Abstract
With the recent approval of methylphenidate (MPH) for treating attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults, the number of patients exposed will increase tremendously. The ongoing debate on the cardiovascular safety of MPH has triggered two large retrospective cohort studies in children and adolescents as well as in young to middle-aged adults. These studies looked into serious cardiovascular events (sudden cardiac death, acute myocardial infarction and stroke) as primary endpoints and concluded that MPH was safe after a mean duration of 2.1 years of follow-up in children and adolescents and mean duration of 0.33 years of current use in adults. The results are encouraging with respect to the short- and medium-term use of MPH. Without the inherent limitations of retrospective cohort studies, a prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial in individuals stratified for cardiovascular risk factors would allow for an optimized risk assessment. With many millions of patients treated per year and drawing parallels to the lately discovered risks of sibutramine, another sympathomimetic with an overlapping mode of action and similar side effects on heart rate and blood pressure, we hypothesize that such a trial might be a dedicated risk mitigation strategy for public health. A critical assessment of cardiovascular side effects of MPH appears particularly warranted, because ADHD is associated with obesity, smoking and poor health in general. We summarize recent findings with the focus on cardiovascular risks of MPH in humans; we additionally analyze the limited number of rodent studies that have addressed cardiovascular risks of MPH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldman HM, Reiff MI (2014) Clinical practice. Attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. N Engl J Med 370(9):838–846. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1307215
Merikangas KR, He JP, Brody D, Fisher PW, Bourdon K, Koretz DS (2010) Prevalence and treatment of mental disorders among US children in the 2001–2004 NHANES. Pediatrics 125(1):75–81. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2598
NIH (1998) NIH Consensus Statement. Diagnosis and treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). NIH Consens Statement 16(2):1–37
Remschmidt H, Global AWG (2005) Global consensus on ADHD/HKD. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 14(3):127–137. doi:10.1007/s00787-005-0439-x
Subcommittee on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity D, Steering Committee on Quality I, Management, Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, DuPaul G, Earls M, Feldman HM, Ganiats TG, Kaplanek B, Meyer B, Perrin J, Pierce K, Reiff M, Stein MT, Visser S (2011) ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 128(5):1007–1022. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2654
Hinney A, Scherag A, Jarick I, Albayrak O, Putter C, Pechlivanis S, Dauvermann MR, Beck S, Weber H, Scherag S, Nguyen TT, Volckmar AL, Knoll N, Faraone SV, Neale BM, Franke B, Cichon S, Hoffmann P, Nothen MM, Schreiber S, Jockel KH, Wichmann HE, Freitag C, Lempp T, Meyer J, Gilsbach S, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Sinzig J, Lehmkuhl G, Renner TJ, Warnke A, Romanos M, Lesch KP, Reif A, Schimmelmann BG, Hebebrand J, Psychiatric GCAs (2011) Genome-wide association study in German patients with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genetics Part B Neuropsychiatr Genetics 156B(8):888–897. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31246
Franke B, Faraone SV, Asherson P, Buitelaar J, Bau CH, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Mick E, Grevet EH, Johansson S, Haavik J, Lesch KP, Cormand B, Reif A, International Multicentre persistent AC (2012) The genetics of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults, a review. Mol Psychiatry 17(10):960–987. doi:10.1038/mp.2011.138
Faraone SV, Doyle AE (2001) The nature and heritability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatric Clin N Am 10(2):299–316, viii–ix
Holtkamp K, Konrad K, Muller B, Heussen N, Herpertz S, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Hebebrand J (2004) Overweight and obesity in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28(5):685–689. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802623
Cortese S, Angriman M, Maffeis C, Isnard P, Konofal E, Lecendreux M, Purper-Ouakil D, Vincenzi B, Bernardina BD, Mouren MC (2008) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 48(6):524–537. doi:10.1080/10408390701540124
Waring ME, Lapane KL (2008) Overweight in children and adolescents in relation to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: results from a national sample. Pediatrics 122(1):e1–e6. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-1955
Byrd HC, Curtin C, Anderson SE (2013) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and obesity in US males and females, age 8–15 years: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2004. Pediatr Obes 8(6):445–453. doi:10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00124.x
Albayrak O, Putter C, Volckmar AL, Cichon S, Hoffmann P, Nothen MM, Jockel KH, Schreiber S, Wichmann HE, Faraone SV, Neale BM, Herpertz-Dahlmann B, Lehmkuhl G, Sinzig J, Renner TJ, Romanos M, Warnke A, Lesch KP, Reif A, Schimmelmann BG, Scherag A, Hebebrand J, Hinney A, Psychiatric GCAS (2013) Common obesity risk alleles in childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genetics Part B Neuropsychiatr Genetics 162B(4):295–305. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32144
