Abstract
Purpose
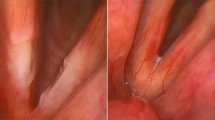
Lipoid proteinosis (LP) or Urbach-Wiethe disease (OMIM 247100) is a rare syndrome characterised by early vocal folds infiltration and subsequent multi-organ involvement. LP is often unrecognised and its associated hoarseness is overlooked. The main objective of the study was to investigate hoarseness in LP and implement a diagnosis among otolaryngologists.
Methods
PubMed/MEDLINE and OMIM databases were systematically searched. Authors concentrated the search on published articles starting from the discovery of the pathogenesis of LP by Hamada et al. in 2002. Only cases in which a diagnosis was reported both clinically and through biopsy and/or genetic molecular testing were included. Characteristics of the LP cases were extracted from each included study. Results were obtained through Generalized Estimating Equations.
Results
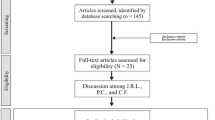
The search strategy yielded 217 articles, of which 74 (34.1%) met the selection criteria. A total of 154 cases were included. Hoarseness was described in all LP cases and clearly stated as the onset symptom in 68.8%. The onset was on average at 19 months of age (CI: 3.00–20.00), while the mean age at diagnosis was 15 years (CI: 10.00–30.00). Therefore, the diagnostic delay amounted to 13.42 years (CI: 8.00–23.83). Hoarseness alone was responsible for an LP diagnosis in only 14.3% of cases. In 43.5% of cases, genetic analysis of the ECM1 gene was performed and exon 6 was the most frequently altered portion.
Conclusion
Analysing the largest number of published cases, the study underlined that hoarseness is the key symptom for diagnosing LP since early childhood, though frequently overlooked.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files. In particular, Online Resource 1 contains the data extracted from each LP case and included in the meta-analysis.
References
Urbach E, Wiethe C (1929) Lipoidosis cutis et mucosae. Virchows Arch Für Pathol Anat Physiol Für Klin Med 273:285–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02158983
Hofer PA (1973) Urbach-Wiethe disease (lipoglycoproteinosis; lipoid proteinosis; hyalinosis cutis et mucosae). A review. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 53:1–52
Hamada T, McLean WHI, Ramsay M et al (2002) Lipoid proteinosis maps to 1q21 and is caused by mutations in the extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1). Hum Mol Genet 11:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/11.7.833
Orphanet Editorial Team (2022) Prevalence of rare diseases: Bibliographic data, Orphanet Report Series, Rare Diseases collection, Number 1: Diseases listed in alphabetical order. https://www.orpha.net/orphacom/cahiers/docs/GB/Prevalence_of_rare_diseases_by_alphabetical_list.pdf. Accessed August 8, 2023
Hamada T (2002) Lipoid proteinosis. Clin Exp Dermatol 27:624–629. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2230.2002.01143.x
Honings J, van Rossum MM, van den Hoogen FJA (2015) Vocal fold hyalinosis in Urbach-Wiethe disease, a rare cause of hoarseness. B-ENT 11:151–155
Gunes B, Karadag R, Uzun L et al (2019) Is it always blepharitis? Urbach-Wiethe syndrome (lipoid proteinosis). Arq Bras Oftalmol 82:242–244. https://doi.org/10.5935/0004-2749.20190051
Kabre V, Rani S, Pai KM, Kamra S (2015) Lipoid proteinosis: a review with two case reports. Contemp Clin Dent 6:233–236. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-237X.156053
Friedman L, Mathews RD, Swanepoel PD (1984) Radiographic and computed tomographic findings in lipid proteinosis. A case report. South Afr Med J Suid-Afr Tydskr Vir Geneeskd 65:734–735
Ally M, Kinshuck AJ, Sandison A, Sandhu GS (2018) The management of laryngeal lipoid proteinosis. J Laryngol Otol 132:936–939. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215118001329
Di Giandomenico S, Masi R, Cassandrini D et al (2006) Lipoid proteinosis: case report and review of the literature. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital Organo Uff Della Soc Ital Otorinolaringol E Chir Cerv-facc 26:162–167
Vahidnezhad H, Youssefian L, Uitto J (1993) Lipoid Proteinosis. In: Adam MP, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, et al (eds) GeneReviews®. University of Washington, Seattle, Seattle (WA)
Muda AO, Paradisi M, Angelo C et al (1995) Lipoid proteinosis: clinical, histologic, and ultrastructural investigations. Cutis 56:220–224
