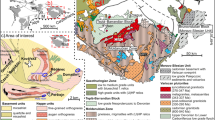
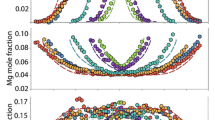
Abstract
The compositional zoning of a garnet population contained within a garnet-grade metapelitic schist from the Lesser Himalayan Sequence of Sikkim (India) provides insight into the rates and kinetic controls of metamorphism, and the extent of chemical equilibration during porphyroblast crystallisation in the sample. Compositional profiles across centrally sectioned garnet crystals representative of the observed crystal size distribution indicate a strong correlation between garnet crystal size and core composition with respect to major end-member components. Systematic steepening of compositional gradients observed from large to small grains is interpreted to reflect a progressive decrease in the growth rate of relatively late-nucleated garnet as a result of an increase in interfacial energies during progressive crystallisation. Numerical simulation of garnet nucleation and growth using an equilibrium approach accounting for chemical fractionation associated with garnet crystallisation reproduces both the observed crystal size distribution and the chemical zoning of the entire garnet population. Simulation of multicomponent intracrystalline diffusion within the population indicates rapid heating along the pressure–temperature path, in excess of 100 \(^{\circ }\)C Myr\(^{-1}\). Radial garnet growth is correspondingly rapid, with minimum rates of 1.4 mm Myr\(^{-1}\). As a consequence of such rapid crystallisation, the sample analysed in this study provides a close to primary record of the integrated history of garnet nucleation and growth. Our model suggests that nucleation of garnet occurred continuously between incipient garnet crystallisation at \(\sim\)520 \(^{\circ }\)C, 4.5 kbar and peak metamorphic conditions at \(\sim\)565 \(^{\circ }\)C, 5.6 kbar. The good fit between the observed and predicted garnet growth zoning suggests that the departure from equilibrium associated with garnet nucleation and growth was negligible, despite the particularly fast rates of metamorphic heating. Consequently, rates of major element diffusion in the intergranular medium during garnet crystallisation are interpreted to have been correspondingly rapid. It is, therefore, possible to simulate the prograde metamorphic history of our sample as a succession of equilibrium states of a chemical system modified by chemical fractionation associated with garnet crystallisation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ague JJ, Baxter EF (2007) Brief thermal pulses during mountain building recorded by Sr diffusion in apatite and multicomponent diffusion in garnet. Earth Planet Sci Lett 261(3):500–516
Anczkiewicz R, Chakraborty S, Dasgupta S, Mukhopadhyay D, Kołtonik K (2014) Timing, duration and inversion of prograde Barrovian metamorphism constrained by high resolution Lu–Hf garnet dating: A case study from the Sikkim Himalaya, NE India. Earth Planet Sci Lett 407:70–81
Anderson DE, Olimpio J (1977) Progressive homogenization of metamorphic garnets, South Morar, Scotland: evidence for volume diffusion. Can Mineral 15(2):205–216
Baldwin J, Powell R, Brown M, Moraes R, Fuck R (2005) Modelling of mineral equilibria in ultrahigh-temperature metamorphic rocks from the Anápolis-Itauçu Complex, central Brazil. J Metamorph Geol 23(7):511–531
Balluffi RW, Allen SM, Carter WC (2005) Kinetics of materials. Wiley, Hoboken
Baumgartner J, Dey A, Bomans PH, Le Coadou C, Fratzl P, Sommerdijk NA, Faivre D (2013) Nucleation and growth of magnetite from solution. Nat Mater 12(4):310–314
Caddick MJ, Konopásek J, Thompson AB (2010) Preservation of garnet growth zoning and the duration of prograde metamorphism. J Petrol 51(11):2327–2347
Cahn JW (1957) Nucleation on dislocations. Acta Metall 5(3):169–172
Carlson WD (1989) The significance of intergranular diffusion to the mechanisms and kinetics of porphyroblast crystallization. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103(1):1–24