Milberger S, Biederman J, Faraone SV, Chen L, Jones J (1997) ADHD is associated with early initiation of cigarette smoking in children and adolescents. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36(1):37–44. doi:10.1097/00004583-199701000-00015
Lingineni RK, Biswas S, Ahmad N, Jackson BE, Bae S, Singh KP (2012) Factors associated with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder among US children: results from a national survey. BMC Pediatr 12:50. doi:10.1186/1471-2431-12-50
Kraut AA, Langner I, Lindemann C, Banaschewski T, Petermann U, Petermann F, Mikolajczyk RT, Garbe E (2013) Comorbidities in ADHD children treated with methylphenidate: a database study. BMC Psychiatry 13:11. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-13-11
Riley AW, Spiel G, Coghill D, Dopfner M, Falissard B, Lorenzo MJ, Preuss U, Ralston SJ, Group AS (2006) Factors related to health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among children with ADHD in Europe at entry into treatment. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 15(Suppl 1):I38–I45. doi:10.1007/s00787-006-1006-9
Gillies D, Sinn J, Lad SS, Leach MJ, Ross MJ (2012) Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CD007986. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007986.pub2
Knight LA, Rooney M, Chronis-Tuscano A (2008) Psychosocial treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Curr Psychiatry Rep 10(5):412–418
Sonuga-Barke EJ, Brandeis D, Cortese S, Daley D, Ferrin M, Holtmann M, Stevenson J, Danckaerts M, van der Oord S, Dopfner M, Dittmann RW, Simonoff E, Zuddas A, Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Coghill D, Hollis C, Konofal E, Lecendreux M, Wong IC, Sergeant J, European AGG (2013) Nonpharmacological interventions for ADHD: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials of dietary and psychological treatments. Am J Psychiatry 170(3):275–289. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12070991
Banaschewski T, Coghill D, Santosh P, Zuddas A, Asherson P, Buitelaar J, Danckaerts M, Dopfner M, Faraone SV, Rothenberger A, Sergeant J, Steinhausen HC, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Taylor E (2006) Long-acting medications for the hyperkinetic disorders. A systematic review and European treatment guideline. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 15(8):476–495. doi:10.1007/s00787-006-0549-0
Faraone SV, Buitelaar J (2010) Comparing the efficacy of stimulants for ADHD in children and adolescents using meta-analysis. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 19(4):353–364. doi:10.1007/s00787-009-0054-3
Hanwella R, Senanayake M, de Silva V (2011) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of methylphenidate and atomoxetine in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis. BMC psychiatry 11:176. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-11-176
Chai G, Governale L, McMahon AW, Trinidad JP, Staffa J, Murphy D (2012) Trends of outpatient prescription drug utilization in US children, 2002–2010. Pediatrics 130(1):23–31. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2879
Schubert I, Koster I, Lehmkuhl G (2010) The changing prevalence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and methylphenidate prescriptions: a study of data from a random sample of insurees of the AOK Health Insurance Company in the German State of Hesse, 2000–2007. Deutsches Arztebl Int 107(36):615–621. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2010.0615
BARMER (2013) BARMER GEK Arztreport 2013. http://bkj-ev.de/documents/PDF-digitale-PressemappepropertyData.pdf. Accessed May 2013
Getahun D, Jacobsen SJ, Fassett MJ, Chen W, Demissie K, Rhoads GG (2013) Recent trends in childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. JAMA Pediatr 167(3):282–288. doi:10.1001/2013.jamapediatrics.401
Graf WD, Nagel SK, Epstein LG, Miller G, Nass R, Larriviere D (2013) Pediatric neuroenhancement: ethical, legal, social, and neurodevelopmental implications. Neurology 80(13):1251–1260. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318289703b
Burgard DA, Fuller R, Becker B, Ferrell R, Dinglasan-Panlilio MJ (2013) Potential trends in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) drug use on a college campus: wastewater analysis of amphetamine and ritalinic acid. Sci Total Environ 450–451:242–249. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.020
Drye LT, Scherer RW, Lanctot KL, Rosenberg PB, Herrmann N, Bachman D, Mintzer JE, Group AR (2013) Designing a trial to evaluate potential treatments for apathy in dementia: the apathy in dementia methylphenidate trial (ADMET). Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 21(6):549–559. doi:10.1016/j.jagp.2012.12.018
Kooij SJ, Bejerot S, Blackwell A, Caci H, Casas-Brugue M, Carpentier PJ, Edvinsson D, Fayyad J, Foeken K, Fitzgerald M, Gaillac V, Ginsberg Y, Henry C, Krause J, Lensing MB, Manor I, Niederhofer H, Nunes-Filipe C, Ohlmeier MD, Oswald P, Pallanti S, Pehlivanidis A, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rastam M, Ryffel-Rawak D, Stes S, Asherson P (2010) European consensus statement on diagnosis and treatment of adult ADHD: the European Network Adult ADHD. BMC Psychiatry 10:67. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-10-67
Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ, Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating G (2002) Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 360(9343):1347–1360. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11403-6
