Abstract
Introduction
During the last decade, physical activity (PA) (or “exercise”) has been identified as one of the main modifiable factors that influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathophysiology. We performed an umbrella review to summarize the evidence on the association between PA/exercise and the risk of developing AD risk, and the effect of exercise interventions on the progression of AD.
Methods
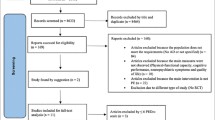
A systematic search was performed in PubMed, SportDiscus, Cochrane Library and Web of Science (March 2022) to identify meta-analyses assessing the association between PA and the incidence of AD, and assessing the effect of exercise interventions on patients with AD.
Results
Twenty-one studies were included. The results with strongest evidence revealed the positive effects of PA on AD risk. Specifically, meeting the WHO recommendations for PA was associated with a lower risk of AD. They also revealed positive effects of exercise on cognitive function, physical performance, and functional independence.
Conclusions
There is strong evidence of a protective effect of regular PA against AD risk; however, the dose–response association remains unclear. Physical exercise seems to improve several dimensions in patients with AD, although research is warranted to elucidate the exercise characteristics that promote the greatest benefits.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alty J, Farrow M, Lawler K (2020) Exercise and dementia prevention. Pract Neurol 20:234–240
Andrade A, Siqueira TC, D'Oliveira A, Dominski FH (2021) Effects of exercise in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J Aging Phys Act 30:1–17
Beckett MW, Ardern CI, Rotondi MA (2015) A meta-analysis of prospective studies on the role of physical activity and the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease in older adults. BMC Geriatr 15:9
Beydoun MA, Beydoun HA, Gamaldo AA, Teel A, Zonderman AB, Wang Y (2014) Epidemiologic studies of modifiable factors associated with cognition and dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 14:643
Cai H, Li G, Hua S, Liu Y, Chen L (2017) Effect of exercise on cognitive function in chronic disease patients: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Interv Aging 12:773–783
Chen WW, Zhang X, Huang WJ (2016) Role of physical exercise in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Reports 4:403–407
Cui MY, Lin Y, Sheng JY, Zhang X, Cui RJ (2018) Exercise intervention associated with cognitive improvement in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Plast 2018:9234105
Dauwan M, Begemann MJH, Slot MIE, Lee EHM, Scheltens P, Sommer IEC (2019) Physical exercise improves quality of life, depressive symptoms, and cognition across chronic brain disorders: a transdiagnostic systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Neurol 268:1222–1246
Daviglus ML, Plassman BL, Pirzada A, Bell CC, Bowen PE, Burke JR, Connolly ES Jr, Dunbar-Jacob JM, Granieri EC, McGarry K, Patel D, Trevisan M, Williams JW Jr (2011) Risk factors and preventive interventions for Alzheimer disease: state of the science. Arch Neurol 68:1185–1190
Demurtas J, Schoene D, Torbahn G, Marengoni A, Grande G, Zou L, Petrovic M, Maggi S, Cesari M, Lamb S, Soysal P, Kemmler W, Sieber C, Mueller C, Shenkin SD, Schwingshackl L, Smith LP, Veronese N, European Society of Geriatric Medicine Special Interest Group in Systematic R, Meta-Analyses FS, Dementia (2020) Physical activity and exercise in mild cognitive impairment and dementia: an umbrella review of intervention and observational studies. J Am Med Dir Assoc 21:1415–1422 (e1416)
Du Z, Li Y, Li J, Zhou C, Li F, Yang X (2018) Physical activity can improve cognition in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Interv Aging 13:1593–1603
Farina N, Rusted J, Tabet N (2014) The effect of exercise interventions on cognitive outcome in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Int Psychogeriatr 26:9–18
Firth J, Stubbs B, Vancampfort D, Schuch F, Lagopoulos J, Rosenbaum S, Ward PB (2018) Effect of aerobic exercise on hippocampal volume in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroimage 166:230–238
Fusar-Poli P, Radua J (2018) Ten simple rules for conducting umbrella reviews. Evid Based Ment Health 21:95–100
Groot C, Hooghiemstra AM, Raijmakers PG, van Berckel BN, Scheltens P, Scherder EJ, van der Flier WM, Ossenkoppele R (2016) The effect of physical activity on cognitive function in patients with dementia: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Ageing Res Rev 25:13–23
Guure CB, Ibrahim NA, Adam MB, Said SM (2017) Impact of physical activity on cognitive decline, dementia, and its subtypes: meta-analysis of prospective studies. Biomed Res Int 2017:9016924
Hamer M, Chida Y (2009) Physical activity and risk of neurodegenerative disease: a systematic review of prospective evidence. Psychol Med 39:3–11
Patterson C (2018) World Alzheimer Report 2018. The state of the art of dementia research: new frontiers. Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI), London
Ioannidis J (2017) Next-generation systematic reviews: prospective meta-analysis, individual-level data, networks and umbrella reviews. Br J Sports Med 51:1456–1458
