Abstract
Background
Oxidative damage resulting from ROS is a known causal factor for cataractogenesis. The mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) pathway plays an important role in the apoptosis of HLE cells. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in H2O2-induced apoptosis in cultured human lens epithelial (HLE) cells.
Methods
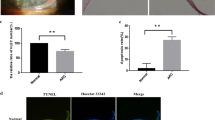
The effect of SB203580 on HLE cells treated with H2O2 was determined by various assays. Cell viability was monitored by the MTT assay. The rates of apoptosis and ROS generation were determined by flow cytometric analysis. The numbers of mitotic and apoptotic cell nuclei were determined after staining with Hoechst 33342. The protein level of phospho-p38 was measured using western blot analysis.
Results
SB203580 reduced H2O2-induced cellular apoptosis and inhibited the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS); it also delayed the progression of H2O2-induced opacification of lenses. The level of p-p38 was increased when cells were exposed to H2O2 and significantly SB203580-inhibited phosphorylation of p38. The p38MAPK pathway plays an important role in H2O2-induced apoptosis of HLE cells.
Conclusions
The study demonstrates that activation of p38MAPK plays an important role in H2O2-induced apoptosis of HLE cells. SB203580 may potentially be exploited as a useful tool for cataract prevention.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paz ML, Gonzalez Maglio DH, Weill FS, Bustamante J, Leoni J (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular stress progression after ultraviolet B irradiation in human keratinocytes. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 24:115–122
Babizhayev MA (2011) Mitochondria induce oxidative stress, generation of reactive oxygen species and redox state unbalance of the eye lens leading to human cataract formation: disruption of redox lens organization by phospholipid hydroperoxides as a common basis for cataract disease. Cell Biochem Funct 29:183–206
Fletcher AE (2010) Free radicals, antioxidants and eye diseases: evidence from epidemiological studies on cataract and age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmic Res 44:191–198
Roux PP, Blenis J (2004) ERK and p38MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:320–344
Kawasaki H, Morooka T, Shimohama S, Kimura J, Hirano T, Gotoh Y, Nishida E (1997) Activation and involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in glutamate-induced apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells. J Biol Chem 272:18518–18521
Krumschnabel G, Maehr T, Nawaz M, Schwarzbaum PJ, Manzl C (2007) Staurosporine-induced cell death in salmonid cells: the role of apoptotic volume decrease, ion fluxes and MAP kinase signaling. Apoptosis 12:1755–1768
Yang Y, Liu X, Huang J, Zhong Y, Mao Z, Xiao H, Li M, Zhuo Y (2012) Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation decrease tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis in human trabecular meshwork cells. Mol Vis 18:2127–2136
Zheng Y, Liu Y, Ge J, Wang X, Liu L, Bu Z, Liu P (2010) Resveratrol protects human lens epithelial cells against H2O2-induced oxidative stress by increasing catalase, SOD-1, and HO-1 expression. Mol Vis 16:1467–1474
Yuan L, Wang J, Xiao H, Wu W, Wang Y, Liu X (2013) MAPK signaling pathways regulate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis induced by isoorientin in human hepatoblastoma cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 53:62–68
Wu WC, Hu DN, Gao HX, Chen M, Wang D, Rosen R, McCormick SA (2010) Subtoxic levels hydrogen peroxide-induced production of interleukin-6 by retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Vis 16:1864–1873
Law AH, Tam AH, Lee DC, Lau AS (2013) A role for protein phosphatase 2A in regulating p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression during influenza virus infection. Int J Mol Sci 14(4):7327–7340
Jia Z, Song Z, Zhao Y, Wang X, Liu P (2011) Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract protects human lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress via reducing NF-кB and MAPK protein expression. Mol Vis 17:210–217
Sharma SD, Meeran SM, Katiyar SK (2007) Dietary grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit UVB-induced oxidative stress and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in in vivo SKH-1 hairless mice. Mol Cancer Ther 6:995–1005
Aoki C, Suzuki K, Yanagi K, Satoh H, Niitani M, Aso Y (2012) Miglitol, an anti-diabetic drug, inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial ROS over-production in endothelial cells by enhancement of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Pharmacol Sci 120:121–128
Yao H, Tang X, Shao X, Feng L, Wu N, Yao K (2007) Parthenolide protects human lens epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via inhibition of activation of caspase-3 andcaspase-9. Cell Res 17:565–571
Natarajan SK, Becker DF (2012) Role of apoptosis-inducing factor, proline dehydrogenase, and NADPH oxidase in apoptosis and oxidative stress. Cell Health Cytoskelet 2012(4):11–27
Wegner A, Khoramnia R (2011) Cataract is a self-defence reaction to protect the retina from oxidative damage. Med Hypotheses 76:741–744
Huang L, Estrada R, Yappert MC, Borchman D (2006) Oxidation-induced changes in human lens epithelial cells.1. Phospholipids. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1425–1432
Hasegawa Y, Shimizu T, Takahashi N, Okada Y (2012) The apoptotic volume decrease is an upstream event of MAP kinase activation during staurosporine-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Int J Mol Sci 13:9363–9379
Fubini B, Hubbard A (2003) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med 34:1507–1516
Gu J, Chi M, Sun X, Wang G, Li M, Liu L, Li X (2013) Propofol-induced protection of SH-SY5Y cells against hydrogen peroxide is associated with the HO-1 via the ERK pathway. Int J Med Sci 10(5):599–606
Ryazantseva NV, Novitsky VV, Chasovskih NY, Kaygorodova EV, Starikova EG, Starikov YV, Radzivil TT (2008) Role of recombinant mitogen-activated protein kinases JNK and p38 in the regulation of apoptosis in blood mononuclear cells under conditions of oxidative stress in vitro. Bull Exp Biol Med 145:569–572
Kim DS, Kim JH, Lee GH, Kim HT, Lim JM, Chae SW, Chae HJ, Kim HR (2010) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death and autophagy in human gingival fibroblasts. Biol Pharm Bull 33:545–549
Kikuchi M, Tenneti L, Lipton SA (2000) Role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in axotomy-induced apoptosis of rat retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 20:5037–5044
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation (30973275) and Heilongjiang Postdoctoral Fund (LBH-Z14161).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, J., Zheng, Y., Dong, L. et al. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation decreases H2O2-induced apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 253, 1933–1940 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-015-3090-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-015-3090-3