NHBP-EPWG (2004) National high blood pressure education program working group on high blood pressure in children and adolescents: the fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114:555–576
Neuhauser HK, Thamm M, Ellert U, Hense HW, Rosario AS (2011) Blood pressure percentiles by age and height from nonoverweight children and adolescents in Germany. Pediatrics 127(4):e978–e988. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-1290
Spagnolo A, Giussani M, Ambruzzi AM, Bianchetti M, Maringhini S, Matteucci MC, Menghetti E, Salice P, Simionato L, Strambi M, Virdis R, Genovesi S (2013) Focus on prevention, diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in children and adolescents. Ital J Pediatr 39:20. doi:10.1186/1824-7288-39-20
Lurbe E, Cifkova R, Cruickshank JK, Dillon MJ, Ferreira I, Invitti C, Kuznetsova T, Laurent S, Mancia G, Morales-Olivas F, Rascher W, Redon J, Schaefer F, Seeman T, Stergiou G, Wuhl E, Zanchetti A, European Society of H (2009) Management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents: recommendations of the European Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens 27(9):1719–1742. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832f4f6b
Hansen ML, Gunn PW, Kaelber DC (2007) Underdiagnosis of hypertension in children and adolescents. JAMA 298(8):874–879. doi:10.1001/jama.298.8.874
Chen X, Wang Y (2008) Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 117(25):3171–3180. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.730366
Bao W, Threefoot SA, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS (1995) Essential hypertension predicted by tracking of elevated blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Hypertens 8(7):657–665. doi:10.1016/0895-7061(95)00116-7
Rascher W, Kiess W, Korner A (2013) High blood pressure in obese children and adolescents. Bundesgesundheitsblatt, Gesundheitsforschung, Gesundheitsschutz 56(4):492–499. doi:10.1007/s00103-012-1638-5
Reinehr T, Wiegand S, Siegfried W, Keller KM, Widhalm K, l’Allemand D, Zwiauer K, Holl RW (2013) Comorbidities in overweight children and adolescents: do we treat them effectively? Int J Obes 37(4):493–499. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.184
Giudice R, Izzo R, Manzi MV, Pagnano G, Santoro M, Rao MA, Di Renzo G, De Luca N, Trimarco V (2012) Lifestyle-related risk factors, smoking status and cardiovascular disease. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 19(2):85–92. doi:10.2165/11632140-000000000-00000
Rodrigues AN, Abreu GR, Resende RS, Goncalves WL, Gouvea SA (2013) Cardiovascular risk factor investigation: a pediatric issue. Int J General Med 6:57–66. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S41480
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Hypertension E-ETFotMoA (2007) 2007 ESH-ESC practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: ESH-ESC task force on the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 25(9):1751–1762. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f0580f
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Struijker Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Kjeldsen SE, Erdine S, Narkiewicz K, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Cifkova R, Dominiczak A, Fagard R, Heagerty AM, Laurent S, Lindholm LH, Mancia G, Manolis A, Nilsson PM, Redon J, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Viigimaa M, Filippatos G, Adamopoulos S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Erdine S, Farsang C, Gaita D, Kiowski W, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O’Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Williams B, Zamorano JL, The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of H, The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of C (2007) 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 28(12):1462–1536. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm236
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ, Joint National Committee on Prevention DE, Treatment of High Blood Pressure. National Heart L, Blood I, National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating C (2003) Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 42(6):1206–1252. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2
Whitworth JA, World Health Organization ISoHWG (2003) 2003 World Health Organization (WHO)/International Society of Hypertension (ISH) statement on management of hypertension. J Hypertens 21(11):1983–1992. doi:10.1097/01.hjh.0000084751.37215.d2
Williams B, Poulter NR, Brown MJ, Davis M, McInnes GT, Potter JF, Sever PS, Mc GTS, British Hypertension S (2004) Guidelines for management of hypertension: report of the fourth working party of the British Hypertension Society, 2004-BHS IV. J Hum Hypertens 18(3):139–185. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001683
Carretero OA, Oparil S (2000) Essential hypertension. Part I: definition and etiology. Circulation 101(3):329–335
Erdine S, Ari O, Zanchetti A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Kjeldsen S, Mancia G, Poulter N, Rahn KH, Rodicio JL, Ruilope LM, Staessen J, van Zwieten P, Waeber B, Williams B (2006) ESH-ESC guidelines for the management of hypertension. Herz 31(4):331–338. doi:10.1007/s00059-006-2829-3
Arnold JM, Fitchett DH, Howlett JG, Lonn EM, Tardif JC (2008) Resting heart rate: a modifiable prognostic indicator of cardiovascular risk and outcomes? Can J Cardiol 24(Suppl A):3A–8A
