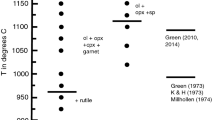
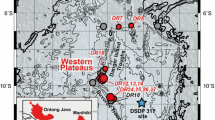
Abstract
This experimental study is the first comprehensive investigation of the melting behavior of an olivine + orthopyroxene ± spinel—bearing fertile mantle (FM) composition as a function of variable pressure and water content. The fertile composition was enriched with a metasomatic slab component of ≤0.5 % alkalis and investigated from 1135 to 1470 °C at 1.0–2.0 GPa. A depleted lherzolite with 0.4 % alkali addition was also studied from 1225 to 1240 °C at 1.2 GPa. Melts of both compositions were water-undersaturated: fertile lherzolite melts contained 0–6.4 wt% H2O, and depleted lherzolite melts contained ~2.5 wt% H2O. H2O contents of experimental glasses are measured using electron microprobe, secondary ion mass spectrometry, and synchrotron-source reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, a novel technique for analyzing H2O in petrologic experiments. Using this new dataset in conjunction with results from previous hydrous experimental studies, a thermobarometer and a hygrometer–thermometer are presented to determine the conditions under which primitive lavas were last in equilibration with the mantle. These predictive models are functions of H2O content and pressure, respectively. A predictive melting model is also presented that calculates melt compositions in equilibrium with an olivine + orthopyroxene ± spinel residual assemblage (harzburgite). This model quantitatively predicts the following influences of H2O on mantle lherzolite melting: (1) As melting pressure increases, melt compositions become more olivine-normative, (2) as melting extent increases, melt compositions become depleted in the normative plagioclase component, and (3) as melt H2O content increases, melts become more quartz-normative. Natural high-Mg# [molar Mg/(Mg + Fe2+)], high-MgO basaltic andesite and andesite lavas—or primitive andesites (PAs)—contain high SiO2 contents at mantle-equilibrated Mg#s. Their compositional characteristics cannot be readily explained by melting of mantle lherzolite under anhydrous conditions. This study shows that experimental melts of a FM peridotite plus the addition of alkalis reproduce the compositions of natural PAs in SiO2, Al2O3, TiO2, Cr2O3, MgO, and Na2O at 1.0–1.2 GPa and H2O contents of 0–7 wt%. Our results also suggest that PAs form under a maximum range of extents of melting from F = 0.2–0.3. The CaO contents of the melts produced are 1–5 wt% higher than the natural samples. This is not a result of a depleted source composition or of extremely high extents of melt but is potentially caused by a very low CaO content contribution from deeper in the mantle wedge.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723
Armstrong JT (1995) CITZAF: a package of correction programs for the quantitative electron microbeam X-ray analysis of thick polished materials, thin films, and particles. Microbeam Anal 4:177–200
Baboshina VA, Tereschenkov AA, Kharakhinov VV (1984) Deep structure of the Sea of Okhotsk according to geophysical data, overview information. Vses Nauchno-Issledovatelskiy Inst (VNII) Gazprom 3:41
Baker MB, Stolper EM (1994) Determining the composition of high-pressure mantle melts using diamond aggregates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58(13):2811–2827
Baker MB, Grove TL, Price R (1994) Primitive basalts and andesites from the Mt. Shasta region, N. California: products of varying melt fraction and water content. Contrib Miner Petrol 118(2):111–129
Baker MB, Hirschmann MM, Ghiorso MS, Stolper EM (1995) Compositions of near-solidus peridotite melts from experiments and thermodynamic calculation. Nature 375(6529):308–311
Barr JA (2010) Primitive magmas of the Earth and Moon: a petrologic investigation of magma genesis and evolution. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Barr JA, Grove TL (2010) AuPdFe ternary solution model and applications to understanding the fO2 of hydrous, high-pressure experiments. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160(5):631–643
