Abstract
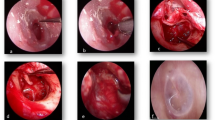
Tympanoplasty was conventionally performed using a microscope for decades. However, since the endoscope began to be used in middle ear surgery in the 1970s, endoscopic tympanoplasty has gained increasing attention. The main objective of this study was to compare endoscopic and microscopic tympanoplasty with and without ossiculoplasty, demonstrating the potential advantages, disadvantages, and outcomes of each. This retrospective study included 126 patients with chronic otitis media who received tympanoplasty from 2013 to 2015 in our hospital. The clinical follow-up continued for at least 3 months postoperatively. Otoscopy and audiometry were conducted before and after the procedure. The different variables affecting surgical outcomes were thoroughly documented in each case. A total of 126 patients (131 ears) were included in this retrospective study. Moreover, 74 and 57 ears underwent endoscopic and microscopic tympanoplasty, respectively. The overall endoscopic tympanoplasty graft uptake rate was 97.7% (128/131). The operation time was significantly shorter in the endoscopic group statistically. A paired t test was used to compare pre- and postoperative audiometry results and showed significant differences between the endoscopic and microscopic groups. However, no statistically significant difference was observed in audiometry improvement between the two groups. No major complications were observed in any of the patients. Our study demonstrated that endoscopic tympanoplasty can be feasibly applied in middle ear surgery. The success rate, audiometry improvement, and complication rate are comparable between endoscopic tympanoplasty and conventional microscopic tympanoplasty. Moreover, the endoscopic group had smaller operation wounds and lower medical expenditures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozin ED, Gulati S, Kaplan AB et al (2015) Systematic review of outcomes following observational and operative endoscopic middle ear surgery. Laryngoscope 125:1205–1214
Bedajit RK, Mallik P, Kumar P et al (2015) Endoscopic transcanal mastoidectomy with tympanoplasty. Natl J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 3(12):10–11
Bonali M, Anschuetz L, Fermi M, Villari D, Mariani GA, Manzoli L, Caversaccio M, Presutti L (2017) The variants of the retro- and hypotympanum: an endoscopic anatomical study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(5):2141–2148. doi:10.1007/s00405-017-4492-0
Sudhir Babu V, Sreenivasulu M (2015) Endoscopic middle ear surgery case study. Indian J Appl Res 5(3):71–73
Farahani F, Shariatpanahi E, Jahanshahi J, Poorolajal J (2015) Diagnostic performance of endoscopic and microscopic procedures for identifying different middle ear structures and remaining disease in patients with chronic otitis media: a prospective cohort study. PLOS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132890
Tarabichi M, Ayache S, Nogueira JF, Al Qahtani M (2013) Endoscopic management of chronic otitis media and tympanoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 46:155–163
Bennett Marc L, Zhang Dongqing, Labadie Robert F, Noble Jack H (2016) Comparison of middle ear visualization with endoscopy and microscopy. Otol Neurotol 37:362–366
Kanona H, Virk JS, Owa A (2015) Endoscopic ear surgery: a case series and first United Kingdom experience. World J Clin Cases 3(3):310–317
Martellucci S, Pagliuca G, de Vincentiis M (2015) Myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion with endoscopic or microscopic technique in adults: a pilot study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(5):927–930
Cohen MS, Landegger LD, Kozin ED, Lee DJ (2016) Pediatric endoscopic ear surgery in clinical practice: lessons learned and early outcomes. Laryngoscope 126:732–738
Poe DS (2003) Chapter 21: Endoscopic middle ear and mastoid surgery. In: Haberman RS II (ed) Middle ear and mastoid surgery. Thieme Medical Publishers Inc., New York, pp 168–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Che-hung Kuo declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hsing-mei Wu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, Ch., Wu, Hm. Comparison of endoscopic and microscopic tympanoplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 2727–2732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4570-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4570-3