Dalby M, Gjesdal K (2012) Resting pulse rate as an indicator of health and disease. Tidsskrift for den Norske laegeforening : tidsskrift for praktisk medicin, ny raekke 132(11):1348–1351. doi:10.4045/tidsskr.11.0629
Zhang GQ, Zhang W (2009) Heart rate, lifespan, and mortality risk. Ageing Res Rev 8(1):52–60. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2008.10.001
Ostchega Y, Porter KS, Hughes J, Dillon CF, Nwankwo T (2011) Resting pulse rate reference data for children, adolescents, and adults: United States, 1999-2008. Natl Health Stat Rep 41:1–16
Stessman J, Jacobs JM, Stessman-Lande I, Gilon D, Leibowitz D (2013) Aging, resting pulse rate, and longevity. J Am Geriatr Soc 61(1):40–45. doi:10.1111/jgs.12060
Samuels JA, Franco K, Wan F, Sorof JM (2006) Effect of stimulants on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in children with ADHD: a double-blind, randomized, cross-over trial. Pediatr Nephrol 21(1):92–95. doi:10.1007/s00467-005-2051-1
Stowe CD, Gardner SF, Gist CC, Schulz EG, Wells TG (2002) 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in male children receiving stimulant therapy. Ann Pharmacother 36(7–8):1142–1149
Nissen SE (2006) ADHD drugs and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 354(14):1445–1448. doi:10.1056/NEJMp068049
McCarthy S, Cranswick N, Potts L, Taylor E, Wong IC (2009) Mortality associated with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) drug treatment: a retrospective cohort study of children, adolescents and young adults using the general practice research database. Drug Saf 32(11):1089–1096. doi:10.2165/11317630-000000000-00000
Wilens TE, Prince JB, Spencer TJ, Biederman J (2006) Stimulants and sudden death: what is a physician to do? Pediatrics 118(3):1215–1219. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-0942
Gould MS, Walsh BT, Munfakh JL, Kleinman M, Duan N, Olfson M, Greenhill L, Cooper T (2009) Sudden death and use of stimulant medications in youths. Am J Psychiatry 166(9):992–1001. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09040472
Newstadt M (2006) To box OR NOT TO box. J Ky Med Assoc 104(8):344–345
Fegert JM, Hebebrand J, Kommission Entwicklungspsychopharmakologie der drei F (2006) [Attitude to questionable cadiac risks in stimulant administration]. Zeitschrift fur Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und Psychotherapie 34(4):295–297
Hackford R (2006) With the recent Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Advisory Committee’s recommendation to put a black box warning on stimulants, the government has joined the media in raising alarm about the medical treatment of attention-deficit disorder. J Dev Behav Pediatr 27(2):179
Young D (2006) FDA ponders cardiovascular risks of ADHD drugs. Am J health-Syst Pharm 63(6):492–494. doi:10.2146/news050058
Gutgesell H, Atkins D, Barst R, Buck M, Franklin W, Humes R, Ringel R, Shaddy R, Taubert KA (1999) AHA Scientific Statement: cardiovascular monitoring of children and adolescents receiving psychotropic drugs. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38(8):1047–1050. doi:10.1097/00004583-199908000-00022
Gutgesell H, Atkins D, Barst R, Buck M, Franklin W, Humes R, Ringel R, Shaddy R, Taubert KA (1999) Cardiovascular monitoring of children and adolescents receiving psychotropic drugs: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Congenital Cardiac Defects, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 99(7):979–982
Westover AN, Halm EA (2012) Do prescription stimulants increase the risk of adverse cardiovascular events?: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 12:41. doi:10.1186/1471-2261-12-41
Winterstein AG, Gerhard T, Shuster J, Johnson M, Zito JM, Saidi A (2007) Cardiac safety of central nervous system stimulants in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 120(6):e1494–e1501. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-0675
Winterstein AG, Gerhard T, Shuster J, Saidi A (2009) Cardiac safety of methylphenidate versus amphetamine salts in the treatment of ADHD. Pediatrics 124(1):e75–e80. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-3138
Winterstein AG, Gerhard T, Kubilis P, Saidi A, Linden S, Crystal S, Zito J, Shuster JJ, Olfson M (2012) Cardiovascular safety of central nervous system stimulants in children and adolescents: population based cohort study. BMJ 345:e4627. doi:10.1136/bmj.e4627
Olfson M, Huang C, Gerhard T, Winterstein AG, Crystal S, Allison PD, Marcus SC (2012) Stimulants and cardiovascular events in youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(2):147–156. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.11.008
Cooper WO, Habel LA, Sox CM, Chan KA, Arbogast PG, Cheetham TC, Murray KT, Quinn VP, Stein CM, Callahan ST, Fireman BH, Fish FA, Kirshner HS, O’Duffy A, Connell FA, Ray WA (2011) ADHD drugs and serious cardiovascular events in children and young adults. N Engl J Med 365(20):1896–1904. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1110212
Habel LA, Cooper WO, Sox CM, Chan KA, Fireman BH, Arbogast PG, Cheetham TC, Quinn VP, Dublin S, Boudreau DM, Andrade SE, Pawloski PA, Raebel MA, Smith DH, Achacoso N, Uratsu C, Go AS, Sidney S, Nguyen-Huynh MN, Ray WA, Selby JV (2011) ADHD medications and risk of serious cardiovascular events in young and middle-aged adults. JAMA 306(24):2673–2683. doi:10.1001/jama.2011.1830
Schelleman H, Bilker WB, Kimmel SE, Daniel GW, Newcomb C, Guevara JP, Cziraky MJ, Strom BL, Hennessy S (2012) Methylphenidate and risk of serious cardiovascular events in adults. Am J Psychiatry 169(2):178–185. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11010125
