Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the status of paranasal sinus and to identify risk factors associated with the development of chronic sinusitis based on imaging studies in head and neck cancer patients.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 186 patients who were diagnosed with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma at Korea University Guro Hospital from February 2003 to July 2015. Only patients with at least 1 year of follow-up after treatment were included.
Results
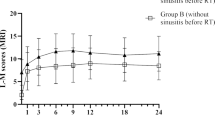
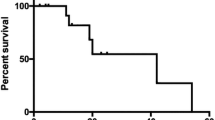
Chronic sinusitis occurred in 32 patients (17.2%), including seven patients (16.3%) in non-radiotherapy group and 25 patients (17.5%) in radiotherapy group. Maxillary sinus was most commonly involved (56.9%), followed by ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid sinuses. Age (1.006; 0.874–1.158; p = 0.936), TNM stage (0.104; 0.007–1.598; p = 0.105), and underlying disease (0.242; 0.036–1.646; p = 0.147) were not significantly associated with the need for surgery due to sinusitis. Although radiotherapy itself (1.319; 0.019–2.821; p = 0.251) was not significantly associated with surgery due to sinusitis, concurrent chemotherapy (10.729; 1.361–84.611; p = 0.024) was significantly associated with surgical procedures.
Conclusion
Higher T stage and concurrent chemotherapy with radiotherapy showed significant association with chronic sinusitis. Concurrent chemotherapy also showed significant association with surgical treatment in head and neck cancer patients. Therefore, more careful surveillance and aggressive treatment of chronic sinusitis is needed in head and neck cancer patients who receive radiotherapy with concurrent chemotherapy or higher T stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE et al (1991) Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:109–122
Kamel R, Al-Badawy S, Khairy A, Kandil T, Sabry A (2004) Nasal and paranasal sinus changes after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Otolaryngol 124:532–535
Lou PJ, Chen WP, Tai CC (1999) Delayed irradiation effects on nasal epithelium in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. An ultrastructural study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:474–480
Zubizarreta PA, D’Antonio G, Raslawski E, Gallo G, Preciado MV, Casak SJ et al (2000) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in childhood and adolescence: a single-institution experience with combined therapy. Cancer 89:690–695
Huang CC, Huang SF, Lee TJ, Ng SH, Chang JT (2007) Postirradiation sinus mucosa disease in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Laryngoscope 117:737–742
Yuan TZ, Guo X, Zheng L, Cao SM, Li NW, Xiang YQ (2008) Occurrence and influencing factors of paranasal sinusitis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after radiotherapy. Ai Zheng 27:866–869
Teo PM, Ma BB, Chan AT (2004) Radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma—transition from two-dimensional to three-dimensional methods. Radiother Oncol 73:163–172
Wu VW, Kwong DL, Sham JS (2004) Target dose conformity in 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 71:201–206
Nutting CM, Morden JP, Harrington KJ, Urbano TG, Bhide SA, Clark C et al (2011) Parotid-sparing intensity modulated versus conventional radiotherapy in head and neck cancer (PARSPORT): a phase 3 multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12:127–136
Fujiwara K, Håkansson CH, Toremalm NG (1972) Influence of ionizing radiation on ciliary cell activity in the respiratory tract. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol 11:513–520
Hu KH, Tan CT, Lin KN, Cheng YJ, Huang HM (2008) Effect of endoscopic sinus surgery on irradiation-induced rhinosinusitis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139:575–579
Si Y, Wei H, Huang B (2005) Histomorphological changes of ethmoid sinus mucosa in sinusitis patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy. Chin Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 12:729–732
Kuhar HN, Tajudeen BA, Heilingoetter A, Mahdavinia M, Gattuso P, Ghai R et al (2017) Distinct histopathologic features of radiation-induced chronic sinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 7:990–998
Beachler DC, Engels EA (2017) Chronic sinusitis and risk of head and neck cancer in the US elderly population. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143:25–31
Hung SH, Chen PY, Lin HC, Ting J, Chung SD (2014) Association of rhinosinusitis with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a population-based study. Laryngoscope 124:1515–1520
Tsou YA, Lin CC, Tai CJ, Tsai MH, Tsai TC, Chen CM (2014) Chronic rhinosinusitis and the risk of nasopharyngeal cancer in a Taiwanese health study. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:168–172
Lang Kuhs KA, Gonzalez P, Struijk L, Castro F, Hildesheim A, van Doorn LJ et al (2013) Prevalence of and risk factors for oral human papillomavirus among young women in Costa Rica. J Infect Dis 208:1643–1652
Su YX, Liu LP, Li L, Li X, Cao XJ, Dong W et al (2014) Factors influencing the incidence of sinusitis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients after intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:3195–3201
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y.M., Cho, JG. & Woo, JS. Chronic sinusitis in head and neck cancer patients who received radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275, 2805–2811 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5114-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-5114-1