Boyd FR, England JL (1960) Apparatus for phase-equilibrium measurements at pressures up to 50 kilobars and temperatures up to 1750 C. J Geophys Res 65(2):741–748
Bryant JA, Yogodzinski GM, Churikova TG (2010) High-Mg# andesitic lavas of the Shisheisky Complex, Northern Kamchatka: implications for primitive calc-alkaline magmatism. Contrib Miner Petrol 161(5):791–810
Cottrell E, Kelley KA (2011) The oxidation state of Fe in MORB glasses and the oxygen fugacity of the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 305(3):270–282
Falloon TJ, Danyushevsky LV (2000) Melting of refractory mantle at 1· 5, 2 and 2· 5 GPa under anhydrous and H2O-undersaturated conditions: implications for the petrogenesis of high-Ca boninites and the influence of subduction components on mantle melting. J Petrol 41(2):257–283
Gaetani GA, Grove TL (1998) The influence of water on melting of mantle peridotite. Contrib Miner Petrol 131(4):323–346
Gómez-Tuena A, Orozco-Esquivel MT, Ferrari L (2007) Igneous petrogenesis of the Trans-Mexican volcanic belt. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 422:129–181
Green DH (1973) Experimental melting studies on a model upper mantle composition at high pressure under water-saturated and water-undersaturated conditions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 19(1):37–53
Grove TL (1993) Corrections to expressions for calculating mineral components in “origin of calc-alkaline series lavas at medicine lake volcano by fractionation, assimilation and mixing” and “experimental petrology of normal MORB near the kane fracture zone: 22°–25° N, mid-atlantic ridge”. Contrib Miner Petrol 114(3):422–424
Grove TL, Juster TC (1989) Experimental investigations of low-Ca pyroxene stability and olivine-pyroxene-liquid equilibria at 1-atm in natural basaltic and andesitic liquids. Contrib Miner Petrol 103(3):287–305
Grove T, Parman S, Bowring S, Price R, Baker M (2002) The role of an H2O-rich fluid component in the generation of primitive basaltic andesites and andesites from the Mt. Shasta region, N California. Contrib Miner Petrol 142(4):375–396
Grove TL, Elkins-Tanton LT, Parman SW, Chatterjee N, Müntener O, Gaetani GA (2003) Fractional crystallization and mantle-melting controls on calc-alkaline differentiation trends. Contrib Miner Petrol 145(5):515–533
Grove TL, Chatterjee N, Parman SW, Médard E (2006) The influence of H2O on mantle wedge melting. Earth Planet Sci Lett 249(1):74–89
Guilbaud MN, Siebe C, Layer P, Salinas S, Castro-Govea R, Garduño-Monroy VH, Le Corvec N (2011) Geology, geochronology, and tectonic setting of the Jorullo Volcano region, Michoacán, México. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 201(1):97–112
Guilhaumou N, Dumas P, Carr GL, Williams GP (1998) Synchrotron infrared microspectrometry applied to petrography in micrometer-scale range: fluid chemical analysis and mapping. Appl Spectrosc 52(8):1029–1034
Hart S, Zindler A (1986) In search of a bulk-Earth composition. Chem Geol 57(3–4):247–267
Hays, J. F. (1966). Lime-alumina-silica. Carnegie Institute Washington Yearbook, 65, 234-239
Herzberg C (2004) Geodynamic information in peridotite petrology. J Petrol 45(12):2507–2530
Hesse M, Grove TL (2003) Absarokites from the western Mexican Volcanic Belt: constraints on mantle wedge conditions. Contrib Miner Petrol 146(1):10–27
Hirose K (1997) Melting experiments on lherzolite KLB-1 under hydrous conditions and generation of high-magnesian andesitic melts. Geology 25(1):42–44
Hirose K, Kawamoto T (1995) Hydrous partial melting of lherzolite at 1 GPa: the effect of H2O on the genesis of basaltic magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 133(3):463–473
