Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the etiology, microbiological isolates, and antibiotic susceptibilities of endophthalmitis in pediatric patients.
Methods
Patients aged < 18 years with culture-positive endophthalmitis in Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center between January 2010 and December 2018 were included retrospectively.
Results
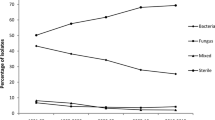
A total of 127 patients (127 eyes) were included, and 108 (85%) had posttraumatic endophthalmitis. Streptococcus (21.4%), coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (14.5%), Aspergillus (6.9%), and Bacillus cereus (5.3%) were the common organisms. The proportion of Streptococcus decreased with age (40.0% in 0–3 years, 16.3% in 4–12 years, and 6.3% in 13–17 years), while coagulase-negative Staphylococcus increased from 5.7% to 18.8%. Overall, fluoroquinolones achieved the highest antibiotic susceptibility rate (> 95%), while the susceptibility of isolated bacteria to tobramycin and cefazolin was only 60.2% and 59.4%, respectively. The susceptibility rates of Gram-positive cocci to cephalosporins were nearly 90%. For Gram-negative bacilli, susceptibility to neomycin was 91.3%.
Conclusion
Trauma was the main etiology for pediatric endophthalmitis. Although Streptococcus was the most prevalent organism in general, the dominant pathogen varied with age, which merits clinical attention. Fluoroquinolones showed the highest antibiotic efficacy; however, commonly used antibiotics tobramycin and cefazolin showed relatively low antibiotic susceptibility. Thus, antibiotic resistance in pediatric populations merits clinical attention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.

Introduction
Pediatric endophthalmitis is a rare but devastating condition, resulting in visual impairment and even blindness. The reported incidence of pediatric endophthalmitis following cataract surgery ranges from 0.38 to 0.45% [1, 2]. The incidence is estimated at 2.8–54.2% in the pediatric age group with ocular trauma, which varies by country [3,4,5]. Children endogenous endophthalmitis is rare; it constitutes only 0.1–4% of all cases of endogenous endophthalmitis [6]. Although the clinical features and microbiological profile of pediatric endophthalmitis are different from those of adult endophthalmitis [3, 7], few studies have focused on the pediatric form.
Recent reports on pediatric endophthalmitis mostly focused on endophthalmitis due to a specific etiology such as pediatric cataract surgery [8], trauma [3, 9], and endogenous infection [6] or focused on a specific type of endophthalmitis caused by a certain pathogen [10]. Only a few studies focused on pediatric endophthalmitis from all causes. Among these, the sample sizes in most studies were small, with an even smaller number culture-positive cases, thereby providing limited information for clinical practice [11,12,13]. Zhang and colleagues reported the etiology and microorganism spectrum of 271 pediatric endophthalmitis cases in eastern China, of which 147 cases were culture positive; yet antibiotic susceptibility was not provided [14]. Information on antibiotic susceptibilities of endophthalmitis in children is critical for guiding empiric antibiotic treatment. Data on microbiologic isolates and antibiotic susceptibility, as well as changing trends in pediatric endophthalmitis, could help guide empiric antibiotic treatment but are currently limited.
In this study, we reviewed a comparatively large sample of 127 inpatient, culture-proven cases of pediatric endophthalmitis, with the following aims: (1) to describe the distribution of etiology, microbiological isolates, and antibiotic susceptibilities in pediatric patients with endophthalmitis and (2) to identify the changing trends in microbiological profile in pediatric endophthalmitis. Our findings provide information to ophthalmologists for the empiric treatment of pediatric endophthalmitis.
Methods
This study was performed in compliance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-sen University. The requirement for patient consent was waived given the retrospective nature of the study.
Study population
We retrospectively collected data of 127 consecutive cases of culture-positive pediatric endophthalmitis in Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, southern China, from January 2010 to December 2018. Patients ≥ 18 years old, without positive culture outcomes, or without culture were excluded.