Carlson WD (2002) Presidential address. Scales of disequilibrium and rates of equilibration during metamorphism. Am Mineral 87(2–3):185–204
Carlson WD (2012) Rates and mechanism of Y, REE, and Cr diffusion in garnet. Am Mineral 97(10):1598–1618
Carlson WD, Denison C (1992) Mechanisms of porphyroblast crystallization: results from high-resolution computed X-ray tomography. Science 257(5074):1236–1239
Carlson WD, Pattison DR, Caddick MJ (2015) Beyond the equilibrium paradigm: How consideration of kinetics enhances metamorphic interpretation. Am Mineral 100(8–9):1659–1667
Casey WH, Ludwig C (1996) The mechanism of dissolution of oxide minerals. Nature 381(6582):506
Cashman KV, Ferry JM (1988) Crystal size distribution (CSD) in rocks and the kinetics and dynamics of crystallization. Contrib Mineral Petrol 99(4):401–415
Castro AE, Spear FS (2016) Reaction overstepping and re-evaluation of peak P–T conditions of the blueschist unit Sifnos, Greece: implications for the Cyclades subduction zone. Int Geol Rev 59(5–6):548–562
Chakraborty S, Anczkiewicz R, Gaidies F, Rubatto D, Sorcar N, Faak K, Mukhopadhyay D, Dasgupta S (2016) A review of thermal history and timescales of tectonometamorphic processes in Sikkim Himalaya (NE India) and implications for rates of metamorphic processes. J Metamorph Geol 34(8):785–803
Chakraborty S, Ganguly J (1992) Cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets: experimental determination in spessartine-almandine diffusion couples, evaluation of effective binary diffusion coefficients, and applications. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111(1):74–86
Chernoff C, Carlson W (1997) Disequilibrium for Ca during growth of pelitic garnet. J Metamorph Geol 15(4):421–438
Christian JW (2002) The theory of transformations in metals and alloys. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Coggan R, Holland T (2002) Mixing properties of phengitic micas and revised garnet-phengite thermometers. J Metamorph Geol 20:683–696
Connolly JAD (2005) Computation of phase equilibria by linear programming: a tool for geodynamic modeling and its application to subduction zone decarbonation. Earth Planetary Sci Lett 236(1–2):524–541
Connolly J, Cesare B (1993) C-O-H-S fluid composition and oxygen fugacity in graphitic metapelites. J Metamorph Geol 11(3):379–379
Cottle J, Waters D, Riley D, Beyssac O, Jessup M (2011) Metamorphic history of the South Tibetan detachment system, Mt. Everest region, revealed by RSCM thermometry and phase equilibria modelling. J Metamorph Geol 29(5):561–582
Daniel C, Spear F (1999) The clustered nucleation and growth processes of garnet in regional metamorphic rocks from north-west Connecticut, USA. J Metamorph Geol 17(5):503–520
Daniel CG, Spear FS (1998) Three-dimensional patterns of garnet nucleation and growth. Geology 26(6):503–506
Dasgupta S, Chakraborty S, Neogi S (2009) Petrology of an inverted Barrovian sequence of metapelites in Sikkim Himalaya, India: constraints on the tectonics of inversion. Am J Sci 309(1):43–84
Dasgupta S, Ganguly J, Neogi S (2004) Inverted metamorphic sequence in the Sikkim Himalayas: crystallization history, P–T gradient and implications. J Metamorph Geol 22(5):395–412
de Capitani C, Brown TH (1987) The computation of chemical equilibrium in complex systems containing non-ideal solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 51(10):2639–2652
de Capitani C, Petrakakis K (2010) The computation of equilibrium assemblage diagrams with Theriak/Domino software. Am Mineral 95(7):1006–1016
de Sigoyer J, Chavagnac V, Blichert-Toft J, Villa IM, Luais B, Guillot S, Cosca M, Mascle G (2000) Dating the Indian continental subduction and collisional thickening in the northwest Himalaya: multichronology of the Tso Morari eclogites. Geology 28(6):487–490
