Abstract
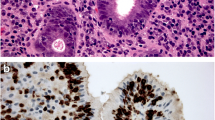
Even after appropriate surgical therapy, a significant number of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) experience recurrences. The end-point of this prospective study was to apply univariate and multivariate statistical models to identify clinical, pathological, and laboratory variables that could predict CRSwNP recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery. The study enrolled 143 patients between 2010 and 2013, who were all treated by the same surgeon for CRSwNP. Twenty-one patients developed recurrent polyposis. The recurrence rate was significantly higher for the eosinophilic than for the non-eosinophilic type (p = 0.020). Among the patients who developed a recurrence, the disease-free interval was significantly shorter for those with eosinophilic-type polyposis (p = 0.003). Univariate statistical analysis disclosed significant associations between CRSwNP recurrence and age (p = 0.035), allergy (p = 0.014), and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (p = 0.01). The multivariate model showed that only histological evidence of the eosinophilic type of CRSwNP retained an independent prognostic significance in relation to recurrent polyposis (p = 0.033). Judging from our results, it is reasonable to consider both stricter follow-up protocols and postoperative adjuvant medical treatments for patients with a histological diagnosis of eosinophilic-type CRSwNP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babeto E, De Freitas Calmon M, Scarin Provazzi PJ et al (2010) Gene expression analysis reveals novel altered genes in nasal polyps. Mol Med Rep 3:485–490
Orlandi RR, Smith TL, Marple BF et al (2014) Update on evidence-based reviews with recommendations in adult chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 4(Suppl 1):S1–S15
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J et al (2012) European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. Rhinol Suppl (23):3 (preceding table of contents, 1–298)
Hopkins C, Browne JP, Slack R et al (2006) The national comparative audit of surgery for nasal polyposis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin Otolarygol 31:390–398
Gelardi M, Fiorella R, Fiorella ML et al (2009) Nasal sinus polyposis: clinical cytological grading and prognostic index of relapse. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 23:181–188
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA et al (2006) Rhinosinusitis: developing guidance for clinical trials. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118(5 Suppl):S17–S61
Stjärne P, Olsson P, Alenius M (2009) Use of mometasone furoate to prevent polyp relapse after endoscopic sinus surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:296–302
Van Zele T, Gevaert P, Holtappels G et al (2010) Oral steroids and doxycycline: two different approaches to treat nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125:1069–1076
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA et al (2013) 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11
Tezer I, Celebi Erdivanli O, Sanli A, Aydin S (2013) Could cellular proliferation be a predictive index for the relapse of nasal polyposis and down-regulated by nasal steroid treatment? Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65(Suppl 2):329–332
Katz MH (2003) Multivariable analysis: a primer for readers of medical research. Ann Intern Med 138:644–650
Katz MH (1999) Introduction. In: Katz MH (ed) Multivariate analysis: a practical guide for clinicians. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–16
Albu S, Tomescu E, Mexca Z et al (2004) Recurrence rates in endonasal surgery for polyposis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg 58:79–86
Ottaviano G, Cappellesso R, Mylonakis I et al (2015) Endoglin (CD105) expression in sinonasal polyposis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. doi:10.1007/s00405-014-3456-x
Kaldenbach T, Schäfer D, Gosepath J et al (1999) Significance of eosinophilic granulocytes in relation to allergy and aspirin intolerance in patients with sinusitis polyposa. Laryngorhinootologie 78:429–434
Tosun F, Arslan HH, Karslioglu Y et al (2010) Relationship between postoperative recurrence rate and eosinophil density of nasal polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 119:455–459
Nakayama T, Yoshikawa M, Asaka D et al (2011) Mucosal eosinophilia and recurrence of nasal polyps—new classification of chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 49:392–396
Vlaminck S, Vauterin T, Hellings PW et al (2014) The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: a 3-year prospective observational study. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:260–264
Mendelsohn D, Jeremic G, Wright ED, Rotenberg BW (2011) Revision rates after endoscopic sinus surgery: a recurrence analysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 120:162–166
Van Zele T, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, Bachert C (2014) Differences in initial immunoprofiles between recurrent and nonrecurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28:192–198
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Frances Coburn for correcting the English version of this paper. This study was partly supported by Grant No. 60A07-8983/13 (A. Martini) from the University of Padova, Italy.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brescia, G., Marioni, G., Franchella, S. et al. A prospective investigation of predictive parameters for post-surgical recurrences in sinonasal polyposis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273, 655–660 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3598-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3598-5