Procedures
Epidemiological data including patient age and sex were collected. Based on the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and signs, the etiology of endophthalmitis was classified and recorded by a senior ophthalmologist during hospitalization. All endophthalmitis cases were then divided into four endophthalmitis groups: posttraumatic, postoperative, endogenous, and others (including infections associated with keratitis and corneal-suture removal). Patients were also divided into three age groups: 0–3 years, 4–12 years, and 13–17 years. The 9-year study period was divided into 2010–2014 and 2015–2018 to analyze microbiological profile trends.
Aqueous/vitreous taps for culture were performed during surgery under general anesthesia. Aqueous humor from the anterior chamber was aspirated through the corneal limbus with a needle on a 1-mL syringe. Vitreous specimens were collected through the pars plana prior to antibiotic injection or vitrectomy, using a needle or vitrector. Samples were then inoculated in trypticase soy broth (BACT/ALERT® SA and BACT/ALERT® SN, BioMerieux, Inc., Marcy-l’Étoile, France) overnight at 37 °C. Subsequently, the broth was inoculated onto sheep blood agar and potato glucose agar for the growth of bacterial cultures and fungal cultures, respectively. [15,16,17]. All bacterial isolates were subjected to species identification on an automated microbiological system Vitek 2 Compact (BioMerieux, Inc., Marcy-l’Étoile, France); all fungi isolates were identified by experienced technicians according to fungal morphology. Antibiotic susceptibility testing of isolated bacteria was performed using both the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) methods, according to different antibiotics. The antibiotic susceptibility was determined in accordance with the methods of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Bacterial susceptibilities were recorded as “sensitive,” “intermediate,” or “resistant.” For the purpose of this study, being “sensitive” and being “intermediate” were both considered sensitive. The following antibiotics were used for susceptibility tests: fluoroquinolones (moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, ofloxacin), cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefazolin, and cefuroxime), aminoglycosides (tobramycin and neomycin), penicillin, vancomycin, and chloramphenicol. There are very few results for vancomycin and moxifloxacin, as routine tests were started in 2017. It was not until 2016 that we began routine penicillin susceptibility testing.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed using SPSS version 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results of all culture-positive specimens were analyzed. The culture results and susceptibility data are presented as categorical variables and expressed as percentages. Differences between groups were compared using the chi-square test. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
During the 9-year study period, 127 of 459 pediatric patients (< 18 years) with clinically diagnosed endophthalmitis had positive cultures, and all infections were monocular. The mean age of patients was 6.5 ± 4.0 years (range, 8 months to 17 years), and the proportion of male to female was 2.4:1 (90:37). With respect to age distribution, patients in the 4–12-year-old group accounted for the largest proportion (60.6%, n = 77), followed by those in the 0–3 years group (26.8%, n = 34) (Table 1).
Based on etiology, 108 (85.0%) endophthalmitis cases occurred after eye trauma. There were 95 and 13 cases of penetrating and rupture injury, respectively; injuries caused by metal wire/nail (18.5%) were the most common cause, followed by plants (17.6%), and scissors (13.0%). Twelve (9.4%) patients were diagnosed as having endogenous endophthalmitis; four (33.3%) of them had potential systemic risk factors for endophthalmitis: one with prior upper respiratory tract infection and fever; one with acute sinusitis; one had recurrent pneumonia and arthritis before onset; and one received systemic steroid therapy. In four (3.1%) patients, endophthalmitis occurred after intraocular surgery, of which two were associated with trabeculectomy and the remaining two occurred after penetrating keratoplasty and Ahmed glaucoma valve implantation, respectively. The group of other endophthalmitis included three (2.4%) patients with infectious keratitis (n = 2) and after corneal suture removal (n = 1).