Dohmen R, Chakraborty S (2003) Mechanism and kinetics of element and isotopic exchange mediated by a fluid phase. Am Mineral 88(8–9):1251–1270
Dragovic B, Samanta LM, Baxter EF, Selverstone J (2012) Using garnet to constrain the duration and rate of water-releasing metamorphic reactions during subduction: an example from Sifnos, Greece. Chem Geol 314:9–22
Dubey CS, Catlos E, Sharma B (2005) Modelling of PTt paths constrained by mineral chemistry and monazite dating of metapelites in relationship to MCT activity in Sikkim Eastern Himalayas. Metamorphism and crustal evolution. Atlantic Publishers, New Delhi
Faryad SW, Chakraborty S (2005) Duration of Eo-Alpine metamorphic events obtained from multicomponent diffusion modeling of garnet: a case study from the Eastern Alps. Contrib Mineral Petrol 150(3):306–318
Finlay C, Kerr A (1987) Evidence for differences in growth rate among garnets in pelitic schists from northern Sutherland, Scotland. Mineral Mag 51(62):569–576
Finlay CA, Kerr A (1979) Garnet growth in a metapelite from the Moinian rocks of northern Sutherland, Scotland. Contrib Mineral Petrol 71(2):185–191
Fisher GW (1973) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics as a model for diffusion-controlled metamorphic processes. Am J Sci 273(10):897–924
Fisher GW (1978) Rate laws in metamorphism. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 42(7):1035–1050
Florence FP, Spear FS (1991) Effects of diffusional modification of garnet growth zoning on PT path calculations. Contrib Mineral Petrol 107(4):487–500
Gaidies F (2017) Nucleation in geological materials. EMU Notes in Mineralogy, vol 16. European Mineralogical Union, book section 1, pp 347–371
Gaidies F, Abart R, De Capitani C, Schuster R, Connolly J, Reusser E (2006) Characterization of polymetamorphism in the Austroalpine basement east of the Tauern Window using garnet isopleth thermobarometry. J Metamorph Geol 24(6):451–475
Gaidies F, De Capitani C, Abart R (2008) THERIA_G: a software program to numerically model prograde garnet growth. Contrib Mineral Petrol 155(5):657–671
Gaidies F, Heinrich W, Milke R, Abart R (2017) Metamorphic mineral reactions. EMU Notes in Mineralogy, vol 16. European Mineralogical Union, book section 14, pp 469–540
Gaidies F, Pattison D, De Capitani C (2011) Toward a quantitative model of metamorphic nucleation and growth. Contrib Mineral Petrol 162(5):975–993
Gaidies F, Petley-Ragan A, Chakraborty S, Dasgupta S, Jones P (2015) Constraining the conditions of Barrovian metamorphism in Sikkim, India: P–T–t paths of garnet crystallization in the Lesser Himalayan Belt. J Metamorph Geol 33(1):23–44
Hirsch DM, Prior DJ, Carlson WD (2003) An overgrowth model to explain multiple, dispersed high-Mn regions in the cores of garnet porphyroblasts. Am Mineral 88(1):131–141
Holland T, Powell R (1998) An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J Metamorph Geol 16(3):309–343
Kelly E, Carlson W, Ketcham R (2013) Magnitudes of departures from equilibrium during regional metamorphism of porphyroblastic rocks. J Metamorph Geol 31(9):981–1002
Ketcham RA (2005) Computational methods for quantitative analysis of three-dimensional features in geological specimens. Geosphere 1(1):32–41
Kohn MJ (2004) Oscillatory- and sector-zoned garnets record cyclic (?) rapid thrusting in central Nepal. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 5(12):1–9
Konrad-Schmolke M, Halama R (2014) Combined thermodynamic-geochemical modeling in metamorphic geology: boron as tracer of fluid-rock interaction. Lithos 208:393–414
Konrad-Schmolke M, Handy MR, Babist J, O’Brien PJ (2005) Thermodynamic modelling of diffusion-controlled garnet growth. Contrib Mineral Petrol 149(2):181–195
Kretz R (1966) Interpretation of the shape of mineral grains in metamorphic rocks. J Petrol 7(1):68–94
Kretz R (1969) On the spatial distribution of crystals in rocks. Lithos 2(1):39–65
