Abstract
Background
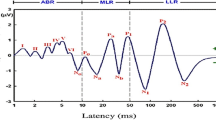
Speech-ABR is an auditory brainstem response that evaluates the integrity of the temporal and spectral coding of speech in the upper levels of the brainstem. It reflects the acoustic properties of the stimulus used and consists of seven major waves. Waves V and A represent the onset of the response; wave C transition region; D, E, and F waves periodic region (frequency following response); and wave O reflects the offset of the response.
Purpose
The aim of this study is to evaluate the clinical availability of the speech-ABR procedure through a literature review.
Methods
Literature search was conducted in Pubmed, Google Scholar, Scopus and Science Direct databases. Clinical studies of the last 15 years have been included in this review and 60 articles have been reviewed.
Results
As a result of the articles reviewed, it was seen that most of the studies on speech ABR were conducted with children and young people and generally focused on latency analysis measurements. Most used stimulus is the /da/ syllable.
Conclusions
Speech ABR can objectively measure the auditory cues important for speech recognition and has many clinical applications. It can be used as a biomarker for auditory processing disorders, learning disorders, dyslexia, otitis media, hearing loss, language disorders and phonological disorders. S-ABR is an effective procedure that can be used in speech and language evaluations in people with hearing aids or cochlear implant. It may also be of benefit to the aging auditory system's ability to encode temporal cues.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Johnson KL, ve Nicol TG, Kraus N (2005) Brain stem response to speech: a biological marker of auditory processing. Ear Hear 26(5):424–434
Banai K, Hornickel J, Skoe E, Nicol T, Zecker S, Kraus N (2009) Reading and subcortical auditory function. Cereb Cortex 19(11):2699–2707
Skoe E, Kraus N (2010) Auditory brainstem response to complex sounds: a tutorial. Ear Hear 31(3):302–324
Hornickel J, Skoe E, Kraus N (2009) Subcortical laterality of speech encoding. Audiol Neurotol 14(3):198–207
Sanfins MD, Hatzopoulos S, Donadon C, Diniz TA, Borges LR, Skarzynski PH, Francisca Colella-Santos M (2018) An analysis of the parameters used in speech ABR assessment protocols. J Int Adv Otol 14(1):100–105
Sanfins MD, Skarzynski PH, Colella-Santos M (2017) Speech-evoked brainstem response. In: Hatzopoulos S (ed) Advances in clinical audiology. InTech, London, pp 9–28
Chandrasekaran B, Kraus N (2010) The scalp-recorded brainstem response to speech: neural origins and plasticity. Psychophysiology 47(2):236–246
Banai K, Abrams D, Kraus N (2007) Sensory-based learning disability: insights from brainstem processing of speech sounds. Int J Audiol 46(9):524–532
Abrams D, Kraus N (2015) Auditory pathway representations of speech sounds in humans. In: Katz J, Chasin M, English K, Hood L, Tillery K (eds) Handbook of clinical audiology. Wolters Kluwer Health, Philadelphia, pp 527–544
Johnson KL, Nicol TG, Zecker SG, Kraus N (2007) Auditory brainstem correlates of perceptual timing deficits. J Cognit Neurosci 19(3):376–385
Johnson KL, Nicol T, Zecker SG, Krause N (2008) Developmental plasticity in the human auditory brainstem. J Neurosci 28(15):4000–4007
Rocha-Muniz CN, Befi-Lopes DM, Schochat E (2014) Sensitivity, specificity and efficiency of speech-evoked ABR. Hear Res 317:15–22
Sanfins MD, Borges LR, Ubiali T, Colella-Santos MF (2017) Speech-evoked auditory brainstem response in the differential diagnosis of scholastic difficulties. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 83(1):112–116
Rocha CN, Filippini R, Moreira RR, Neves IF, Schochat E (2010) Brainstem auditory evoked potential with speech stimulus. Pro-fono revista de atualizacao cientifica 22(4):479–484