The microbiological profile is shown in Table 2. Of the 127 cases, 4 were polymicrobial infections; therefore, in effect, the total number of isolates was 131. Of these, 61.1% were Gram-positive bacteria including 48.1% Gram-positive cocci and 13.0% Gram-positive bacillus, 22.9% were Gram-negative bacillus, and 16.0% were fungal isolates. No Gram-negative cocci were isolated. All isolates in the postoperative endophthalmitis group were bacterial, while fungal isolates accounted for 50.0% of all endogenous endophthalmitis cases.
We analyzed the changing trends of microbiological profile between the periods of 2010–2014 and 2015–2018. Overall, the proportion of Gram-positive bacterial infection increased. Gram-positive cocci increased from 43.4% to 53.5% (P = 0.25), and Gram-positive bacillus increased from 9.2% to 17.9% (P = 0.13). The proportion of Gram-negative bacillus infections decreased from 26.3% to 17.9% (P = 0.25), and that of fungal infections decreased from 21.1% to 10.7% (P = 0.12).
Streptococcus (21.4%) was the most prevalent organism in our study, followed by coagulase-negative staphylococcus (14.5%), of which Staphylococcus epidermidis accounted for 4.6% infections. Bacillus cereus (5.3%) and Bacillus subtilis (4.6%) were the most common Gram-positive bacilli. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (4.6%) accounted for the highest rate of Gram-negative bacillus infections. The most prevalent isolated fungus was Aspergillus (6.9%). The distribution of isolated organisms in different age groups is shown in Table 3. Streptococcus was the most prevalent isolates in the 0–3-year-old age group and accounted for 40% infections; it decreased to 16.3% in 4–12-year-old group, slightly lower than coagulase-negative staphylococcus (17.5%). It further decreased to 6.3% in the 13–17-year-old group, in whom coagulase-negative staphylococci were the predominant isolates. The proportion of fungal infection was 11.4% in the 0–3-year-old group and increased with age, reaching 31.2% in the 13–17-year-old group.
Table 4 shows the total susceptibility rates of isolated bacteria. In general, isolated bacteria showed the highest susceptibility (> 95%) to fluoroquinolones including levofloxacin, ofloxacin, and moxifloxacin. Gram-positive cocci had relatively high susceptibility to ceftazidime, cefuroxime, and cefazolin (84.8%, 89.5%, 87.9%, respectively), while the susceptibility to penicillin was only 59.3%. However, Gram-positive bacilli showed low susceptibility to ceftazidime, cefuroxime, and penicillin, with sensitivity rates of < 30%. The susceptibility of Gram-negative bacilli to fluoroquinolones and neomycin were > 90%, compared with 95.2% to ofloxacin.
Discussion
In this study, we analyzed the clinical data of 127 pediatric patients with culture-positive endophthalmitis in the southern China over a 9-year period. Gram-positive cocci comprised the majority of infections. Streptococcus was the most prevalent isolated pathogen, especially in the youngest age group. Fluoroquinolones including moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, and ofloxacin showed the highest antibiotic susceptibility rates. The commonly used antibiotics tobramycin and cefazolin showed relatively low antibiotic susceptibilities.
Previous studies regarding pediatric endophthalmitis are listed in Table 5. Trauma was the most prevalent etiology in our pediatric population, consistent with previous studies on pediatric endophthalmitis in the USA [12, 13]. However, the proportion of posttraumatic endophthalmitis was less than that of postoperative endophthalmitis in a predominantly adult population in the USA [21, 22]. In our study, the proportion of posttraumatic endophthalmitis (85.0%) among children was much higher than adult-dominated population reported from the same region (58.0–58.5%) [15, 23]. The higher proportion of traumatic endophthalmitis in the pediatric population could be explained by that fact that children are generally unable to either recognize or explain their symptoms after injury, thereby resulting in delayed presentation and treatment, leading to a higher incidence of endophthalmitis [24].