Stewart LA, Clarke M, Rovers M et al (2015) Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of individual participant data: the PRISMA-IPD Statement. JAMA 313:1657–1665. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.3656
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283:2008–2012. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Ganger J, Brent MR (2004) Reexamining the vocabulary spurt. Dev Psychol 40:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.40.4.621
Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, Daneshpazhooh M et al (2015) Lipoid proteinosis: phenotypic heterogeneity in Iranian families with c.507delT mutation in ECM1. Exp Dermatol 24:220–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12620
GBD 2015 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators. Electronic address: cjlm@uw.edu, GBD 2015 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators (2017) Healthcare Access and Quality Index based on mortality from causes amenable to personal health care in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: a novel analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Lond Engl 390:231–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30818-8
GBD 2016 Healthcare Access and Quality Collaborators (2018) Measuring performance on the Healthcare Access and Quality Index for 195 countries and territories and selected subnational locations: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Lond Engl 391:2236–2271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30994-2
Jackson D, Daly J, Saltman DC (2014) Aggregating case reports: a way for the future of evidence-based health care? Clin Case Rep 2:23–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.58
Nakamura T, Igarashi H, Ito T, Jensen RT (2014) Important of case-reports/series, in rare diseases: Using neuroendocrine tumors as an example. World J Clin Cases 2:608–613. https://doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i11.608
Murad MH, Sultan S, Haffar S, Bazerbachi F (2018) Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid-Based Med 23:60–63. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2017-110853
The R Foundation (2016) What is R? https://www.r-project.org/about.html. Accessed 9 Aug 2023
Riley DS, Barber MS, Kienle GS et al (2017) CARE guidelines for case reports: explanation and elaboration document. J Clin Epidemiol 89:218–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.04.026
Carey JC (2010) The importance of case reports in advancing scientific knowledge of rare diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol 686:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9485-8_5
Nissen T, Wynn R (2014) The clinical case report: a review of its merits and limitations. BMC Res Notes 7:264. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-264
Frenkel B, Vered M, Taicher S, Yarom N (2017) Lipoid proteinosis unveiled by oral mucosal lesions: a comprehensive analysis of 137 cases. Clin Oral Investig 21:2245–2251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-2017-7
Acar A, Eryilmaz A, Gocer C et al (2004) Lipoid proteinosis of larynx: review of four cases. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 68:1557–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2004.07.012
Loos E, Kerkhofs L, Laureyns G (2019) Lipoid proteinosis: a rare cause of hoarseness. J Voice Off J Voice Found 33:155–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2017.05.024
Uchida T, Hayashi H, Inaoki M et al (2007) A failure of mucocutaneous lymphangiogenesis may underlie the clinical features of lipoid proteinosis. Br J Dermatol 156:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07583.x
Oz F, Kalekoğlu N, Karakullukçu B et al (2002) Lipoid proteinosis of the larynx. J Laryngol Otol 116:736–739. https://doi.org/10.1258/002221502760238082
Xu W, Wang L, Zhang L et al (2010) Otolaryngological manifestations and genetic characteristics of lipoid proteinosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119:767–771
Kartal D, Çınar SL, Kartal L et al (2016) Lipoid proteinosis. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat 25:19–21. https://doi.org/10.15570/actaapa.2016.5
Meletti S, Cantalupo G, Santoro F et al (2014) Temporal lobe epilepsy and emotion recognition without amygdala: a case study of Urbach-Wiethe disease and review of the literature. Epileptic Disord Int Epilepsy J Videotape 16:518–527. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2014.0696