Sinha SK, Basavaraj V (2010) Speech evoked auditory brainstem responses: a new tool to study brainstem encoding of speech sounds. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62(4):395–399
Lee J, Han W (2017) Auditory brainstem encoding of plosives in Korean normal hearing listeners. Audiol Speech Res 13(2):101–107
Karawani H, Banai K (2010) Speech-evoked brainstem responses in Arabic and Hebrew speakers. Int J Audiol 49(11):844–849
Song JH, Nicol T, Kraus N (2011) Test–retest reliability of the speech-evoked auditory brainstem response. Clin Neurophysiol 122(2):346–355
Sanfins MD, Borges LR, Ubiali T, Donadon C, Diniz Hein TA, Hatzopoulos S, Colella-Santos MF (2016) Speech-evoked brainstem response in normal adolescent and children speakers of Brazilian Portuguese. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol 90:12–19
Hornickel J, Knowles E, Kraus N (2012) Test-retest consistency of speech-evoked auditory brainstem responses in typically-developing children. Hear Res 284(1–2):52–58
Zakaria MN, Jalaei B (2017) Test-retest reliability of speech-evoked auditory brainstem response in healthy children at a low sensation level. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol 102:28–31
Dhar S, Abel R, Hornickel J, Nicol T, Skoe E, Zhao W, Kraus N (2009) Exploring the relationship between physiological measures of cochlear and brainstem function. Clin Neurophysiol 120(5):959–966
Rana B, Barman A (2011) Correlation between speech-evoked auditory brainstem responses and transient evoked otoacoustic emissions. J Laryngol Otol 125(9):911–916
Pinto E, Martinelli MC (2020) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials with speech stimulus in neonates. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 86(2):191–200
Sanfins MD, Hatzopoulos S, Hein TAD, Bordin T, Skarzynski PH, Colella-Santos MF (2019) Evaluation of the frequency following response in Italian children: a pilot study. J Hear Sci 9(2):45–50
Vander Werff KR, Burns KS (2011) Brain stem responses to speech in younger and older adults. Ear Hear 32(2):168–180
Lotfi Y, Moossavi A, Javanbakht M, Faghih Zadeh S (2019) Speech-ABR in contralateral noise: a potential tool to evaluate rostral part of the auditory efferent system. Med Hypotheses 132:109355
Moossavi A, Lotfi Y, Javanbakht M, Faghihzadeh S (2020) Speech-evoked auditory brainstem response; electrophysiological evidence of upper brainstem facilitative role on sound lateralization in noise. Neurol Sci 41(3):611–617
Filippini R, Schochat E (2009) Brainstem evoked auditory potentials with speech stimulus in the auditory processing disorder. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 75(3):449–455
Rocha-Muniz CN, Filippini R, Neves-Lobo IF, Rabelo CM, Morais AA, Murphy CF, Calarga KS, Leite LC, Pires MM, Sena-Yoshinaga TA, Schochat E (2016) Can speech-evoked Auditory Brainstem Response become a useful tool in clinical practice? CoDAS 28(1):77–80
Kumar P, Singh NK (2015) BioMARK as electrophysiological tool for assessing children at risk for (central) auditory processing disorders without reading deficits. Hear Res 324:54–58
Rocha-Muniz CN, Befi-Lopes DM, Schochat E (2012) Investigation of auditory processing disorder and language impairment using the speech-evoked auditory brainstem response. Hear Res 294(1–2):143–152
Filippini R, Befi-Lopes DM, Schochat E (2012) Efficacy of auditory training using the auditory brainstem response to complex sounds: auditory processing disorder and specific language impairment. Folia Phoniatr Logop 64(5):217–226
Gabr TA, Darwish ME (2016) Speech auditory brainstem response audiometry in children with specific language impairment. Hear Balance Commun 14(1):50–58
Gonçalves IC, Wertzner HF, Samelli AG, Matas CG (2011) Speech and non-speech processing in children with phonological disorders: an electrophysiological study. Clinics 66(2):293–298
