Abstract
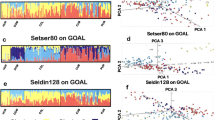
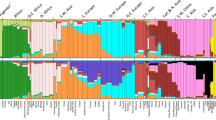
Previously, we developed and validated a multiplex assay of 27 ancestry-informative markers (AIMs) for analyzing African (AFR), European (EUR), and East Asian (EAS) ancestry components. In this study, we typed and collectively analyzed a large Uyghur sample of 979 individuals to estimate the genetic coefficients of the 27 AIMs and investigate differentiation parameters between Uyghur and Han. The Uyghur allele frequencies ranged from 0.243 to 0.952, and heterozygosities ranged from 0.091 to 0.500. Values of F st3 and I n3 for EUR, Uyghur, and EAS ranged from 0.028 to 0.550 and 0.0002 to 0.345, respectively. The Uyghur population displays a substantial ancestry contribution of 50.3:49.7 (EUR:EAS) and was efficiently discriminated from Han Chinese with an accuracy of 99.285 %. All populations were clustered into AFR, EUR, EAS, and admixture groups of these three ancestries. Central Asian was obviously stratified from the other admixture populations of South Asians, North Asians, and the Americans. The 27 SNPs yield a circle with an average distance of 0.936 from the center (0, 0) in PCA analysis. Using this set, Chinese Uyghur and Han populations achieved accurate differentiation, and our updated genotype database (by citing 1000 Genomes data) of 43 worldwide populations is a useful resource for forensic applications and disease association studies.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 February 2020
‘Concerns have been raised about the ethics approval and informed consent procedures related to the research reported in this paper. The paper includes the following author declarations: “Samples from all subjects were obtained with written informed consent and self-declared ancestry information. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Forensic Science, Ministry of Public Security, People’s Republic of China, and the experiment was conducted according to the approved guidelines.” Editorial action will be taken as appropriate once an investigation of the concerns is complete and all parties have been given an opportunity to respond in full.’
References
Epstein MP, Allen AS, Satten GA (2007) A simple and improved correction for population stratification in case-control studies. Am J Hum Genet 80:921–930
Tishkoff SA, Reed FA, Friedlaender FR, Ehret C, Ranciaro A, Froment A, Hirbo JB, Awomoyi AA, Bodo JM, Doumbo O, Ibrahim M, Juma AT, Kotze MJ, Lema G, Moore JH, Mortensen H, Nyambo TB, Omar SA, Powell K, Pretorius GS, Smith MW, Thera MA, Wambebe C, Weber JL, Williams SM (2009) The genetic structure and history of Africans and African Americans. Science 324:1035–1044
Bigham A, Bauchet M, Pinto D, Mao X, Akey JM, Mei R, Scherer SW, Julian CG, Wilson MJ, Lopez Herraez D, Brutsaert T, Parra EJ, Moore LG, Shriver MD (2010) Identifying signatures of natural selection in Tibetan and Andean populations using dense genome scan data. PLoS Genet 6:e1001116
Rosenberg NA, Li LM, Ward R, Pritchard JK (2003) Informativeness of genetic markers for inference of ancestry. Am J Hum Genet 73:1402–1422
Phillips C (2015) Forensic genetic analysis of bio-geographical ancestry. Forensic Sci Int Genet
Halder I, Shriver M, Thomas M, Fernandez JR, Frudakis T (2008) A panel of ancestry informative markers for estimating individual biogeographical ancestry and admixture from four continents: utility and applications. Hum Mutat 29:648–658
Kersbergen P, van Duijn K, Kloosterman AD, den Dunnen JT, Kayser M, de Knijff P (2009) Developing a set of ancestry-sensitive DNA markers reflecting continental origins of humans. BMC Genet 10:69
Kosoy R, Nassir R, Tian C, White PA, Butler LM, Silva G, Kittles R, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Gregersen PK, Belmont JW, De La Vega FM, Seldin MF (2009) Ancestry informative marker sets for determining continental origin and admixture proportions in common populations in America. Hum Mutat 30:69–78
Phillips C, Parson W, Lundsberg B, Santos C, Freire-Aradas A, Torres M, Eduardoff M, Borsting C, Johansen P, Fondevila M, Morling N, Schneider P, Carracedo A, Lareu MV (2014) Building a forensic ancestry panel from the ground up: The EUROFORGEN Global AIM-SNP set. Forensic Sci Int Genet 11:13–25
Kim JJ, Verdu P, Pakstis AJ, Speed WC, Kidd JR, Kidd KK (2005) Use of autosomal loci for clustering individuals and populations of East Asian origin. Hum Genet 117:511–519
Galanter JM, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Gignoux CR, Barnholtz-Sloan J, Fernandez-Rozadilla C, Via M, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Contreras AV, Figueroa LU, Raska P, Jimenez-Sanchez G, Zolezzi IS, Torres M, Ponte CR, Ruiz Y, Salas A, Nguyen E, Eng C, Borjas L, Zabala W, Barreto G, Gonzalez FR, Ibarra A, Taboada P, Porras L, Moreno F, Bigham A, Gutierrez G, Brutsaert T, Leon-Velarde F, Moore LG, Vargas E, Cruz M, Escobedo J, Rodriguez-Santana J, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Chapela R, Ford JG, Bustamante C, Seminara D, Shriver M, Ziv E, Burchard EG, Haile R, Parra E, Carracedo A, Consortium L (2012) Development of a panel of genome-wide ancestry informative markers to study admixture throughout the Americas. PLoS Genet 8:e1002554
