Abstract
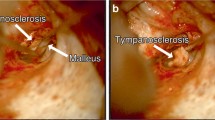
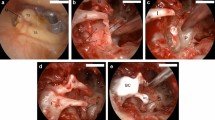
The aim of the present study was to describe our surgical approach for isolated malleus fixation in patients with tympanosclerosis and to analyze the postoperative results. A total of 30 patients presented with isolated malleus fixation were operated. The fixation was reached via canalplasty. Fixated areas were cleaned without damaging the ossicle. Pre- and postoperative audiometric results were evaluated for each patient. Improvement of the pure-tone average (PTA) by at least 10 dB and an air-bone gap (ABG) of less than 20 dB after 12 months of follow-up was accepted to indicate success. The recovery of the postoperative PTA and ABG measurements was significant. Pre- and postoperative PTA was 48.00 ± 11.86 and 24.90 ± 12.45 dB, respectively (p < 0.001). According to PTA measurements, 40–50 dB recovery was achieved in four (13.3 %) patients, 31–40 dB in six (20 %) patients, 21–30 dB in ten (33.3 %) patients, and 11–20 dB in five (16.6 %) patients, with a total success rate of 25/30 (83.2 %). Pre- and postoperative ABG levels were 38.95 ± 9.92 and 16.10 ± 7.79 dB (p < 0.001), respectively. The ABG level was between 0 and 10 dB for 8 (26.6 %) patients, and 11–20 dB for 16 (53.3 %), with a total success rate of 24/30 (80 %). In cases of isolated malleus fixation with tympanosclerosis, performing a canalplasty to clean the sclerotic plaques without damaging the normal anatomy of the ossicle system using a diamond burr is a safe surgical option that provides significant recovery in hearing levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erdurak SC, Coskun BU, Sakalli E, Tansuker HD, Turan F, Kaya D (2014) Does the use of radiofrequency myringotomy for insertion of a ventilation tube reduce the incidence of myringosclerosis? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(3):459–462
Tos M, Lau T, Arndal H et al (1990) Tympanosclerosis of the middle ear: late results of surgical treatment. J Laryngol Otol 104:685–689
Teufert KB, De La Cruz A (2002) Tympanosclerosis: long-term hearing results after ossicular reconstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:264–272
Seidman FACS, Babu S (2004) A new approach for malleus/incus fixation: no prosthesis necessary. Otol Neurotol 25:669–673
Martin C, Oletski A, Prades JM (2009) Surgery of idiopathic malleus fixation. Otol Neurotol 30:165–169
American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head Neck Surgery Foundation Inc. (1995) Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of results of treatment of conductive hearing loss. Otolarnygol Head Neck Surg 113:186–187
Mehta RP, Harris JP, Nadol JB (2002) Malleus fixation: clinical and histopathologic findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111:246–254
Schuknecht HF (1993) Pathology of the Ear, 2nd edn. Lea & Febiger, Malvern
Martin C, Timoshenko AP, Dumollard JM, Tringali S, Peoc h M, Prades JM (2006) Malleus head fixation: histopathology revisited. Acta Otolaryngol 126:353–357
Katzke D, Plester D (1981) Idiopathic malleus head fixation as a cause of combined conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Clin Otolaryngol 6:39–44
Tos M (2000) Surgical solutions for conductive hearing loss. Thieme, Stuttgart
Bayazit YA, Ozer E, Kara C, Gokpinar S, Kanlikama M, Mumbuc S (2004) An analysis of the single-stage tympanoplasty with over-underlay grafting in tympanosclerosis. Otol Neurotol 25:211–214
Kamal SA (1997) Surgery of tympanosclerosis. J Laryngol Otol 111:917–923
Yetiser S, Hidir Y, Karatas E, Karapinar U (2007) Management of tympanosclerosis with ossicular fixation: review and presentation of long term results of 30 new cases. J Otolaryngol 36:303–308
Armstrong BW (1976) Epitympanic malleus fixation: correction without disrupting the ossicular chain. Laryngoscope 86:1203–1208
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakalli, E., Celikyurt, C., Guler, B. et al. Surgery of isolated malleus fixation due to tympanosclerosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3663–3667 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3445-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3445-0