El-Beltagy R, Galhom D, Hassan EHM (2019) Auditory brainstem response and speech mismatch negativity in children with phonological disorders. Egypt J Otolaryngol 35(1):79–85
Tahaei AA, Ashayeri H, Pourbakht A, Kamali M (2014) Speech evoked auditory brainstem response in stuttering. Scientifica 2014:1–7
Crivellaro Goncalves I, Furquim de Andrade CR, Gentile Matas C (2015) Auditory processing of speech and non-speech stimuli in children who stutter: electrophysiological evidences. Brain Disord Therapy 4(5):1–5
Wible B, Nicol T, Kraus N (2005) Correlation between brainstem and cortical auditory processes in normal and language-impaired children. Brain J Neurol 128(2):417–423
Ghannoum MT, Shalaby AA, Dabbous AO, Abd-El-Raouf ER, Abd-El-Hady HS (2014) Speech evoked auditory brainstem response in learning disabled children. Hear Balance Commun 12(3):126–142
Sachin MS, Kohli A, Panda N, Arya S (2019) Speech evoked auditory brainstem responses in children with learning disability. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 5(1):101–105
Malayeri S, Lotfi Y, Moossavi SA, Rostami R, Faghihzadeh S (2014) Brainstem response to speech and non-speech stimuli in children with learning problems. Hear Res 313:75–82
Song JH, Banai K, Russo NM, Kraus N (2006) On the relationship between speech- and nonspeech-evoked auditory brainstem responses. Audiol Neuro-otol 11(4):233–241
Billiet CR, Bellis TJ (2011) The relationship between brainstem temporal processing and performance on tests of central auditory function in children with reading disorders. J Speech Lang Hear Res 54(1):228–242
Kouni SN, Giannopoulos S, Ziavra N, Koutsojannis C (2013) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials with the use of acoustic clicks and complex verbal sounds in young adults with learning disabilities. Am J Otolaryngol 34(6):646–651
Kouni SN, Papadeas ES, Varakis IN, Kouvelas HD, Koutsojannis CM (2006) Auditory brainstem responses in dyslexia: comparison between acoustic click and verbal stimulus events. J Otolaryngol 35(5):305–309
Hornickel J, Kraus N (2013) Unstable representation of sound: a biological marker of dyslexia. J Neurosci 33(8):3500–3504
Ramezani M, Lotfi Y, Moossavi A, Bakhshi E (2019) Auditory brainstem response to speech in children with high functional autism spectrum disorder. Neurol Sci 40(1):121–125
Kamita MK, Silva L, Magliaro F, Kawai R, Fernandes F, Matas CG (2020) Brainstem auditory evoked potentials in children with autism spectrum disorder. J Pediatr (Rio J) 96(3):386–392
Russo N, Nicol T, Trommer B, Zecker S, Kraus N (2009) Brainstem transcription of speech is disrupted in children with autism spectrum disorders. Dev Sci 12(4):557–567
Chen J, Liang C, Wei Z, Cui Z, Kong X, Dong CJ et al (2019) Atypical longitudinal development of speech-evoked auditory brainstem response in preschool children with autism spectrum disorders. Autism Res 12(7):1022–1031
Azzam H, Hassan DM (2010) Speech-evoked auditory potentials in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Audiol Med 8(3):129–136
Jafari Z, Malayeri S, Rostami R (2015) Subcortical encoding of speech cues in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Clin Neurophysiol 126(2):325–332
Peixe BP, Silva D, Biaggio E, Bruno RS, Sanguebuche TR, Garcia MV (2018) Applicability of evoked auditory brainstem responses with complex stimuli in adults with hearing loss. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 22(3):239–244
Koravand A, Al Osman R, Rivest V, Poulin C (2017) Speech-evoked auditory brainstem responses in children with hearing loss. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol 99:24–29
Leite RA, Magliaro FC, Raimundo JC, Gândara M, Garbi S, Bento RF et al (2018) Effect of hearing aids use on speech stimulus decoding through speech-evoked ABR. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 84(1):66–73
