Abstract
Purpose
Sialendoscopy is a new, minimally invasive method that is becoming increasingly more popular than traditional methods for the treatment of sialolithiasis. In this systematic review and meta-analysis, the effectiveness and safety of this method in children with sialolithiasis are investigated.
Methods
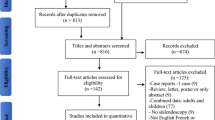
Inclusion criteria were children with sialolithiasis. The information sources were databases MEDLINE and PubMed Central (through PubMed), ScienceDirect, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), citation indexes Scopus and Google Scholar, trial registries, and “gray literature”. The last search was performed on September 18, 2022. The risk of bias in included studies was assessed using ROBINS-I tool (Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions). The pooled proportion of weighted means was calculated for the quantitative synthesis of available data.
Results
The effectiveness of the method was estimated at 95.5% (95% CI 89.8–99.3%), from 13 studies including 133 cases. The safety was estimated at 97.2% (95% CI 91.8–100%), from 10 studies including 113 cases.
Conclusion
The limitations of this study, briefly summarized, are the small number of included studies, the fact that they are mostly retrospective, the difficult application of the guidelines suggested by the PRISMA statement (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) and Cochrane handbook due to the nature of this specific condition and intervention, and the difficulty in assessing reporting bias. The results of the current study indicate that sialendoscopy is an effective and safe method for the treatment of sialolithiasis in children and should be implemented in daily clinical practice.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Konigsberger R, Feyh J, Goetz A, Schilling V, Kastenbauer E (1990) Endoscopic controlled laser lithotripsy in the treatment of sialolithiasis. Laryngorhinootologie 69:322–323. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-998200
Konigsberger R, Feyh J, Goetz A, Kastenbauer E (1993) Endoscopically-controlled electrohydraulic intracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (EISL) of salivary stones. J Otolaryngol 22:12–13
Katz P (1993) New treatment method for salivary lithiasis. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 114:379–382
Katz P (1991) Endoscopy of the salivary glands. Ann Radiol (Paris) 34:110–113
Katz P (1990) New method of examination of the salivary glands: the fiberscope. Inf Dent 72:785–786
Gundlach P, Scherer H, Hopf J, Leege N, Müller G, Hirst L et al (1990) Endoscopic-controlled laser lithotripsy of salivary calculi. In vitro studies and initial clinical use. HNO 38:247–250
Zenk J, Koch M, Bozzato A, Iro H (2004) Sialoscopy–initial experiences with a new endoscope. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2004.03.006
Marchal F, Becker M, Dulguerov P, Lehmann W (2000) Interventional sialendoscopy. Laryngoscope 110:318–320. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200002010-00026
Nahlieli O, Baruchin AM (1999) Endoscopic technique for the diagnosis and treatment of obstructive salivary gland diseases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:1394–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-2391(99)90716-4
Marchal F, Dulguerov P, Lehmann W (1999) Interventional sialendoscopy. N Engl J Med 341:1242–1243. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199910143411620
Nahlieli O, Baruchin AM (1997) Sialoendoscopy: three years’ experience as a diagnostic and treatment modality. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:912–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0278-2391(97)90056-2
Iro H, Zenk J, Benzel W (1995) Laser lithotripsy of salivary duct stones. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 49:148–152. https://doi.org/10.1159/000424360
Nahlieli O, Neder A, Baruchin AM (1994) Salivary gland endoscopy: a new technique for diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:1240–1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(94)90043-4
Arzoz E, Santiago A, Garatea J, Gorriaran M (1994) Removal of a stone in Stensen’s duct with endoscopic laser lithotripsy: report of case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 52:1329–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(94)90059-0
Marchal F, Chossegros C, Faure F, Delas B, Bizeau A, Mortensen B et al (2008) Salivary stones and stenosis. A comprehensive classification. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 109:233–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stomax.2008.07.004
Iro H, Zenk J, Koch M, Bozzato A (2008) Storz. The Erlangen salivary gland project, Part I, Sialendoscopy in obstructive diseases of the major salivary glands. Tuttlingen Endo-Press, Tuttlingen
Nahlieli O, Shacham R, Zagury A, Bar T, Yoffe B (2007) The ductal stretching technique: an endoscopic-assisted technique for removal of submandibular stones. Laryngoscope 117:1031–1035. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLG.0b013e31804f8163
Nahlieli O, Nakar LH, Nazarian Y, Turner MD (2006) Sialoendoscopy: a new approach to salivary gland obstructive pathology. J Am Dent Assoc 137:1394–1400. https://doi.org/10.14219/jada.archive.2006.0051
Katz P (2004) New techniques for the treatment of salivary lithiasis: sialoendoscopy and extracorporal lithotripsy: 1773 cases. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 121:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-438x(04)95499-0
Marchal F, Dulguerov P (2003) Sialolithiasis management: the state of the art. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:951–956. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.129.9.951
Nahlieli O, London D, Zagury A, Eliav E (2002) Combined approach to impacted parotid stones. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1418–1423. https://doi.org/10.1053/joms.2002.36097
Zenk J, Zikarsky B, Hosemann WG, Iro H (1998) The diameter of the Stenon and Wharton ducts. Significance for diagnosis and therapy. HNO 46:980–985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001060050345