Ioannidis JP, Trikalinos TA (2007) An exploratory test for an excess of significant findings. Clin Trials 4:245–253
Jia RX, Liang JH, Xu Y, Wang YQ (2019) Effects of physical activity and exercise on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr 19:181
Kivipelto M, Mangialasche F, Ngandu T (2018) Lifestyle interventions to prevent cognitive impairment, dementia and Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 14:653–666
Lee J (2018) The relationship between physical activity and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Gerontol Nurs 44:22–29
Lopez-Ortiz S, Valenzuela PL, Seisdedos MM, Morales JS, Vega T, Castillo-Garcia A, Nistico R, Mercuri NB, Lista S, Lucia A, Santos-Lozano A (2021) Exercise interventions in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ageing Res Rev 72:101479
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hrobjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg 88:105906
Pisani S, Mueller C, Huntley J, Aarsland D, Kempton MJ (2021) A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of physical activity in people with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment with a comparison to donepezil. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 36:1471–1487
Rao AK, Chou A, Bursley B, Smulofsky J, Jezequel J (2014) Systematic review of the effects of exercise on activities of daily living in people with Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Occup Ther 68:50–56
Rezende LFM, Sa TH, Markozannes G, Rey-Lopez JP, Lee IM, Tsilidis KK, Ioannidis JPA, Eluf-Neto J (2018) Physical activity and cancer: an umbrella review of the literature including 22 major anatomical sites and 770,000 cancer cases. Br J Sports Med 52:826–833
Santos-Lozano A, Pareja-Galeano H, Sanchis-Gomar F, Quindos-Rubial M, Fiuza-Luces C, Cristi-Montero C, Emanuele E, Garatachea N, Lucia A (2016) Physical activity and Alzheimer disease: a protective association. Mayo Clin Proc 91:999–1020
Strohle A, Schmidt DK, Schultz F, Fricke N, Staden T, Hellweg R, Priller J, Rapp MA, Rieckmann N (2015) Drug and exercise treatment of Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of effects on cognition in randomized controlled trials. Am J Geriatric Psychiatry 23:1234–1249
Valenzuela PL, Castillo-Garcia A, Morales JS, de la Villa P, Hampel H, Emanuele E, Lista S, Lucia A (2020) Exercise benefits on Alzheimer’s disease: state-of-the-science. Ageing Res Rev 62:101108
Whiting P, Savovic J, Higgins JP, Caldwell DM, Reeves BC, Shea B, Davies P, Kleijnen J, Churchill R, group R (2016) ROBIS: a new tool to assess risk of bias in systematic reviews was developed. J Clin Epidemiol 69:225–234
Xu W, Tan L, Wang HF, Jiang T, Tan MS, Tan L, Zhao QF, Li JQ, Wang J, Yu JT (2015) Meta-analysis of modifiable risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86:1299–1306
Xu W, Wang HF, Wan Y, Tan CC, Yu JT, Tan L (2017) Leisure time physical activity and dementia risk: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ Open 7:e014706
Yu JT, Xu W, Tan CC, Andrieu S, Suckling J, Evangelou E, Pan A, Zhang C, Jia J, Feng L, Kua EH, Wang YJ, Wang HF, Tan MS, Li JQ, Hou XH, Wan Y, Tan L, Mok V, Tan L, Dong Q, Touchon J, Gauthier S, Aisen PS, Vellas B (2020) Evidence-based prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of 243 observational prospective studies and 153 randomised controlled trials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 91:1201–1209
Zhou S, Chen S, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhao M, Li W (2022) Physical activity improves cognition and activities of daily living in adults with Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(3):1216
Zhu XC, Yu Y, Wang HF, Jiang T, Cao L, Wang C, Wang J, Tan CC, Meng XF, Tan L, Yu JT (2015) Physiotherapy intervention in Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimer’s Dis 44:163–174
Funding
Research by SL-O is funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (grant number FPU19/02117). Research by AL is funded by grants from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and Fondos FEDER (Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias, grant number PI18/00139). Research by PLV is supported by a postdoctoral contract from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Sara Borrell, CD21/00138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL-O, SL: conceptualization, data curation, and writing—original draft preparation. PLV: writing—original draft preparation, and writing—reviewing and editing. FC, GC: writing—original draft preparation. JP-F: data curation. FG: data curation. RN: editing. RC, EE: writing—original draft preparation and editing. NT, AL: writing—reviewing and editing. AG, AS-L: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, and writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
López-Ortiz, S., Lista, S., Valenzuela, P.L. et al. Effects of physical activity and exercise interventions on Alzheimer’s disease: an umbrella review of existing meta-analyses. J Neurol 270, 711–725 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11454-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11454-8