Siebert M, Markowitsch HJ, Bartel P (2003) Amygdala, affect and cognition: evidence from 10 patients with Urbach-Wiethe disease. Brain J Neurol 126:2627–2637. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awg271
Claeys KG, Claes LRF, Van Goethem JWM et al (2007) Epilepsy and migraine in a patient with Urbach-Wiethe disease. Seizure 16:465–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2007.02.014
Rickert SM, O’Cathain E (2022) Pediatric voice. Pediatr Clin North Am 69:329–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2022.01.003
Sood S, Street I, Donne A (2017) Hoarseness in children. Br J Hosp Med Lond Engl 78:678–683. https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2017.78.12.678
Savage MM, Crockett DM, McCabe BF (1988) Lipoid proteinosis of the larynx: a cause of voice change in the infant and young child. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 15:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-5876(88)90048-1
Dogramaci AC, Celik MM, Celik E, Bayarogullari H (2012) Lipoid proteinosis in the eastern Mediterranean region of Turkey. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 78:318–322. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.95447
Heyl T (1970) Genealogical study of lipoid proteinosis in South Africa. Br J Dermatol 83:338–340. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1970.tb15712.x
Gordon H, Gordon W, Botha V (1969) Lipoid proteinosis in an inbred Namaqualand community. Lancet Lond Engl 1:1032–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91827-3
Van Hougenhouck-Tulleken W, Chan I, Hamada T et al (2004) Clinical and molecular characterization of lipoid proteinosis in Namaqualand, South Africa. Br J Dermatol 151:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06076.x
Iyandemye J, Thomas MP (2019) Low income countries have the highest percentages of open access publication: a systematic computational analysis of the biomedical literature. PLoS ONE 14:e0220229. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220229
Hamada T, Wessagowit V, South AP et al (2003) Extracellular matrix protein 1 gene (ECM1) mutations in lipoid proteinosis and genotype-phenotype correlation. J Invest Dermatol 120:345–350. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12073.x
Horev L, Wollina DU, Potikha T et al (2009) Lipoid proteinosis: identification of two novel mutations in the human ECM-1 gene and lack of genotype-phenotype correlation. Acta Derm Venereol 89:528–529. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-0673
Rey LK, Kohlhase J, Möllenhoff K et al (2016) A novel ECM1 splice site mutation in lipoid proteinosis: case report plus review of the literature. Mol Syndromol 7:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1159/000444615
Chen Z, Calawerts W, Zhang Y et al (2017) A case report: hybrid treatment approach to lipoid proteinosis of the larynx. J Voice Off J Voice Found. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2015.12.007
Epple A, Hoxha E, Schneiderbauer R et al (2018) Hyalinosis cutis et mucosae: a clinical investigation with special regard to mucosal changes. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges J Ger Soc Dermatol JDDG 16:211–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.13416
Dertlioğlu SB, Çalık M, Çiçek D (2014) Demographic, clinical, and radiologic signs and treatment responses of lipoid proteinosis patients: a 10-case series from Şanlıurfa. Int J Dermatol 53:516–523. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.12254
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patient V.D. who motivated the deep research in Lipoid Proteinosis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: Cocchi, Milanese, Longo; Acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data: Cocchi, Milanese, Longo; Drafting of the manuscript: Cocchi, Abdul-Messie, Milanese; Statistical analysis: Milanese, Vestri; Study supervision: Vestri, Longo; Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. No funding was received for conducting this study.
Ethics approval
No ethical approval or informed consent was required for the present study because all analysed data were already published in scientific journals.
Patient consent
The present study didn’t involve any patients in its phases (collection, analysis and interpretation of data).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cocchi, C., Milanese, A., Abdul-Messie, L. et al. Laryngeal features in Lipoid proteinosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08713-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-024-08713-x