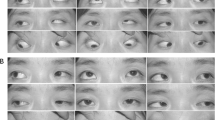
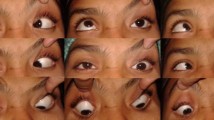
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of inferior oblique muscle belly transposition (IOBT) on vertical deviation (VD) in primary position and inferior oblique overaction (IOOA).
Methods
Twenty-eight patients who underwent unilateral IOBT for mild hypertropia (≤ 10△) due to unilateral IOOA were included. Surgical results regarding the correction of hypertropia, IOOA, and fovea disc angle (FDA) were analyzed and compared between groups A (VD ≤ 5△) and B (5△ < VD ≤ 10△).
Results
IOBT showed an overall reduction of 5.86△ (± 2.24△) of primary position VD, a mean correction of 1.00 (± 0.27) of IOOA, and an average change of 1.83° (± 3.02°) of FDA. The surgical success rate of IOBT for VD correction and IOOA elimination in all patients was 68% and 71%, respectively. The correction of VD was correlated with preoperative VD significantly (r = 0.86, p < 0.001). Consistently, IOBT demonstrated comparable efficacy in reduction of VD between group A and group B (p = 0.507). Furthermore, the two groups were comparable in the success rates for correcting VD and IOOA (both p > 0.05). None of the patients developed consecutive hypotropia, postoperative contralateral IOOA, or anti-elevation syndrome postoperatively.
Conclusions
IOBT achieved satisfactory outcomes in patients with mild primary position VD (≤ 10△) that is associated with unilateral IOOA, without any risk of overcorrection of VD and contralateral IOOA for a follow-up period of up to 12 months. This procedure is considered effective and safe alternative for weakening the IO in patients with appropriate surgical indications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caldeira JA (2004) Some clinical characteristics of V-pattern exotropia and surgical outcome after bilateral recession of the inferior oblique muscle: a retrospective study of 22 consecutive patients and a comparison with V-pattern esotropia. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q 19:139–150
Duane A (1906) Tenotomy of inferior oblique and consideration of the conditions that may call for the operation. Br Med J 2(1867):6
Dyer JA (1962) Tenotomy of the inferior oblique muscle at its scleral insertion. An easy and effective procedure. Arch Ophthalmol 68:176–181
White JW (1942) Surgery of the inferior oblique at or near the insertion. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 40:118–126
Parks MM (1972) The weakening surgical procedures for eliminating overaction of the inferior oblique muscle. Am J Ophthalmol 73:107–122
Gobin MH (1964) Anteroposition of the inferior oblique muscle in V-esotropia. Ophthalmologica 148:325–341
Costenbader FD, Kertesz E (1964) Relaxing procedures of the in- ferior oblique: a comparative study. Am J Ophthalmol 57:276–280
Bahl RS, Marcotty A, Rychwalski PJ, Traboulsi EI (2013) Comparison of inferior oblique myectomy to recession for the treatment of superior oblique palsy. Br J Ophthalmol 97:184–188
Alajbegovic-Halimic J, Zvizdic D, Sahbegovic-Holcner A, Kulanic-Kuduzovic A (2015) Recession Vs myotomy-comparative analysis of two surgical procedures of weakening inferior oblique muscle overaction. Med Arch 69:165–168
Elliott RL, Nankin SJ (1981) Anterior transposition of the inferior oblique. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 18(35–38):8
Burke JP, Scott WE, Kutshke PJ (1993) Anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle for dissociated vertical deviation. Ophthalmology 100:245–250
Guemes A, Wright KW (1998) Effect of graded anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle on versions and vertical deviation in primary position. J AAPOS 2:201–206
Nabie R, Raoufi S, Hassanpour E, Nikniaz L, Kharrazi B, Mamaghani S (2019) Comparing graded anterior transposition with myectomy in primary inferior oblique overaction - a clinical trial. J Curr Ophthalmol 8(31):422–425
Ozsoy E, Gunduz A, Ozturk E (2019) Inferior oblique muscle overaction: clinical features and surgical management. J Ophthalmol 17(2019):9713189
Akbari MR, Sadrkhanlou S, Mirmohammadsadeghi A (2019) Surgical outcome of single inferior oblique myectomy in small and large hypertropia of unilateral superior oblique palsy. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 23(56):23–27