Gram-positive cocci are the predominantly detected organisms in most endophthalmitis studies [12, 22, 25], including ours. Previous studies on pediatric traumatic endophthalmitis from Saudi Arabia and Indian demonstrated that Gram-positive bacteria accounted for 56.4–85.4% of pathogen, and Streptococcus faecalis and Enterococcus were the most common isolates, respectively [3, 18]. In our study, Gram-positive cocci dominated in patients with posttraumatic endophthalmitis, and Streptococcus was the most prevalent isolate. Our study also found fungal isolates accounted for 16.0% of the total, among which Aspergillus was the most frequently detected genus, which is consistent with our previous studies [15, 23] but lower than the values reported in studies from Turkey and India [26, 27]. The causative microorganisms can differ according to the region and environment, which may contribute to the discrepancy.
Our study found that fungi accounted for half of the isolated organisms in endogenous endophthalmitis, similar to other studies in predominantly adult populations in China and the USA [28, 29]. However, fungal infection was reported in 14.2–40% of pediatric endogenous endophthalmitis patients in India, although the sample size was small [6, 20]. The higher rate of fungal infection in our study may be related to the small number of cases and geographic differences. We found that Gram-negative bacteria are the most commonly detected pathogens in pediatric patients with bacterial endogenous endophthalmitis, which is consistent with previous analyses of adult-dominated populations in East Asia [30, 31].
In our study, four cases of endophthalmitis occurred after intraocular surgery. Bacterial infection was reported as the most common cause of endophthalmitis following pediatric intraocular surgery in previous studies [11, 32]. We found that all four cases of postoperative endophthalmitis in our series were due to bacterial infection. Al-Torbak reported that Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae were the causative organisms of pediatric endophthalmitis associated with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant [33]. A study from the UK reported that Streptococcus was predominant in pediatric endophthalmitis which occurred after glaucoma surgery [11]. Similarly, Streptococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, and Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus were isolated in endophthalmitis after glaucoma surgery in our case series.
Two studies reported that pathogen distribution varied over time in a predominantly adult population [25, 34]. However, the shifting microbiological spectrum in pediatric patients in recent years is not adequately understood. We observed an increase in the proportion of Gram-positive bacterial infections, while those of Gram-negative bacilli and fungal infections decreased—albeit not significantly—between 2010–2014 and 2015–2018.
Most previous studies reported that coagulase-negative staphylococci were the dominant pathogens [14, 25, 35]. However, we found that Streptococcus was the most prevalent isolate, followed by coagulase-negative staphylococci. We also observed an obvious changing trend of isolated pathogens among different ages: streptococcus dominated in the 0–3-year-old group (40%), which was exceeded by coagulase-negative staphylococcus in the 4–12-year-old group (16.3% vs. 17.5%). In the 13–17-year-old group, the proportion of coagulase-negative staphylococcus was three times that of Streptococcus (18.8% vs. 6.3%). Simultaneously, the proportion of fungus increased from 11.4% to 31.2%. These shifting trends suggested that age may influence the microbiological spectrum of endophthalmitis. Previous studies demonstrated that streptococcal infection was associated with poor vision outcome in endophthalmitis [36,37,38]; therefore, a higher proportion of streptococcal infections in children, especially in younger children, merits clinical attention.
Antibiotic resistance is a topic of concern worldwide. Overall, bacteria showed the highest susceptibility to fluoroquinolones, consistent with our previous investigation of an adult-dominant population from 2010 to 2014, although the susceptibility rate was higher in this study [15]. Apart from fluoroquinolones, the susceptibility to other antibiotics differed among bacteria: Gram-positive cocci showed a relatively higher susceptibility to cephalosporins (~ 90%); Gram-positive bacilli showed 100% susceptibility to tobramycin, neomycin, and chloramphenicol, while Gram-negative bacilli presented higher susceptibility to neomycin (91.3%). As systemic fluoroquinolone administration is restricted in children, a combination of antibiotics is essential to achieve broader coverage against infection, before culture and susceptibility testing results become available. Since both Gram-positive cocci (84.8%) and Gram-negative bacilli (65.5%) were relatively sensitive to ceftazidime, intravenous injection of ceftazidime is recommended for the treatment of pediatric endophthalmitis. Previous studies on endophthalmitis reported that the susceptibilities of Gram-positive organisms to vancomycin were about 97.7–100% [23, 39]. In our study, the susceptibility rate of Gram-positive cocci to vancomycin was 83.3% (5/6), and the small sample size might explain the difference. As Gram-positive cocci are highly sensitive to vancomycin, intravitreal injection of vancomycin is recommended treatment for children with Gram-positive cocci infection.
