Abstract
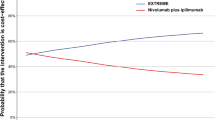
Clinical trial EMR 62202-006 demonstrates prolonged median locoregional control (24.4 vs. 14.9 months), progression-free survival (17.1 vs. 12.4 months) and overall survival (49.0 vs. 29.3 months) for patients who receive cetuximab added to the comparator radiotherapy for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (LA SCCHN). In the Netherlands, hospitals receive reimbursement for cetuximab conditional on cost-effectiveness in daily practice. To estimate the real-world incremental cost per quality adjusted life-year (QALY) gained for radiotherapy + cetuximab over radiotherapy alone in first line treatment of LA SCCHN, a Markov model is constructed with health states “alive without progression”, “alive following progression” and “death”. Transition probabilities per month are estimated from clinical trial data and retrospectively collected real-world data from two Dutch head and neck cancer treatment centres (2007–2010, n = 141). 5-year, 10-year and lifetime horizons are used, without and with discounting (4 % costs, 1.5 % effects) to calculate incremental cost-effectiveness ratios. Two scenarios explore different assumptions on prognosis of real-world versus trial patients. Adding cetuximab to radiotherapy results in increased costs and health gains in both scenarios and across each of the time horizons. Incremental costs per QALY gained range between €14,624 and €38,543 in the base-case. For a willingness to pay of €80,000 per QALY, the acceptability curves for the different scenarios show probabilities between 0.76 and 0.87 of radiotherapy + cetuximab being cost-effective compared to radiotherapy alone. Current results show the combined treatment of radiotherapy + cetuximab to be a cost-effective treatment option for patients with LA SCCHN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell JS, Colevas AD (2012) The use of epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Chemother Res Pract 2012:761518
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur RK et al (2010) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol 11(1):21–28
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB et al (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354(6):567–578
van der Linden N, van Gils CW, Pescott CP, Buter J, Uyl-de Groot CA (2013) Cetuximab in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: generalizability of EMR 062202-006 trial results. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
College voor zorgverzekeringen (2006) Guidelines for pharmacoeconomic research, updated version. Available at:http://www.cvz.nl/binaries/content/documents/zinl-www/documenten/publicaties/publications-in-english/2006/0604-guidelines-for-pharmacoeconomic-research/0604-guidelines-for-pharmacoeconomic-research/Guidelines+for+pharmacoeconomic+research.pdf (accessed Jan 2014)
van der Schroeff MP, van de Schans SA, Piccirillo JF, Langeveld TP, Baatenburg de Jong RJ, Janssen-Heijnen ML (2010) Conditional relative survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: permanent excess mortality risk for long-term survivors. Head Neck 32(12):1613–1618
M-TAG Limited (2005) Head and neck cancer treatment: utility valuation study. Unpublished document prepared for Merck by M-TAG Limited, a Unit of IMS (UK company no. 3959556)
Tan SS, Van Gils CW, Franken MG, Hakkaart-van Roijen L, Uyl-de Groot CA (2010) The unit costs of inpatient hospital days, outpatient visits, and daycare treatments in the fields of oncology and hematology. Value Health 13(6):712–719
Tan SS, Hakkaart-van Roijen L, Al MJ, Bouwmans CA, Hoogendoorn ME, Spronk PE et al (2008) A microcosting study of intensive care unit stay in the Netherlands. J Intensive Care Med 23(4):250–257
Hakkaart-van Roijen L, Tan SS, Bouwmans CAM (2010) Handleiding voor kostenonderzoek. Available at: http://www.cvz.nl/binaries/content/documents/zinl-www/documenten/publicaties/overige-publicaties/1007-handleiding-voor-kostenonderzoek/Handleiding+voor+kostenonderzoek.pdf (accessed Jan 2014)
Nederlandse Werkgroep Hoofd-Hals Tumoren (2010) Landelijke richtlijn hypofarynxcarcinoom, versie 2.0. Available at: http://www.oncoline.nl/hypofarynxcarcinoom (accessed Jan 2014)
Nederlandse Werkgroep Hoofd-Hals Tumoren (2010) Landelijke richtlijn larynxcarcinoom, versie 3.0. Available at: http://www.oncoline.nl/larynxcarcinoom (accessed Jan 2014)
Nederlandse Werkgroep Hoofd-Hals Tumoren (2004) Landelijke richtlijn mondholte- en orofarynxcarcinoom, versie 1.4. Available at:http://www.oncoline.nl/mondholte-en-orofarynxcarcinoom (accessed Jan 2014)
RVZ (2006) Zinnige en duurzame zorg. Available at: http://www.rvz.net/uploads/docs/Advies_Zinnige_en_duurzame_zorg.pdf (accessed Jan 2014)
Griffin S, Walker S, Sculpher M, White S, Erhorn S, Brent S et al (2009) Cetuximab plus radiotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Health Technol Assess 13(Suppl 1):49–54
Chan ALF, Leung HWC, Huang S (2011) Cost effectiveness of cetuximab concurrent with radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer in Taiwan a decision-tree analysis. Clin Drug Investig 31(10):717–726
Brown B, Diamantopoulos A, Bernier J, Schoeffski P, Hieke K, Mantovani L et al (2008) An economic evaluation of cetuximab combined with radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer in Belgium, France, Italy, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. Value Health 11(5):791–799
Sambrook J, Levy AR, Johnston KM, Ricard NJ, Bourgault C, Donato BM, et al (2009) Cost-effectiveness of cetuximab for the first-line treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) in Canada. J Clin Oncol 27(15S (May 20 Supplement)):e17000
(2010) Nederlandse Werkgroep Hoofd-Halstumoren. Hoofd-Hals Journaal 43. Available at: http://www.nwhht.nl/files/user/nr_43.pdf (accessed Jan 2014)
van Gils CW, de Groot S, Redekop WK, Koopman M, Punt CJ, Uyl-de Groot CA (2013) Real-world cost-effectiveness of oxaliplatin in stage iii colon cancer: a synthesis of clinical trial and daily practice evidence. Pharmacoeconomics 31(8):703–718
Franken MG, van Gils CW, Gaultney JG, Delwel GO, Goettsch W, Huijgens PC et al (2013) Practical feasibility of outcomes research in oncology: Lessons learned in assessing drug use and cost-effectiveness in The Netherlands. Eur J Cancer 49(1):8–16
Uyl-de Groot CA, de Groot S, Steenhoek A (2010) The economics of improved cancer survival rates: better outcomes, higher costs. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res 10(3):283–292
Acknowledgments
This study was performed by the Institute for Medical Technology Assessment (iMTA, Erasmus University) and was financially supported by Merck BV, the Marketing Authorisation Holder of Erbitux (cetuximab). NvdL, CvG and CP were responsible for study design. NvdL collected real-world data. NvdL and CvG developed the model and conducted analyses. NvdL and CP developed the manuscript, supervised by CvG and CU-dG. JB provided medical expertise. MV provided expertise on the quality of life aspect of the study. CvG is currently employed by GlaxoSmithKline, who have no involvement in this research. This research was conducted while CvG was employed by iMTA, Erasmus University. CP is employed by Merck BV. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors. All authors read, edited and approved the final manuscript. CU-dG and NvdL are the overall guarantors for the content.
Ethical standards
The study was approved by the medical ethics committee of VU Medical Center. For the patient chart review, no informed consent was required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Linden, N., van Gils, C.W.M., Pescott, C.P. et al. Real-world cost-effectiveness of cetuximab in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 2007–2016 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3106-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3106-3