Schelleman H, Bilker WB, Strom BL, Kimmel SE, Newcomb C, Guevara JP, Daniel GW, Cziraky MJ, Hennessy S (2011) Cardiovascular events and death in children exposed and unexposed to ADHD agents. Pediatrics 127(6):1102–1110. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-3371
Buchhorn R, Muller C, Willaschek C, Norozi K (2012) How to predict the impact of methylphenidate on cardiovascular risk in children with attention deficit disorder: methylphenidate improves autonomic dysfunction in children with ADHD. ISRN Pharmacol 170935. doi:10.5402/2012/170935
Buchhorn R, Conzelmann A, Willaschek C, Stork D, Taurines R, Renner TJ (2012) Heart rate variability and methylphenidate in children with ADHD. Atten Deficit Hyperact Disord 4(2):85–91. doi:10.1007/s12402-012-0072-8
Rash JA, Aguirre-Camacho A (2012) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and cardiac vagal control: a systematic review. Atten Deficit Hyperact Disord 4(4):167–177. doi:10.1007/s12402-012-0087-1
Mick E, McManus DD, Goldberg RJ (2013) Meta-analysis of increased heart rate and blood pressure associated with CNS stimulant treatment of ADHD in adults. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23(6):534–541. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.06.011
Vetter VL, Elia J, Erickson C, Berger S, Blum N, Uzark K, Webb CL, American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young Congenital Cardiac Defects C, American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular N (2008) Cardiovascular monitoring of children and adolescents with heart disease receiving medications for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder [corrected]: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee and the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing. Circulation 117(18):2407–2423. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.189473
Graham J, Banaschewski T, Buitelaar J, Coghill D, Danckaerts M, Dittmann RW, Dopfner M, Hamilton R, Hollis C, Holtmann M, Hulpke-Wette M, Lecendreux M, Rosenthal E, Rothenberger A, Santosh P, Sergeant J, Simonoff E, Sonuga-Barke E, Wong IC, Zuddas A, Steinhausen HC, Taylor E, European Guidelines G (2011) European guidelines on managing adverse effects of medication for ADHD. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 20(1):17–37. doi:10.1007/s00787-010-0140-6
Wilens TE, Hammerness PG, Biederman J, Kwon A, Spencer TJ, Clark S, Scott M, Podolski A, Ditterline JW, Morris MC, Moore H (2005) Blood pressure changes associated with medication treatment of adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 66(2):253–259
Vitiello B, Elliott GR, Swanson JM, Arnold LE, Hechtman L, Abikoff H, Molina BS, Wells K, Wigal T, Jensen PS, Greenhill LL, Kaltman JR, Severe JB, Odbert C, Hur K, Gibbons R (2012) Blood pressure and heart rate over 10 years in the multimodal treatment study of children with ADHD. Am J Psychiatry 169(2):167–177. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10111705
Molina BS, Hinshaw SP, Swanson JM, Arnold LE, Vitiello B, Jensen PS, Epstein JN, Hoza B, Hechtman L, Abikoff HB, Elliott GR, Greenhill LL, Newcorn JH, Wells KC, Wigal T, Gibbons RD, Hur K, Houck PR, Group MTAC (2009) The MTA at 8 years: prospective follow-up of children treated for combined-type ADHD in a multisite study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 48(5):484–500. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e31819c23d0
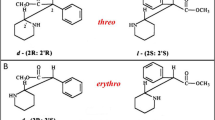
Heal DJ, Pierce DM (2006) Methylphenidate and its isomers: their role in the treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder using a transdermal delivery system. CNS Drugs 20(9):713–738
Quinn D (2008) Does chirality matter? Pharmacodynamics of enantiomers of methylphenidate in patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28(3 Suppl 2):S62–S66. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181744aa6
Markowitz JS, DeVane CL, Pestreich LK, Patrick KS, Muniz R (2006) A comprehensive in vitro screening of d-, l-, and dl-threo-methylphenidate: an exploratory study. J Child adolescent Psychopharmacol 16(6):687–698. doi:10.1089/cap.2006.16.687
Heal DJ, Cheetham SC, Smith SL (2009) The neuropharmacology of ADHD drugs in vivo: insights on efficacy and safety. Neuropharmacology 57(7–8):608–618. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.08.020
Maxwell RA, Sylwestrowicz HD, Holland R, Schneider F, Daniel AI (1961) Some actions of methylphenidate on the vascular system, arterial tissue and the nictitating membrane. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 131:355–365
Ishiguro Y, Morgan JP (1997) Biphasic inotropic effects of methamphetamine and methylphenidate on ferret papillary muscles. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 30(6):744–749
Heal DJ, Smith SL, Gosden J, Nutt DJ (2013) Amphetamine, past and present–a pharmacological and clinical perspective. J Psychopharmacol 27(6):479–496. doi:10.1177/0269881113482532
Faraone SV, Biederman J, Roe C (2002) Comparative efficacy of Adderall and methylphenidate in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychopharmacol 22(5):468–473
Findling RL, Short EJ, Manos MJ (2001) Short-term cardiovascular effects of methylphenidate and adderall. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40(5):525–529. doi:10.1097/00004583-200105000-00011