The retrospective nature of this study is a limitation. This study did not analyze visual outcomes because the patients included in this study were from all over the country, hindering follow-up. In addition, younger children cannot cooperate with visual testing, leading to incomplete follow-up data. Most of the initial origin of endogenous endophthalmitis were not available in medical records either. Furthermore, we only included culture-positive cases, which could have underrepresented the overall etiological factors of pediatric endophthalmitis. Nevertheless, we provide valid data from a relatively large sample size to describe the etiology, microbiological isolates, and antibiotic sensitivities in culture-proven pediatric endophthalmitis.
In conclusion, we analyzed the clinical data of 127 culture-proven pediatric endophthalmitis in southern China. Trauma was the main etiologic factor for pediatric endophthalmitis, and Streptococcus was the most prevalent organism, especially in the youngest age group. Age may therefore be an influencing factor affecting the microbiological spectrum of pediatric endophthalmitis. Fluoroquinolones achieved the highest antibiotic susceptibility rate, however, commonly used antibiotics tobramycin and cefazolin showed relatively low antibiotic susceptibilities. Thus, antibiotic resistance in a pediatric population merits considerable attention.
References
Good WV, Hing S, Irvine AR, Hoyt CS, Taylor DS (1990) Postoperative endophthalmitis in children following cataract surgery. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 27:283–285
Agarkar S, Desai R, Jambulingam M, Sumeer SH, Raman R (2016) Incidence, management, and visual outcomes in pediatric endophthalmitis following cataract surgery by a single surgeon. J AAPOS 20:415–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2016.05.010
Rishi E, Rishi P, Koundanya VV, Sahu C, Roy R, Bhende PS (2016) Post-traumatic endophthalmitis in 143 eyes of children and adolescents from India. Eye (Lond) 30:615–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.9
Lee CH, Lee L, Kao LY, Lin KK, Yang ML (2009) Prognostic indicators of open globe injuries in children. Am J Emerg Med 27:530–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2008.04.004
Narang S, Gupta V, Simalandhi P, Gupta A, Raj S, Dogra MR (2004) Paediatric open globe injuries. Visual outcome and risk factors for endophthalmitis. Indian J Ophthalmol 52:29–34
Murugan G, Shah PK, Narendran V (2016) Clinical profile and outcomes of pediatric endogenous endophthalmitis: a report of 11 cases from South India. World J Clin Pediatr 5:370–373. https://doi.org/10.5409/wjcp.v5.i4.370
Khan S, Athwal L, Zarbin M, Bhagat N (2014) Pediatric infectious endophthalmitis: a review. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 51:140–153. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20140507-01
Gharaibeh AM, Mezer E, Ospina LH, Wygnanski-Jaffe T (2018) Endophthalmitis following pediatric cataract surgery: an international pediatric ophthalmology and strabismus council global perspective. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 55:23–29. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20170823-02
Sheng Y, Sun W, Gu Y, Grzybowski A (2017) Pediatric posttraumatic endophthalmitis in China for twenty years. J Ophthalmol 2017:5248767. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5248767
Rishi E, Rishi P, Bhende P, Raman R, Sen P, Susvar P, Rao C, Therese L, Hirawat R (2018) Enterococcus faecalis endophthalmitis in children - a 21 year study. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 26:543–549. https://doi.org/10.1080/09273948.2017.1385816
Parvizi S, Papadopoulos M, Panteli V, Brookes J, Soothill J, Bloom J, Adams GGW, Theodorou M (2019) Paediatric endophthalmitis: a UK retrospective study. Eye (Lond). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0546-4
Clavell C, Athwal L, Zarbin MA, Langer PD, Bhagat N (2018) Pediatric infectious endophthalmitis: a case series. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 55:69–70. https://doi.org/10.3928/01913913-20170703-07