Kretz R (1974) Some models for the rate of crystallization of garnet in metamorphic rocks. Lithos 7(3):123–131
Kretz R (1993) A garnet population in Yellowknife schist, Canada. J Metamorph Geol 11(1):101–120
Lanari P, Riel N, Guillot S, Vidal O, Schwartz S, Pêcher A, Hattori KH (2013) Deciphering high-pressure metamorphism in collisional context using microprobe mapping methods: application to the stak eclogitic massif (northwest Himalaya). Geology 41(2):111–114
Lasaga AC (1981) Rate laws of chemical reactions. Rev Mineral (United States) 8:1–68
Lasaga AC (1986) Metamorphic reaction rate laws and development of isograds. Mineral Mag 50(3, 357):359–373
Loomis TP (1982) Numerical simulations of crystallization processes of plagioclase in complex melts: the origin of major and oscillatory zoning in plagioclase. Contrib Mineral Petrol 81(3):219–229
Mohan A, Windley B, Searle M (1989) Geothermobarometry and development of inverted metamorphism in the Darjeeling-Sikkim region of the eastern Himalayan. J Metamorph Geol 7(1):95–110
Mottram CM, Argles T, Harris N, Parrish R, Horstwood M, Warren C, Gupta S (2014a) Tectonic interleaving along the Main Central Thrust, Sikkim Himalaya. J Geol Soc 171(2):255–268
Mottram CM, Warren CJ, Regis D, Roberts NM, Harris NB, Argles TW, Parrish RR (2014b) Developing an inverted Barrovian sequence; insights from monazite petrochronology. Earth Planet Sci Lett 403:418–431
Oliver G, Chen F, Buchwaldt R, Hegner E (2000) Fast tectonometamorphism and exhumation in the type area of the Barrovian and Buchan zones. Geology 28(5):459–462
Palin RM, Weller OM, Waters DJ, Dyck B (2016) Quantifying geological uncertainty in metamorphic phase equilibria modelling; a Monte Carlo assessment and implications for tectonic interpretations. Geosci Front 7(4):591–607
Pattison D, DeBuhr C (2015) Petrology of metapelites in the Bugaboo aureole, British Columbia, Canada. J Metamorph Geolgy 33(5):437–462
Pattison DR, De Capitani C, Gaidies F (2011) Petrological consequences of variations in metamorphic reaction affinity. J Metamorph Geol 29(9):953–977
Pattison DR, Tinkham D (2009) Interplay between equilibrium and kinetics in prograde metamorphism of pelites: an example from the Nelson aureole, British Columbia. J Metamorph Geol 27(4):249–279
Paul D, Chandy K, Bhalla J, Prasad N, Sengupta N (1982) Geochronology and geochemistry of Lingtse Gneiss, Darjeeling-Sikkim Himalayas. Indian J Earth Sci 9(1):11–17
Powell R, Holland T, Worley B (1998) Calculating phase diagrams involving solid solutions via non-linear equations, with examples using THERMOCALC. J Metamorph Geol 16(4):577–588
Putnis A (2002) Mineral replacement reactions: from macroscopic observations to microscopic mechanisms. Miner Mag 66(5):689–708
Putnis A (2014) Why mineral interfaces matter. Science 343(6178):1441–1442
Shore M, Fowler AD (1996) Oscillatory zoning in minerals: a common phenomenon. Can Mineral 34:1111–1126
Skora S, Baumgartner LP, Mahlen NJ, Johnson CM, Pilet S, Hellebrand E (2006) Diffusion-limited REE uptake by eclogite garnets and its consequences for Lu–Hf and Sm-Nd geochronology. Contrib Mineral Petrol 152(6):703–720
Smye AJ, Bickle MJ, Holland TJ, Parrish RR, Condon DJ (2011) Rapid formation and exhumation of the youngest Alpine eclogites: a thermal conundrum to Barrovian metamorphism. Earth Planet Sci Lett 306(3):193–204
Spear FS, Daniel CG (1998) Three-dimensional imaging of garnet porphyroblast sizes and chemical zoning: nucleation and growth history in the garnet zone. Geol Mater Res 1(1):1–44
Spear FS, Selverstone J, Hickmott D, Crowley P, Hodges KV (1984) PT paths from garnet zoning: a new technique for deciphering tectonic processes in crystalline terranes. Geology 12(2):87–90
Spear FS, Thomas JB, Hallett BW (2014) Overstepping the garnet isograd: a comparison of QuiG barometry and thermodynamic modeling. Contrib Mineral Petrol 168(3):1–15
