Abstract
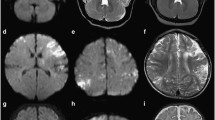
DWI has been described in some reports to be superior to FLAIR in early stage herpes simple virus encephalitis (HSE). Few data exist on detailed topographical MRI analysis in HSE. Our aim was to study DWI and FLAIR, and analyse topographically these sequences in non-neonatal HSE patients with MRI performed within 60 days. Eleven HSE patients were analysed retrospectively. For topographical analysis, we developed a radiological 50-point score (25 points for each hemisphere, with each point corresponding to a brain area). In patients with MRI performed within 2 weeks (n = 9), DWI detected 11 % more areas involved than FLAIR. Thalamic involvement was frequent (67 %) in the early phase on FLAIR, being the only brain substructure better visualized on FLAIR than on DWI. In areas involved on both sequences, DWI showed more extensive (especially cortical) abnormalities in 14 % of the areas. In patients with late MRI (n = 2), FLAIR was superior to DWI (with essentially white matter involvement). From the mesial temporal area, brain signal changes followed a centripetal (i.e. towards anterior, posterior, and superior parts of the brain) gradient. The cut-off score before involving the contralateral hemisphere was 8–9/25 in the initially involved hemisphere. DWI is slightly superior to FLAIR in acute–subacute HSE, except for the thalamus with FLAIR signal changes more frequently seen than earlier reported. Knowledge of typical topographical MRI involvement can help to differentiate from other conditions mimicking HSE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCabe K, Tyler K, Tanabe J (2003) Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as a clue to the diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. Neurology 61:1015–1016
Obeid M, Franklin J, Shrestha S, Johnson L, Quattromani F, Hurst D (2007) Diffusion-weighted imaging findings on MRI as the sole radiographic findings in a child with proven herpes simplex encephalitis. Pediatr Radiol 37:1159–1162
Nouranifar RK, Ali M, Nath J (2003) The earliest manifestation of focal encephalitis on diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Imaging 27:316–320
Dhawan A, Kecskes Z, Jyoti R, Kent AL (2006) Early diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging findings in neonatal herpes encephalitis. J Paediatr Child Health 42:824–826
Kubota T, Ito M, Maruyama K, Kato Y, Miyajima Y, Ogawa A, Kuno K, Okumura A, Watanabe K (2007) Serial diffusion-weighted imaging of neonatal herpes encephalitis: a case report. Brain Dev 29:171–173
Akyldz BN, Gümüş H, Kumandaş S, Coşkun A, Karakukuçu M, Yklmaz A (2008) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance is better than polymerase chain reaction for early diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis: a case report. Pediatr Emerg Care 24:377–379
Chung SP, You JS, Lee HS (2007) Use of the diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for early diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis in the ED: a case report. Am J Emerg Med 25:986.e5–e6
Küker W, Nägele T, Schmidt F, Heckl S, Herrlinger U (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI in herpes simplex encephalitis: a report of three cases. Neuroradiology 46:122–125
Kiroğlu Y, Calli C, Yunten N, Kitis O, Kocaman A, Karabulut N, Isaev H, Yagci B (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of viral encephalitis. Neuroradiology 48:875–880
Sawlani V (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient evaluation of herpes simplex encephalitis and Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 287:221–226
Bajaj M, Mody S, Natarajan G (2014) Clinical and neuroimaging findings in neonatal herpes simplex virus infection. J Pediatr 165:404–407.e1
Noguchi T, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A, Togao O, Yamashita K, Nagao E, Uchino A, Hasuo K, Atsumi K, Matsuura T, Kuroiwa T, Mihara F, Honda H, Kudo S (2010) CT and MRI findings of human herpesvirus 6-associated encephalopathy: comparison with findings of herpes simplex virus encephalitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:754–760
Ohe Y, Hayashi T, Deguchi I, Fukuoka T, Horiuchi Y, Maruyama H, Kato Y, Nagoya H, Uchino A, Tanahashi N (2014) MRI abnormality of the pulvinar in patients with status epilepticus. J Neuroradiol 41:220–226
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical standard
Our study has been approved by the local ethics committee and performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All persons gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renard, D., Nerrant, E. & Lechiche, C. DWI and FLAIR imaging in herpes simplex encephalitis: a comparative and topographical analysis. J Neurol 262, 2101–2105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7818-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-015-7818-0