Glaser PE, Thomas TC, Joyce BM, Castellanos FX, Gerhardt GA (2005) Differential effects of amphetamine isomers on dopamine release in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens core. Psychopharmacology 178(2–3):250–258. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-2012-6
Joyce BM, Glaser PE, Gerhardt GA (2007) Adderall produces increased striatal dopamine release and a prolonged time course compared to amphetamine isomers. Psychopharmacology 191(3):669–677. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0550-9
Adler LA, Weisler RH, Goodman DW, Hamdani M, Niebler GE (2009) Short-term effects of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate on cardiovascular parameters in a 4-week clinical trial in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 70(12):1652–1661. doi:10.4088/JCP.09m05335pur
Mikkelsen E, Lake CR, Brown GL, Ziegler MG, Ebert MH (1981) The hyperactive child syndrome: peripheral sympathetic nervous system function and the effect of d-amphetamine. Psychiatry Res 4(2):157–169
Garnock-Jones KP, Keating GM (2009) Atomoxetine: a review of its use in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Paediatr Drugs 11(3):203–226. doi:10.2165/00148581-200911030-00005
Sert A, Gokcen C, Aypar E, Odabas D (2012) Effects of atomoxetine on cardiovascular functions and on QT dispersion in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Cardiol Young 22(2):158–161. doi:10.1017/S1047951111001211
Arcieri R, Germinario EA, Bonati M, Masi G, Zuddas A, Vella S, Chiarotti F, Panei P, Italian Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Regional Reference C (2012) Cardiovascular measures in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder who are new users of methylphenidate and atomoxetine. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 22(6):423–431
Huang YS, Wang LJ, Chen CK (2012) Long-term neurocognitive effects of methylphenidate in patients with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, even at drug-free status. BMC Psychiatry 12:194. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-12-194
Mitchell J, Read J (2012) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, drug companies and the internet. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry 17(1):121–139. doi:10.1177/1359104510396432
Bange F, Le Heuzey MF, Acquaviva E, Delorme R, Mouren MC (2014) Cardiovascular risks and management during attention deficit hyperactivity disorder treatment with methylphenidate. Archives de pediatrie: organe officiel de la Societe francaise de pediatrie 21(1):108–112. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2013.11.001
(NTP) (1995) National Toxicology Program (NTP): Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride (CAS No. 298-59-9) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (feed studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 439:1–299
Wakamatsu A, Nomura S, Tate Y, Shimizu S, Harada Y (2009) Effects of methylphenidate hydrochloride on the cardiovascular system in vivo and in vitro: a safety pharmacology study. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 59(3):128–134. doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2009.01.003
Witt KL, Malarkey DE, Hobbs CA, Davis JP, Kissling GE, Caspary W, Travlos G, Recio L (2010) No increases in biomarkers of genetic damage or pathological changes in heart and brain tissues in male rats administered methylphenidate hydrochloride (Ritalin) for 28 days. Environ Mol Mutagen 51(1):80–88. doi:10.1002/em.20515
Henderson TA, Fischer VW (1995) Effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) on mammalian myocardial ultrastructure. The American journal of cardiovascular pathology 5(1):68–78
Take G, Bahcelioglu M, Oktem H, Tunc E, Gozil R, Erdogan D, Calguner E, Helvacioglu F, Giray SG, Elmas C (2008) Dose-dependent immunohistochemical and ultrastructural changes after oral methylphenidate administration in rat heart tissue. Anat Histol Embryol 37(4):303–308. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0264.2008.00845.x
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Lerner M, Concerta Study G (2004) Effects of once-daily osmotic-release methylphenidate on blood pressure and heart rate in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: results from a one-year follow-up study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 24(1):36–41. doi:10.1097/01.jcp.0000106223.36344.df
Joyce PR, Nicholls MG, Donald RA (1984) Methylphenidate increases heart rate, blood pressure and plasma epinephrine in normal subjects. Life Sci 34(18):1707–1711
Steinkellner T, Freissmuth M, Sitte HH, Montgomery T (2011) The ugly side of amphetamines: short- and long-term toxicity of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ‘Ecstasy’), methamphetamine and D-amphetamine. Biol Chem 392(1–2):103–115. doi:10.1515/BC.2011.016
Simpson LL (1975) Blood pressure and heart rate responses evoked by d- and l-amphetamine in the pithed rat preparation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 193(1):149–159
Tontodonati M, Fasdelli N, Moscardo E, Giarola A, Dorigatti R (2007) A canine model used to simultaneously assess potential neurobehavioural and cardiovascular effects of candidate drugs. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 56(2):265–275. doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2007.03.005
Goldstein DS, Nurnberger J Jr, Simmons S, Gershon ES, Polinsky R, Keiser HR (1983) Effects of injected sympathomimetic amines on plasma catecholamines and circulatory variables in man. Life Sci 32(10):1057–1063