Stowell H, Zuluaga C, Boyle A, Bulman G (2011) Garnet sector and oscillatory zoning linked with changes in crystal morphology during rapid growth, North Cascades, Washington. Am Mineral 96(8–9):1354–1362
Stünitz H (1998) Syndeformational recrystallization—dynamic or compositionally induced? Contrib Mineral Petrol 131:219–236
Teng HH (2013) How ions and molecules organize to form crystals. Elements 9(3):189–194
Thompson A (1986) The role of mineral kinetics in the development of metamorphic microtextures. In: Fluid—rock interactions during metamorphism. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 154–193
Vance D, Mahar E (1998) Pressure–temperature paths from PT pseudosections and zoned garnets: potential, limitations and examples from the Zanskar Himalaya, NW India. Contrib Mineral Petrol 132(3):225–245
Viete DR, Hermann J, Lister GS, Stenhouse IR (2011) The nature and origin of the Barrovian metamorphism, Scotland: diffusion length scales in garnet and inferred thermal time scales. J Geol Soc 168(1):115–132
Viete DR, Lister GS (2016) On the significance of short-duration regional metamorphism. J Geol Soc 174(3):377–392
Walther JV, Wood BJ (1984) Rate and mechanism in prograde metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 88(3):246–259
Waters D, Lovegrove D (2002) Assessing the extent of disequilibrium and overstepping of prograde metamorphic reactions in metapelites from the Bushveld Complex aureole, South Africa. J Metamorph Geol 20(1):135–149
Weller O, St-Onge M, Waters D, Rayner N, Searle M, Chung S-L, Palin R, Lee Y-H, Xu X (2013) Quantifying Barrovian metamorphism in the Danba structural culmination of eastern Tibet. J Metamorph Geol 31(9):909–935
White R, Pomroy N, Powell R (2005) An in situ metatexite-diatexite transition in upper amphibolite facies rocks from broken hill, australia. J Metamorph Geol 23(7):579–602
White R, Powell R, Holland T, Worley B (2000) The effect of TiO\(_2\) and Fe\(_2\)O\(_3\) on metapelitic assemblages at greenschist and amphibolite facies conditions: mineral equilibria calculations in the system K\(_2\)O-FeO-MgO-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)-SiO\(_2\)-H\(_2\)O-TiO\(_2\)-Fe\(_2\)O\(_3\)-O\(_2\) and Fe\(_2\)O\(_3\) on metapelitic assemblages at greenschist and amphibolite facies conditions: mineral equilibria calculations in the system K\(_2\)O-FeO-MgO-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)-SiO\(_2\)-H\(_2\)O-TiO\(_2\)-Fe\(_2\)O\(_3\). J Metamorph Geol 18(5):497–512
Whitney DL, Evans BW (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. Am Mineral 95(1):185
Zeh A (2006) Calculation of garnet fractionation in metamorphic rocks, with application to a flat-top, Y-rich garnet population from the Ruhla Crystalline Complex, Central Germany. J Petrol 47(12):2335–2356
Zener C (1949) Theory of growth of spherical precipitates from solid solution. J Appl Phys 20(10):950–953
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NSERC research Grant 315857 to F.G.. Thanks to A. Dobosz and S. Carr for assistance with developing the fragmentation and central sectioning method, respectively. Particular thanks to P. Jones and G. Poirer for microprobe assistance. S. Chakraborty is greatly appreciated for comments and discussion on an early form of this manuscript that greatly improved its presentation. We would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for critical and constructive reviews that significantly contributed to the presentation of this work. J. Hoefs is thanked for editorial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jochen Hoefs.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, F.R., Gaidies, F. Characterisation of a garnet population from the Sikkim Himalaya: insights into the rates and mechanisms of porphyroblast crystallisation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 172, 57 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1372-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1372-y