Hirschmann MM, Ghiorso MS, Davis FA, Gordon SM, Mukherjee S, Grove TL, Krawczynski M, Médard E, Till CB (2008) Library of experimental phase relations (LEPR): a database and Web portal for experimental magmatic phase equilibria data. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 9(3)
Ito T, Kojima Y, Kodaira S, Sato H, Kaneda Y, Iwasaki T, Ikawa T (2009) Crustal structure of southwest Japan, revealed by the integrated seismic experiment Southwest Japan 2002. Tectonophysics 472(1):124–134
Iwasaki T, Levin V, Nikulin A, Iidaka T (2013) Constraints on the Moho in Japan and Kamchatka. Tectonophysics 609:184–201
Kay RW (1978) Aleutian magnesian andesites: melts from subducted Pacific Ocean crust. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 4(1):117–132
Kay SM, Coira B, Viramonte J (1994) Young mafic back arc volcanic rocks as indicators of continental lithospheric delamination beneath the Argentine Puna plateau, central Andes. J Geophys Res Solid Earth (1978–2012) 99(B12):24323–24339
Kelemen PB (1995) Genesis of high Mg# andesites and the continental crust. Contrib Miner Petrol 120(1):1–19
Kelemen PB, Yogodzinski GM, Scholl DW (2003) Along-strike variation in the Aleutian island arc: genesis of high Mg# andesite and implications for continental crust. Geophys Monogr Ser 138:223–276
Kelemen PB, Hanghøj K, Greene AR (2014) One view of the geochemistry of subduction-related magmatic arcs, with an emphasis on primitive andesite and lower crust. Treatise Geochem 4:749–806
King PL, Larsen JF (2013) A micro-reflectance IR spectroscopy method for analyzing volatile species in basaltic, andesitic, phonolitic, and rhyolitic glasses. Am Mineral 98(7):1162–1171
Kinzler RJ (1997) Melting of mantle peridotite at pressures approaching the spinel to garnet transition: Application to mid-ocean ridge basalt petrogenesis. J Geophys Res Solid Earth (1978–2012) 102(B1):853–874
Kinzler RJ, Grove TL (1992) Primary magmas of mid-ocean ridge basalts 1. Experiments and methods. J Geophys Res Solid Earth (1978–2012) 97(B5):6885–6906
Krawczynski MJ (2011) Experimental studies of melting and crystallization processes in planetary interiors. Dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Krawczynski MJ, Olive JL (2011) A new fitting algorithm for petrological mass-balance problems. In: AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, vol 1, p 2613
Kress VC, Carmichael IS (1991) The compressibility of silicate liquids containing Fe2O3 and the effect of composition, temperature, oxygen fugacity and pressure on their redox states. Contrib Miner Petrol 108(1–2):82–92
Kushiro I (1969) The system forsterite–diopside–silica with and without water at high pressures. Am J Sci 267:269–294
Kushiro I (1970) Systems bearing on melting of the upper mantle under hydrous conditions. Carnegie Inst. Washington Year Book, vol 68, p 240
Kushiro I (1972) Effect of water on the composition of magmas formed at high pressures. J Petrol 13(2):311–334
Kushiro I (1974) Melting of hydrous upper mantle and possible generation of andesitic magma: an approach from synthetic systems. Earth Planet Sci Lett 22(4):294–299
Kushiro I (1975) On the nature of silicate melt and its significance in magma genesis; regularities in the shift of the liquidus boundaries involving olivine, pyroxene, and silica minerals. Am J Sci 275(4):411–431
Kushiro I (1996) Partial melting of a fertile mantle peridotite at high pressures: an experimental study using aggregates of diamond. In: Basu A, Hart S (eds) Earth processes reading isotopic code. Geophysical Monograph, American Geophysical Union, vol 95, pp 109–122
Kushiro I, Syono Y, Akimoto SI (1968) Melting of a peridotite nodule at high pressures and high water pressures. J Geophys Res 73(18):6023–6029
Laporte D, Toplis MJ, Seyler M, Devidal JL (2004) A new experimental technique for extracting liquids from peridotite at very low degrees of melting: application to partial melting of depleted peridotite. Contrib Miner Petrol 146(4):463–484
