy K, Raman R, Peng L, Webster DR (2019) Performance of a deep-learning algorithm vs manual grading for detecting diabetic retinopathy in India. JAMA Ophthalmol 137(9):987–993. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2019.2004
Li ZX, Keel S, Liu C, He YF, Meng W, Scheetz J, Lee PY, Shaw J, Ting D, Wong TY, Taylor H, Chang R, He MG (2018) An automated grading system for detection of vision-threatening referable diabetic retinopathy on the basis of color fundus photographs. Diabetes Care 41(12):2509–2516. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-0147
Bellemo V, Lim ZW, Lim G, Nguyen QD, Xie YC, Yip MYT, Hamzah H, Ho JY, Lee XQ, Hsu WN, Lee ML, Musonda L, Chandran M, Chipalo-Mutati G, Muma M, Tan GSW, Sivaprasad S, Menon G, Wong TY, Ting DSW (2019) Artificial intelligence using deep learning to screen for referable and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in Africa: a clinical validation study. Lancet Digit Health 1(1):E35–E44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30004-4
Mori K, Takahashi H, Tampo H, Inoue Y, Kawashima H (2017) Applying artificial intelligence to disease staging: deep learning for improved staging of diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 12(6):11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179790
Raumviboonsuk P, Krause J, Chotcomwongse P, Sayres R, Raman R, Widner K, Campana BJL, Phene S, Hemarat K, Tadarati M, Silpa-Archa S, Limwattanayingyong J, Rao C, Kuruvilla O, Jung J, Tan J, Orprayoon S, Kangwanwongpaisan C, Sukumalpaiboon R, Luengchaichawang C, Fuangkaew J, Kongsap P, Chualinpha L, Saree S, Kawinpanitan S, Mitvongsa K, Lawanasakol S, Thepchatri C, Wongpichedchai L, Corrado GS, Peng L, Webster DR (2019) Deep learning versus human graders for classifying diabetic retinopathy severity in a nationwide screening program. NPJ Digit Med 2:25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-019-0099-8
Duh EJ, Sun JK, Stitt AW (2017) Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight 2(14):13. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.93751
Antonetti DA, Klein R, Gardner TW (2012) Mechanisms of disease: diabetic retinopathy. New Engl J Med 366(13):1227–1239. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1005073
Ting DSW, Carin L, Abramoff MD (2019) Observations and lessons learned from the artificial intelligence studies for diabetic retinopathy screening. JAMA Ophthalmol 137(9):994–995. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2019.1997
Acknowledgements
We thank the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University and the Eye Center at Ningbo First Hospital for their contributions to data collection.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (grant number 2019YFC0118401), Zhejiang Provincial Key Research and Development Plan (grant number 2019C03020), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81670888).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.G., K.J., J.W., and J.Y. conceived and designed the experiments. Y.Y., X.L, Y.S, X.P, and Y.W. collected and processed the data. Y.G. and Y.L. analyzed the results. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine (No.Y2020-1027). Informed consent was obtained from the research subjects prior to the study. The research complied with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and the Health Portability and Accessibility Act.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Jin, K., Yan, Y. et al. End-to-end diabetic retinopathy grading based on fundus fluorescein angiography images using deep learning. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 260, 1663–1673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05503-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05503-7