Yang S, Guo X, Tien DR (2018) Inferior oblique belly transposition for small angle hypertropia with inferior oblique overaction: a pilot study. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 1(55):43–46
Wright KW, Hong P (2006) Anatomy and physiology of eye move- ments In Handbook of pediatric strabismus and amblyopia, edited by Wright KW, Spiegel PH and Thompson LS. Springer Science and Business Media, Inc 2:45
Simiera J, Loba P (2017) Cyclocheck: a new web-based software for the assessment of objective cyclodeviation. J AAPOS 21(4):305–308
Xie F, Zhao K, Zhang W (2019) Comparison of surgical outcomes between bilateral recession and unilateral recession-resection in moderate-angle intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS 23:79.e71-79.e7
Al-Hayouti H, Awadein A, Gawdat G, Elhilali H (2020) Augmented medial rectus muscle recession versus medial rectus recession with posterior scleral fixation in partially accommodative esotropia: a randomized clinical trial. J AAPOS 24:274.e1-274.e7
Tomarchio S, Sabetti L, Tomarchio M, Berarducci A (2015) New surgical intervention for the weakening of the inferior oblique muscle: equatorial scleral anchor. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 52:58–60
Sabetti L, Tomarchio S, Piozzi E, Magli A (2017) Equatorial scleral anchor for the weakening of the inferior oblique muscle. Int J Ophthalmic Pathol 6:2
Kasem M, Metwally H, El-Adawy IT, Abdelhameed AG (2020) Retro-equatorial inferior oblique myopexy for treatment of inferior oblique overaction. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 258:1991–1997
Shipman T, Burke J (2003) Unilateral inferior oblique muscle myectomy and recession in the treatment of inferior oblique muscle overaction: a longitudinal study. Eye (Lond) 17:1013–1018
Cruz FC, Robbins SL, Kinori M, Acera EC, Granet DB (2015) Z-myotomy of the inferior oblique for small incomitant hypertropias. J AAPOS 19:130–134
Lee SY, Cho HK, Kim HK, Lee YC (2010) The effect of inferior oblique muscle Z myotomy in patients with inferior oblique overaction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 47:366–372
Simiera J, Ordon AJ, Loba P (2020) Objective cyclodeviation measurement in normal subjects by means of Cyclocheck®application. Eur J Ophthalmol 14:1120672120905312
Ismail MM, Whdan MM, Ali HM, Abbas AS (2020) Comparative study between inferior oblique recession and inferior oblique Retro-equatorial scleral fixation (myopexy) in management of primary inferior oblique over action. Al-Azhar Med J 49:533–540
Wu L, Xia W, Li L, Xi S, Wang X, Wen W, Jiang C, Liu G, Zhao C (2020) The stability of horizontal ocular alignment of triad exotropia after one-step triple surgery. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 258:899–908
Farid MF, Abdelbaset EA (2018) Surgical outcomes of three different surgical techniques for treatment of convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia. Eye (Lond) 32:693–700
Wan MJ, Chiu H, Shah AS, Hunter DG (2018) Long-term surgical outcomes for large-angle infantile esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol 189:155–159
Rajavi Z, Norouzi S, Sabbaghi H, Yaseri M, Abdi S, Faghihi M (2019) The effect of inferior oblique muscle weakening on horizontal alignment. J Curr Ophthalmol 31:298–304
Wang X, Zhang W, Liu L (2020) Effect of isolated oblique muscle weakening procedures on horizontal deviation in A- and V-pattern exotropia. Curr Eye Res 45:211–214
Funding
This study was supported by Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (20ZR1409800 to L.Q.W), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600765 to L.Q.W), Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leaders (2017BR013 to C.Z.), Excellent Academic Leaders of Shanghai (18XD1401000 to C.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board of Eye and ENT Hospital, Fudan University and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Wang, X., Jiang, C. et al. Effect of inferior oblique muscle belly transposition on versions and vertical alignment in primary position. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 259, 3461–3468 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05240-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05240-x