Suo C, Xu H, Khor CC, Ong RT, Sim X, Chen J, Tay WT, Sim KS, Zeng YX, Zhang X, Liu J, Tai ES, Wong TY, Chia KS, Teo YY (2012) Natural positive selection and north-south genetic diversity in East Asia. Eur J Hum Genet 20:102–110
Xu S, Yin X, Li S, Jin W, Lou H, Yang L, Gong X, Wang H, Shen Y, Pan X, He Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, Fu W, An Y, Wang J, Tan J, Qian J, Chen X, Zhang X, Sun Y, Zhang X, Wu B, Jin L (2009) Genomic dissection of population substructure of Han Chinese and its implication in association studies. Am J Hum Genet 85:762–774
Qin P, Li Z, Jin W, Lu D, Lou H, Shen J, Jin L, Shi Y, Xu S (2014) A panel of ancestry informative markers to estimate and correct potential effects of population stratification in Han Chinese. Eur J Hum Genet 22:248–253
Phillips C, Salas A, Sanchez JJ, Fondevila M, Gomez-Tato A, Alvarez-Dios J, Calaza M, de Cal MC, Ballard D, Lareu MV, Carracedo A, Consortium SN (2007) Inferring ancestral origin using a single multiplex assay of ancestry-informative marker SNPs. Forensic Sci Int Genet 1:273–280
Phillips C, Freire Aradas A, Kriegel AK, Fondevila M, Bulbul O, Santos C, Serrulla Rech F, Perez Carceles MD, Carracedo A, Schneider PM, Lareu MV (2013) Eurasiaplex: a forensic SNP assay for differentiating European and South Asian ancestries. Forensic Sci Int Genet 7:359–366
Jia J, Wei YL, Qin CJ, Hu L, Wan LH, Li CX (2014) Developing a novel panel of genome-wide ancestry informative markers for bio-geographical ancestry estimates. Forensic Sci Int Genet 8:187–194
Rogalla U, Rychlicka E, Derenko MV, Malyarchuk BA, Grzybowski T (2015) Simple and cost-effective 14-loci SNP assay designed for differentiation of European East Asian and African samples. Forensic Sci Int Genet 14:42–49
Wells RS, Yuldasheva N, Ruzibakiev R, Underhill PA, Evseeva I, Blue-Smith J, Jin L, Su B, Pitchappan R, Shanmugalakshmi S, Balakrishnan K, Read M, Pearson NM, Zerjal T, Webster MT, Zholoshvili I, Jamarjashvili E, Gambarov S, Nikbin B, Dostiev A, Aknazarov O, Zalloua P, Tsoy I, Kitaev M, Mirrakhimov M, Chariev A, Bodmer WF (2001) The Eurasian heartland: a continental perspective on Y-chromosome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10244–10249
Wei YL, Wei L, Zhao L, Sun QF, Jiang L, Zhang T, Liu HB, Chen JG, Ye J, Hu L, Li CX (2016) A single-tube 27-plex SNP assay for estimating individual ancestry and admixture from three continents. Int J Legal Med 130:27–37
Yao YG, Kong QP, Wang CY, Zhu CL, Zhang YP (2004) Different matrilineal contributions to genetic structure of ethnic groups in the silk road region in china. Mol Biol Evol 21:2265–2280
Xu S, Huang W, Qian J, Jin L (2008) Analysis of genomic admixture in Uyghur and its implication in mapping strategy. Am J Hum Genet 82:883–894
Xu S, Jin L (2008) A genome-wide analysis of admixture in Uyghurs and a high-density admixture map for disease-gene discovery. Am J Hum Genet 83:322–336
Smith MW, O'Brien SJ (2005) Mapping by admixture linkage disequilibrium: advances, limitations and guidelines. Nat Rev Genet 6:623–632
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA, Hurles ME, McVean GA (2010) A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467:1061–1073
Pemberton TJ, Wang C, Li JZ, Rosenberg NA (2010) Inference of unexpected genetic relatedness among individuals in HapMap Phase III. Am J Hum Genet 87:457–464
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Shriver MD, Smith MW, Jin L, Marcini A, Akey JM, Deka R, Ferrell RE (1997) Ethnic-affiliation estimation by use of population-specific DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet 60:957–964
Holsinger KE, Weir BS (2009) Genetics in geographically structured populations: defining, estimating and interpreting F(ST). Nat Rev Genet 10:639–650
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour 9:1322–1332
Santos C, Phillips C, Oldoni F, Amigo J, Fondevila M, Pereira R, Carracedo A, Lareu MV (2015) Completion of a worldwide reference panel of samples for an ancestry informative Indel assay. Forensic Sci Int Genet 17:75–80
Paschou P, Ziv E, Burchard EG, Choudhry S, Rodriguez-Cintron W, Mahoney MW, Drineas P (2007) PCA-correlated SNPs for structure identification in worldwide human populations. PLoS Genet 3:1672–1686
Zeng X, Chakraborty R, King JL, LaRue B, Moura-Neto RS, Budowle B (2015) Selection of highly informative SNP markers for population affiliation of major US populations. Int J Legal Med
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program in the 12th year Plan Period (2012BAK02B01), the National Natural Science Foundation for Young Scholars of China (no. 81202384), and the Science and Technology Innovation Base Program of Beijing (no. Z141106004414084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Samples from all subjects were obtained with written informed consent and self-declared ancestry information. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Forensic Science, Ministry of Public Security, People’s Republic of China, and the experiment was conducted according to the approved guidelines.
Additional information
Yi-Liang Wei and Qi-Fan Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, YL., Sun, QF., Li, Q. et al. Genetic structure and differentiation analysis of a Eurasian Uyghur population by use of 27 continental ancestry-informative SNPs. Int J Legal Med 130, 897–903 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-016-1335-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-016-1335-2