Thordsen JE, Harris L, Hubbard GB 3rd (2008) Pediatric endophthalmitis. A 10-year consecutive series. Retina 28:S3–S7. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e318159ec7f
Zhang M, Xu GZ, Jiang R, Ni YQ, Wang KY, Gu RP, Ding XY (2016) Pediatric infectious endophthalmitis: a 271-case retrospective study at a single center in China. Chin Med J (Engl) 129:2936–2943. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.195473
Duan F, Wu K, Liao J, Zheng Y, Yuan Z, Tan J, Lin X (2016) Causative microorganisms of infectious endophthalmitis: a 5-year retrospective study. J Ophthalmol 2016:6764192. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6764192
Duan F, Yang Y, Yuan Z, Zheng Y, Cheng Z, Lin X (2017) Clinical features and visual acuity outcomes in culture-positive endogenous fungal endophthalmitis in southern China. J Ophthalmol 2017:3483497. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3483497
Lin L, Duan F, Yang Y, Lou B, Liang L, Lin X (2019) Nine-year analysis of isolated pathogens and antibiotic susceptibilities of microbial keratitis from a large referral eye center in southern China. Infect Drug Resist 12:1295–1302. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S206831
Al-Rashaed SA, Abu El-Asrar AM (2006) Exogenous endophthalmitis in pediatric age group. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 14:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1080/09273940600954323
Wu H, Ding X, Zhang M, Xu G (2016) Pediatric posttraumatic endophthalmitis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 254:1919–1922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-016-3330-1
Maitray A, Rishi E, Rishi P, Gopal L, Bhende P, Ray R, Therese KL (2019) Endogenous endophthalmitis in children and adolescents: case series and literature review. Indian J Ophthalmol 67:795–800. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_710_18
Moloney TP, Park J (2014) Microbiological isolates and antibiotic sensitivities in culture-proven endophthalmitis: a 15-year review. Br J Ophthalmol 98:1492–1497. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-305030
Benz MS, Scott IU, Flynn HW Jr, Unonius N, Miller D (2004) Endophthalmitis isolates and antibiotic sensitivities: a 6-year review of culture-proven cases. Am J Ophthalmol 137:38–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9394(03)00896-1
Lin L, Mei F, Liao J, Yang Y, Duan F, Lin X (2020) Nine-year analysis of isolated pathogens and antibiotic susceptibilities of infectious endophthalmitis from a large referral eye Center in Southern China. Infect Drug Resist 13:493–500. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S235954
Yang Y, Yang C, Zhao R, Lin L, Duan F, Lou B, Yuan Z, Lin X (2019) Intraocular foreign body injury in children: clinical characteristics and factors associated with endophthalmitis. Br J Ophthalmol. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2019-314913
Gentile RC, Shukla S, Shah M, Ritterband DC, Engelbert M, Davis A, Hu DN (2014) Microbiological spectrum and antibiotic sensitivity in endophthalmitis: a 25-year review. Ophthalmology 121:1634–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.02.001
Celiker H, Kazokoglu H (2019) Ocular culture-proven endogenous endophthalmitis: a 5-year retrospective study of the microorganism spectrum at a tertiary referral center in Turkey. Int Ophthalmol 39:1743–1751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-018-0997-9
Ratra D, Saurabh K, Das D, Nachiappan K, Nagpal A, Rishi E, Bhende P, Sharma T, Gopal L (2015) Endogenous Endophthalmitis: a 10-year retrospective study at a tertiary hospital in South India. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila) 4:286–292. https://doi.org/10.1097/APO.0000000000000120
Schiedler V, Scott IU, Flynn HW Jr, Davis JL, Benz MS, Miller D (2004) Culture-proven endogenous endophthalmitis: clinical features and visual acuity outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol 137:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2003.11.013