Lee CTA, Luffi P, Plank T, Dalton H, Leeman WP (2009) Constraints on the depths and temperatures of basaltic magma generation on Earth and other terrestrial planets using new thermobarometers for mafic magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 279(1):20–33
Longhi J (2005) Temporal stability and pressure calibration of barium carbonate and talc/pyrex pressure media in a piston-cylinder apparatus. Am Mineral 90(1):206–218
Médard E, McCammon CA, Barr JA, Grove TL (2008) Oxygen fugacity, temperature reproducibility, and H2O contents of nominally anhydrous piston-cylinder experiments using graphite capsules. Am Mineral 93(11–12):1838–1844
Meriggi L, Macías JL, Tommasini S, Capra L, Conticelli S (2008) Heterogeneous magmas of the Quaternary Sierra Chichinautzin volcanic field (central Mexico): the role of an amphibole-bearing mantle and magmatic evolution processes. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geológicas 25(2):197–216
Mooney WD, Weaver CS (1989) Regional crustal structure and tectonics of the Pacific coastal states; California, Oregon, and Washington. Geol Soc Am Mem 172:129–162
Morgan GB, London D (2005) Effect of current density on the electron microprobe analysis of alkali aluminosilicate glasses. Am Mineral 90(7):1131–1138
Mysen BO, Kushiro I, Nicholls IA, Ringwood AE (1974) A possible mantle origin for andesitic magmas: discussion of a paper by Nicholls and Ringwood. Earth Planet Sci Lett 21(3):221–229
Nicholls IA, Ringwood AE (1972) Production of silica-saturated tholeiitic magmas in island arcs. Earth Planet Sci Lett 17(1):243–246
Parman SW, Grove TL (2004) Harzburgite melting with and without H2O: experimental data and predictive modeling. J Geophys Res 109(B2):B02201
Pearce JA, Peate DW (1995) Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 23:251–286
Pérez‐Campos, X., Kim, Y., Husker, A., Davis, P. M., Clayton, R. W., Iglesias, A., Pacheco, J.F., Singh, S.K., Manea, V.C., Gurnis, M. (2008). Horizontal subduction and truncation of the Cocos Plate beneath central Mexico. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(18)
Ritter JR, Evans JR (1997) Deep structure of Medicine Lake volcano, California. Tectonophysics 275(1):221–241
Sisson TW, Grove TL (1993) Experimental investigations of the role of H2O in calc-alkaline differentiation and subduction zone magmatism. Contrib Miner Petrol 113(2):143–166
Spear FS, Ferry JM, Rumble D (1982) Analytical formulation of phase equilibria; the Gibbs’ method. Rev Mineral Geochem 10(1):105–152
Stolper E, Newman S (1994) The role of water in the petrogenesis of Mariana trough magmas. Earth Planet Sci Lett 121(3):293–325
Straub, S. M., LaGatta, A. B., Pozzo, M. D., Lillian, A., Langmuir, C. H. (2008) Evidence from high‐Ni olivines for a hybridized peridotite/pyroxenite source for orogenic andesites from the central Mexican Volcanic Belt. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 9(3)
Straub SM, Gómez-Tuena A, Stuart FM, Zellmer GF, Espinasa-Perena R, Cai Y, Iizuka Y (2011) Formation of hybrid arc andesites beneath thick continental crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 303(3):337–347
Streck MJ, Leeman WP, Chesley J (2007) High-magnesian andesite from Mount Shasta: a product of magma mixing and contamination, not a primitive mantle melt. Geology 35(4):351–354
Tatsumi Y (1981) Melting experiments on a high-magnesian andesite. Earth Planet Sci Lett 54(2):357–365
Tatsumi Y (1982) Origin of high-magnesian andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, southwest Japan, II. Melting phase relations at high pressures. Earth Planet Sci Lett 60(2):305–317
Tatsumi Y (2001) Geochemical modeling of partial melting of subducting sediments and subsequent melt-mantle interaction: generation of high-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, southwest Japan. Geology 29(4):323–326