Katz P (1998) A new therapeutic approach to salivary calculi: extracorporeal lithotripsy. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 99(Suppl 1):109–111
Nahlieli O, Eliav E, Hasson O, Zagury A, Baruchin AM (2000) Pediatric sialolithiasis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90:709–712. https://doi.org/10.1067/moe.2000.109075a
Iro H, Zenk J (2014) Salivary gland diseases in children. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:Doc06. https://doi.org/10.3205/cto000109
Francis CL, Larsen CG (2014) Pediatric sialadenitis. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 47:763–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2014.06.009
Bruch JM, Setlur J (2012) Pediatric sialendoscopy. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 73:149–152. https://doi.org/10.1159/000334474
Faure F, Froehlich P, Marchal F (2008) Paediatric sialendoscopy. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:60–63. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0b013e3282f45fe1
Konstantinidis I, Chatziavramidis A, Tsakiropoulou E, Malliari H, Constantinidis J (2011) Pediatric sialendoscopy under local anesthesia: limitations and potentials. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.11.009
Schwarz Y, Bezdjian A, Daniel SJ (2018) Sialendoscopy in treating pediatric salivary gland disorders: a systematic review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275:347–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4830-2
Chen T, Szwimer R, Daniel SJ (2022) The changing landscape of pediatric salivary gland stones: a half-century systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 159:111216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2022.111216
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n160. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n160
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). London: Cochrane Collaboration; 2021. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
McGowan J, Sampson M, Salzwedel DM, Cogo E, Foerster V, Lefebvre C (2016) PRESS peer review of electronic search strategies: 2015 guideline statement. J Clin Epidemiol 75:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.01.021
Hoffmann TC, Glasziou PP, Boutron I, Milne R, Perera R, Moher D et al (2014) Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ Br Med J 348:g1687. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g1687
Sterne JA, Hernan MA, Reeves BC, Savovic J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355:i4919. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT (2020) Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Synthesis Methods. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411
Lin YK, Geddes A, Lloyd TE, Jones SD (2021) Paediatric sialendoscopy under local anaesthesia: a case report. Adv Oral Maxillofacial Surg 3:100139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adoms.2021.100139
Miller JJ (1978) The inverse of the Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation. Am Stat 32:138. https://doi.org/10.2307/2682942
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P et al (2008) GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 336:924–926. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Schünemann HJ (2008) What is “quality of evidence” and why is it important to clinicians? BMJ 336:995–998. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39490.551019.BE
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Vist GE, Liberati A et al (2008) Going from evidence to recommendations. BMJ 336:1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39493.646875.AE
Kanerva M, Tapiovaara L, Aro K, Saarinen R (2020) Pediatric sialendoscopy: an 11-year study from a single tertiary care center. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 131:109869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.109869
Velasquez N, Gardiner L, Ramprasad V, Shaffer A, Jabbour N, Stapleton A (2022) Cost analysis of sialendoscopy for the treatment of salivary gland disorders in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 153:111020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.111020
Ziegler CM, Steveling H, Seubert M, Mühling J (2004) Endoscopy: a minimally invasive procedure for diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the salivary glands. Six years of practical experience. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0266-4356(03)00188-8
Martins-Carvalho C, Plouin-Gaudon I, Quenin S, Lesniak J, Froehlich P, Marchal F et al (2010) Pediatric sialendoscopy: a 5-year experience at a single institution. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2009.184
Iro H, Zenk J, Escudier MP, Nahlieli O, Capaccio P, Katz P et al (2009) Outcome of minimally invasive management of salivary calculi in 4,691 patients. Laryngoscope 119:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20008
Zenk J, Koch M, Klintworth N, Konig B, Konz K, Gillespie MB et al (2012) Sialendoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of sialolithiasis: a study on more than 1000 patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147:858–863. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812452837
Chung MK, Jeong HS, Ko MH, Cho HJ, Ryu NG, Cho DY et al (2007) Pediatric sialolithiasis: what is different from adult sialolithiasis? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:787–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2007.01.019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This is a systematic review using publicly available data from published studies and performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. The Scientific Council of the Papageorgiou Hospital of Thessaloniki has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Skalias, A., Garefis, K., Markou, K. et al. The effectiveness and safety of sialendoscopy for sialolithiasis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 3053–3063 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07877-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07877-2