Jalaeia B, Zakariab MN (2019) Speech-evoked auditory brainstem response in children with sensorineural hearing loss. Glob J Otolaryngol 20(4):71–80
Nada NM, Kolkaila EA, Gabr TA, El-Mahallawi TH (2016) Speech auditory brainstem response audiometry in adults with sensorineural hearing loss. Egypt J Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci 17(2):87–94
Abd El-Ghaffar NM, El-Gharib AM, Kolkaila EA, Elmahallawy TH (2018) Speech-evoked auditory brainstem response with ipsilateral noise in adults with unilateral hearing loss. Acta oto-laryngol 138(2):145–152
Anderson S, Parbery-Clark A, White-Schwoch T, Drehobl S, Kraus N (2013) Effects of hearing loss on the subcortical representation of speech cues. J Acoust Soc Am 133(5):3030–3038
Sanfins MD, Borges LR, Donadon C, Hatzopoulos S, Skarzynski PH, Colella-Santos MF (2017) Electrophysiological responses to speech stimuli in children with otitis media. J Hear Sci 7(4):9–19
El-Kabarity RH, Abdel Rahman TT, Abdel Kader HA, Sanyelbhaa H (2015) Effect of otitis media with effusion on brainstem timing in children. Hear Balance Commun 14(1):20–24
BinKhamis G, Forte AE, Reichenbach T, O’Driscoll M, Kluk K (2019) Speech auditory brainstem responses in adult hearing aid users: effects of aiding and background noise, and prediction of behavioral measures. Trends Hear 23:1–20
Shetty HN, Puttabasappa M (2017) Encoding of speech sounds at auditory brainstem level in good and poor hearing aid performers. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 83(5):512–522
Hassaan MR, Ibraheem OA, Galhom DH (2016) Brainstem encoding of aided speech in hearing aid users with cochlear dead region(s). Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 20(3):226–234
Bellier L, Veuillet E, Vesson JF, Bouchet P, Caclin A, Thai-Van H (2015) Speech Auditory Brainstem Response through hearing aid stimulation. Hear Res 325:49–54
Gabr TA, Hassaan MR (2015) Speech processing in children with cochlear implant. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol 79(12):2028–2034
Rahman TTA, Nada IM, Kader HAAA, Monem AAA (2017) Neural representation of speech in pediatric cochlear implant recipients. Egypt J Otolaryngol 33:535–545
Jarollahi F, Valadbeigi A, Jalaei B, Maarefvand M, Zarandy MM, Haghani H et al (2020) Sound-field speech evoked auditory brainstem response in cochlear-implant recipients. J Audiol Otol 24(2):71–78
Nassar AAM, Hassan DM, Younis A, Abdel Rahman TT (2020) Speech evoked potentials in cochlear implant recipients with auditory neuropathy spectrum disorder. Hear Balance Commun 1–11
BinKhamis G, Perugia E, O’Driscoll M, Kluk K (2019) Speech-ABRs in cochlear implant recipients: feasibility study. Int J Audiol 58(10):678–684
Omidvar S, Mahmoudian S, Khabazkhoob M, Ahadi M, Jafari Z (2018) Tinnitus impacts on speech and non-speech stimuli. Otol Neurotol 39(10):921–928
Kelly A, Purdy S (2016) Change in speech perception and auditory evoked potentials over time after unilateral cochlear implantation in postlingually deaf adults. Semin Hear 37(1):62–73
Kolkaila EA, Emara AA, Gabr TA (2012) Cortical auditory evoked potentials in children using hearing aids. Audiol Med 10(3):132–142
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
There are no financial resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. MBB; acquisition and analysis of data, drafting and reviewing of the manuscript. NG; acquisition and analysis of data. EK; drafting and reviewing of the manuscript. NB; conception and design of the study. OGT; conception and design of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Basoz Behmen, M., Guler, N., Kuru, E. et al. Speech auditory brainstem response in audiological practice: a systematic review. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 280, 2099–2118 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07830-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-07830-3