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Molina PE, Logan J, Gatley SJ, Gifford A, Ding YS, Wong C, Pappas NR, Zhu W, Swanson JM (2003) Cardiovascular effects of methylphenidate in humans are associated with increases of dopamine in brain and of epinephrine in plasma. Psychopharmacology 166(3):264–270. doi:10.1007/s00213-002-1340-7
Thomas F, Blacher J, Benetos A, Safar ME, Pannier B (2008) Cardiovascular risk as defined in the 2003 European blood pressure classification: the assessment of an additional predictive value of pulse pressure on mortality. J Hypertens 26(6):1072–1077. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282fcc22b
Perret-Guillaume C, Joly L, Benetos A (2009) Heart rate as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52(1):6–10. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2009.05.003
Cacoub PP, Zeymer U, Limbourg T, Baumgartner I, Poldermans D, Rother J, Bhatt DL, Steg PG, Investigators RR (2011) Effects of adherence to guidelines for the control of major cardiovascular risk factors on outcomes in the REduction of Atherothrombosis for Continued Health (REACH) Registry Europe. Heart 97(8):660–667. doi:10.1136/hrt.2010.213710
ADDUCE (2012) ADDUCE. http://www.adhd-adduce.org/page/view/2/Home. Accessed May 2013
Kintscher U (2012) Reuptake inhibitors of dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin. Handb Exp Pharmacol 209:339–347. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-24716-3_15
Heal DJ, Aspley S, Prow MR, Jackson HC, Martin KF, Cheetham SC (1998) Sibutramine: a novel anti-obesity drug. A review of the pharmacological evidence to differentiate it from d-amphetamine and d-fenfluramine. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22(Suppl 1):S18–S28; discussion S29
Nisoli E, Carruba MO (2000) An assessment of the safety and efficacy of sibutramine, an anti-obesity drug with a novel mechanism of action. Obes Rev 1(2):127–139
Scheen AJ (2010) Cardiovascular risk-benefit profile of sibutramine. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 10(5):321–334. doi:10.2165/11584800-000000000-00000
Schroeder C, Jordan J (2012) Norepinephrine transporter function and human cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 303(11):H1273–H1282. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00492.2012
Schlaich MP, Lambert E, Kaye DM, Krozowski Z, Campbell DJ, Lambert G, Hastings J, Aggarwal A, Esler MD (2004) Sympathetic augmentation in hypertension: role of nerve firing, norepinephrine reuptake, and Angiotensin neuromodulation. Hypertension 43(2):169–175. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000103160.35395.9E
Heusser K, Tank J, Diedrich A, Engeli S, Klaua S, Kruger N, Strauss A, Stoffels G, Luft FC, Jordan J (2006) Influence of sibutramine treatment on sympathetic vasomotor tone in obese subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 79(5):500–508. doi:10.1016/j.clpt.2006.02.002
Heusser K, Engeli S, Tank J, Diedrich A, Wiesner S, Janke J, Luft FC, Jordan J (2007) Sympathetic vasomotor tone determines blood pressure response to long-term sibutramine treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(4):1560–1563. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-2499
WPT J (2005) The SCOUT study: risk-benefit profile of sibutramine in overweight high-risk cardiovascular patients. Euro Heart J Suppl 7(Supplement L):L44–L48
Westover AN, Nakonezny PA, Winhusen T, Adinoff B, Vongpatanasin W (2013) Risk of methylphenidate-induced prehypertension in normotensive adult smokers with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Hypertens 15(2):124–132. doi:10.1111/jch.12039
Scholze J, Grimm E, Herrmann D, Unger T, Kintscher U (2007) Optimal treatment of obesity-related hypertension: the Hypertension-Obesity-Sibutramine (HOS) study. Circulation 115(15):1991–1998. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.625400
Scholze J (2002) Sibutramine in clinical practice—a PMS-study with positive effects on blood pressure and metabolic parameters. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 127(12):606–610. doi:10.1055/s-2002-22671
James WP, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal LF, Maggioni AP, Torp-Pedersen C, Sharma AM, Shepherd GM, Rode RA, Renz CL, Investigators S (2010) Effect of sibutramine on cardiovascular outcomes in overweight and obese subjects. N Engl J Med 363(10):905–917. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1003114
Van Gaal LF, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Maggioni AP, Sharma AM, Torp-Pedersen C, Ge H, Moran SA, Shepherd GM, James WP, Investigators S (2010) Weight and blood pressure response to weight management and sibutramine in diabetic and non-diabetic high-risk patients: an analysis from the 6-week lead-in period of the sibutramine cardiovascular outcomes (SCOUT) trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(1):26–34. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01090.x
Sharma AM, Caterson ID, Coutinho W, Finer N, Van Gaal L, Maggioni AP, Torp-Pedersen C, Bacher HP, Shepherd GM, James WP, Investigators S (2009) Blood pressure changes associated with sibutramine and weight management—an analysis from the 6-week lead-in period of the sibutramine cardiovascular outcomes trial (SCOUT). Diabetes Obes Metab 11(3):239–250. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00930.x
Ferland A, Poirier P, Series F (2009) Sibutramine versus continuous positive airway pressure in obese obstructive sleep apnoea patients. Eur Respir J 34(3):694–701. doi:10.1183/09031936.00167308