Zhang H, Liu Z (2010) Endogenous endophthalmitis: a 10-year review of culture-positive cases in northern China. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 18:133–138. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273940903494717
Lim HW, Shin JW, Cho HY, Kim HK, Kang SW, Song SJ, Yu HG, Oh JR, Kim JS, Moon SW, Chae JB, Park TK, Song Y (2014) Endogenous endophthalmitis in the Korean population: a six-year retrospective study. Retina 34:592–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0b013e3182a2e705
Wong JS, Chan TK, Lee HM, Chee SP (2000) Endogenous bacterial endophthalmitis: an East Asian experience and a reappraisal of a severe ocular affliction. Ophthalmology 107:1483–1491. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(00)00216-5
Wheeler DT, Stager DR, Weakley DR Jr (1992) Endophthalmitis following pediatric intraocular surgery for congenital cataracts and congenital glaucoma. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 29:139–141
Al-Torbak AA, Al-Shahwan S, Al-Jadaan I, Al-Hommadi A, Edward DP (2005) Endophthalmitis associated with the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant. Br J Ophthalmol 89:454–458. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2004.049015
Joseph J, Sontam B, Guda SJM, Gandhi J, Sharma S, Tyagi M, Dave VP, Das T (2019) Trends in microbiological spectrum of endophthalmitis at a single tertiary care ophthalmic hospital in India: a review of 25 years. Eye (Lond) 33:1090–1095. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0380-8
Liu C, Ji J, Li S, Wang Z, Tang L, Cao W, Sun X (2017) Microbiological isolates and antibiotic susceptibilities: a 10-year review of culture-proven endophthalmitis cases. Curr Eye Res 42:443–447. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2016.1188118
Kuriyan AE, Weiss KD, Flynn HW Jr, Smiddy WE, Berrocal AM, Albini TA, Miller D (2014) Endophthalmitis caused by streptococcal species: clinical settings, microbiology, management, and outcomes. Am J Ophthalmol 157:774–780.e771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.12.026
Yospaiboon Y, Meethongkam K, Sinawat S, Laovirojjanakul W, Ratanapakorn T, Sanguansak T, Bhoomibunchoo C (2018) Predictive factors in the treatment of streptococcal endophthalmitis. Clin Ophthalmol 12:859–864. https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S161217
Ong AP, Angbue Te N, Zagora SL, Symes RJ, Yates W, Chang AA, McCluskey PJ, Simunovic MP (2019) Post-surgical versus post-intravitreal injection endophthalmitis: changing patterns in causative flora. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 47:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/ceo.13345
Schimel AM, Miller D, Flynn HW Jr (2013) Endophthalmitis isolates and antibiotic susceptibilities: a 10-year review of culture-proven cases. Am J Ophthalmol 156:50–52.e51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2013.01.027
Funding
This study was funded in part by funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81900851), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (grant number: 2018A030313585), and Fundamental Research Funds of the State Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (grant numbers: 30306020240020130 and 3030902113030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY, FD, and XFL conceived and designed the study. YY, LXL, YJL, and MLL acquired the data. YY, LXL, ZXJ, and CL analyzed and interpreted the data. YY, FD, and XFL drafted the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center (Guangzhou, China) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is waived.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Lin, L., Li, Y. et al. Etiology, microbiological isolates, and antibiotic susceptibilities in culture-proven pediatric endophthalmitis: a 9-year review. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 259, 197–204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-020-04866-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-020-04866-7