Tatsumi Y (2006) High-Mg andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, southwestern Japan: analogy to Archean magmatism and continental crust formation? Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 34:467–499
Tatsumi Y, Ishizaka K (1982) Origin of high-magnesian andesites in the Setouchi volcanic belt, southwest Japan, I. Petrographical and chemical characteristics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 60(2):293–304
Till CB, Grove TL, Krawczynski MJ (2012a) A melting model for variably depleted and enriched lherzolite in the plagioclase and spinel stability fields. J Geophys Res Solid Earth (1978–2012) 117(B6)
Till CB, Grove TL, Withers AC (2012b). The beginnings of hydrous mantle wedge melting. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163(4):669–688
Tormey DR, Grove TL, Bryan WB (1987) Experimental petrology of normal MORB near the Kane Fracture Zone: 22–25 N, mid-Atlantic ridge. Contrib Miner Petrol 96(2):121–139
Walter MJ (1998) Melting of garnet peridotite and the origin of komatiite and depleted lithosphere. J Petrol 39(1):29–60
Wasylenki LE, Baker MB, Kent AJ, Stolper EM (2003) Near-solidus melting of the shallow upper mantle: partial melting experiments on depleted peridotite. J Petrol 44(7):1163–1191
Watson E, Wark D, Price J, Van Orman J (2002) Mapping the thermal structure of solid-media pressure assemblies. Contrib Miner Petrol 142(6):640–652
Weaver SL, Wallace PJ, Johnston AD (2011) A comparative study of continental vs. intraoceanic arc mantle melting: experimentally determined phase relations of hydrous primitive melts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 308(1):97–106
Weber JN, Roy R (1965) Complex stable<--> metastable solid reactions illustrated with the Mg (OH) 2<--> MgO reaction. Am J Sci 263(8):668–677
Weber RM, Wallace PJ, Johnston AD (2011) Experimental insights into the formation of high-Mg basaltic andesites in the trans-Mexican volcanic belt. Contrib Miner Petrol 163(5):825–840
Wood BJ, Turner SP (2009) Origin of primitive high-Mg andesite: constraints from natural examples and experiments. Earth Planet Sci Lett 283(1):59–66
Yoshii T, Sasaki Y, Tada T, Okada H, Asano S, Muramatu I, Hashizume M, Moriya T (1974) The third Kurayosi explosion and the crustal structure in the western part of Japan. J Phys Earth 22(1):109–121
Zucca JJ, Fuis GS, Milkereit B, Mooney WD, Catchings RD (1986) Crustal structure of northeastern California. J Geophys Res Solid Earth (1978–2012) 91(B7):7359–7382
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Bernard Charlier for his guidance early on in the laboratory, Neel Chatterjee for assistance with the electron microprobe, Brian Monteleone for his help with the ion microprobe, as well as Lisa Miller and Randy Smith for their assistance using the U2B beamline at the NSLS. Many thanks to Oliver Jagoutz for his thoughtful suggestions and help testing the excel spreadsheet, as well as Benjamin Mandler, Stephanie Brown, and Max Collinet for their insights during our many discussions. In addition, the authors would like to thank Peter Kelemen and an anonymous reviewer for their thoughtful comments and suggestions, as well as Othmar Müntener for his remarks and editorial handling of the manuscript. The work in this manuscript was supported by the National Science Foundation EAR-1118598 granted to Timothy L. Grove. Use of the National Synchrotron Light Source, Brookhaven National Laboratory, was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, under Contract No. DE-AC02-98CH10886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Othmar Müntener.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, A.L., Grove, T.L. Melting the hydrous, subarc mantle: the origin of primitive andesites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 170, 13 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1161-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1161-4