FDA (2010) FDA recommends against the continued use of meridia (sibutramine). U.S. Food and Drug Administration: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm228746.htm. Accessed May 2013. FDA Drug Safety Communication
Pollack A (2010) Abbott labs withdraws meridia from market. The New York Times (October 8th)
Tyczynski JE, Oleske DM, Klingman D, Ferrufino CP, Lee WC (2012) Safety assessment of an anti-obesity drug (sibutramine): a retrospective cohort study. Drug Saf 35(8):629–644. doi:10.2165/11599220-000000000-00000
Sprigg N, Bath PM (2009) Speeding stroke recovery? A systematic review of amphetamine after stroke. J Neurol Sci 285(1–2):3–9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.04.040
Smith ME, Farah MJ (2011) Are prescription stimulants “smart pills”? The epidemiology and cognitive neuroscience of prescription stimulant use by normal healthy individuals. Psychol Bull 137(5):717–741. doi:10.1037/a0023825
Hazell P (2011) The challenges to demonstrating long-term effects of psychostimulant treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry 24(4):286–290. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32834742db
Prasad V, Brogan E, Mulvaney C, Grainge M, Stanton W, Sayal K (2013) How effective are drug treatments for children with ADHD at improving on-task behaviour and academic achievement in the school classroom? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 22(4):203–216. doi:10.1007/s00787-012-0346-x
Langberg JM, Becker SP (2012) Does long-term medication use improve the academic outcomes of youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder? Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev 15(3):215–233. doi:10.1007/s10567-012-0117-8
Shaw M, Hodgkins P, Caci H, Young S, Kahle J, Woods AG, Arnold LE (2012) A systematic review and analysis of long-term outcomes in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: effects of treatment and non-treatment. BMC Med 10:99. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-99
Bogle KE, Smith BH (2009) Illicit methylphenidate use: a review of prevalence, availability, pharmacology, and consequences. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 2(2):157–176
Davis C, Fattore L, Kaplan AS, Carter JC, Levitan RD, Kennedy JL (2012) The suppression of appetite and food consumption by methylphenidate: the moderating effects of gender and weight status in healthy adults. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15(2):181–187. doi:10.1017/S1461145711001039
Poulton A, Briody J, McCorquodale T, Melzer E, Herrmann M, Baur LA, Duque G (2012) Weight loss on stimulant medication: how does it affect body composition and bone metabolism?—a prospective longitudinal study. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol 1:30. doi:10.1186/1687-9856-2012-30
Ginsberg Y, Langstrom N, Larsson H, Lichtenstein P (2013) ADHD and criminality: could treatment benefit prisoners with ADHD who are at higher risk of reoffending? Expert Rev Neurother 13(4):345–348. doi:10.1586/ern.13.22
Padala PR, Burke WJ, Shostrom VK, Bhatia SC, Wengel SP, Potter JF, Petty F (2010) Methylphenidate for apathy and functional status in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 18(4):371–374. doi:10.1097/JGP.0b013e3181cabcf6
Martinez-Raga J, Knecht C, Szerman N, Martinez MI (2013) Risk of serious cardiovascular problems with medications for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. CNS Drugs 27(1):15–30. doi:10.1007/s40263-012-0019-9
Leslie LK, Rodday AM, Saunders TS, Cohen JT, Wong JB, Sheldrick RC, Parsons SK (2012) Survey of United States child and adolescent psychiatrists’ cardiac screening practices prior to starting patients on stimulants. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 22(5):375–384. doi:10.1089/cap.2011.0141
Lindemann C, Langner I, Kraut AA, Banaschewski T, Schad-Hansjosten T, Petermann U, Petermann F, Schreyer-Mehlhop I, Garbe E, Mikolajczyk RT (2012) Age-specific prevalence, incidence of new diagnoses, and drug treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in Germany. Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 22(4):307–314
Ford T, Goodman R, Meltzer H (2003) The British Child and Adolescent Mental Health Survey 1999: the prevalence of DSM-IV disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(10):1203–1211
McCarthy S, Wilton L, Murray ML, Hodgkins P, Asherson P, Wong IC (2012) The epidemiology of pharmacologically treated attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children, adolescents and adults in UK primary care. BMC Pediatr 12:78
Acknowledgments
This review was written without any dedicated funding source.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Banaschewski served in an advisory or consultancy role for Hexal Pharma, Lilly, Medice, Novartis, PCM scientific, Shire and Viforpharma. He received conference attendance support and conference support or received speaker’s fee by Lilly, Janssen McNeil, Medice, Novartis and Shire. He is/has been involved in clinical trials conducted by Lilly, Shire & Viforpharma. The present work is unrelated to the above grants and relationships. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antel, J., Albayrak, Ö., Heusch, G. et al. Assessment of potential cardiovascular risks of methylphenidate in comparison with sibutramine: do we need a SCOUT (trial)?. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 265, 233–247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0522-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0522-8