Abstract
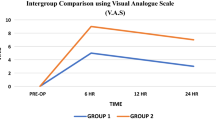
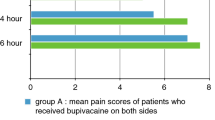
The objective of this study is to compare the topical administration of bupivacaine hydrochloride, saline and bupivacaine hydrochloride infiltration on post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Sixty children undergoing tonsillectomy were enrolled in the study. Patients were randomized into three groups using sealed envelopes. Group 1 (n = 20) received topical 0.5 % bupivacaine hydrochloride, group 2 (n = 20) received topical 0.9 % NaCl (saline), and group 3 (n = 20) received 0.5 % bupivacaine hydrochloride infiltrated around each tonsil. Pain was evaluated using McGrath’s face scale. Pain scores in topical bupivacaine hydrochloride group was significantly lesser than the topical saline group at 5th, 13th, 17th and 21st hours, until the 6th day (p < 0.017). Moreover, pain scores of topical bupivacaine hydrochloride group was superior to bupivacaine hydrochloride infiltration group at 5th, 13th, 17th hours and 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th day (p < 0.017). There were significantly lesser morbidities in topical bupivacaine hydrochloride than saline group in 1st and 4th day (p < 0.017). Topical administration of bupivacaine hydrochloride proved to provide more efficient pain control than bupivacaine hydrochloride infiltration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park AH, Pappas AL, Fluder E, Creech S, Lugo AR, Hotaling A (2004) Effect of perioperative administration of ropivacaine with epinephrine on postoperative pediatric adenotonsillectomy recovery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:459–464
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I (1990) The effect of pre-incisional infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. Pain 47:305–308
Hung T, Moore-Gillon V, Hern J, Hinton A, Patel N (2002) Topical bupivacaine in paediatric day-case tonsillectomy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Laryngol Otol 116:33–36
Yilmaz S, Demiraran Y, Akkan N, Yaman H, Iskender A, Güçlü E et al (2009) The effects of topical levobupivacaine on morbidity in pediatric tonsillectomy patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1208–1210
Oghan F, Harputluoglu U, Guclu E, Kocaman B, Ozturk O (2008) Does topical ropivacaine reduce the post-tonsillectomy morbidity in pediatric patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72:361–365
Karaaslan K, Yilmaz F, Gulcu N, Sarpkaya A, Colak C, Kocoglu H (2008) The effects of levobupivacaine versus levobupivacaine plus magnesium infiltration on postoperative analgesia and laryngospasm in pediatric tonsillectomy patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72:675–681
McGrath PA, deVeber LL, Hearn MT (1985) Multidimensional pain assessment in children. In: Fields HL, Dubner R, Cervero F (eds) Advances in pain research and therapy, vol 9. Raven Press, New York, pp 387–393
Molliex S, Haond P, Baylot D (1996) Effect of pre- vs. postoperative tonsillar infiltration with local anesthetics on postoperative pain after tonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 40:1210–1211
Sun J, Wub X, Meng Y, Jin L (2010) Bupivacaine versus normal saline for relief of post-adenotonsillectomy pain in children: a meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 74:369–373
Kountakis SE (2002) Effectiveness of perioperative bupivacaine infiltration in tonsillectomy patients. Am J Otolaryngol 23:76–80
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF, Bradley EL Jr, Kissin I (1993) Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy pain reduction by local bupivacaine infiltration in children. Int J Pediatr Otolaryngol 25:149–154
Schoem SR, Watkins GL, Kuhn JJ, Thompson DH (1993) Control of early post-operative pain with bupivacaine in pediatric tonsillectomy. Ear Nose Throat J 72:560–563
Broadman LM, Patel RI, Feldman BA, Sellman GL, Milmoe G, Camilon F (1989) The effects of peritonsillar infiltration on the reduction of intraoperative blood loss and post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Laryngoscope 99:578–581
Orntoft S, Longreen A, Moiniche S, Dhal JB (1994) A comparison of pre- and post-operative tonsillar infiltration with bupivacaine on pain after tonsillectomy: a preemptive effect? Anaesthesia 49:151–154
Arikan OK, Ozcan S, Kazkayasi M, Akpinar S, Koc C (2006) Preincisional infiltration of tonsils with ropivacaine in post-tonsillectomy pain relief: double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled intraindividual study. J Otolaryngol 35:167–172
Giannoni C, White S, Enneking FK, Morey T (2001) Ropivacaine with or without clonidine improves pediatric tonsillectomy pain. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:1265–1270
Unal Y, Pampal K, Korkmaz S, Arslan M, Zengin A, Kurtipek O (2007) Comparison of bupivacaine and ropivacaine on post-operative pain after tonsillectomy in paediatric patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:83–87
Marwick PC, Levin AI, Coetzee AR (2009) Recurrence of cardiotoxicity after lipid rescue from bupivacaine-induced cardiac arrest. Anesth Analg 108:1344–1346
Gunter JB (2002) Benefit and risks of local anesthetics in infants and children. Paediatr Drugs 4:649–672
Bean-Lijewski JD (1998) Glossopharyngeal nerve block for pain relief after pediatric tonsillectomy: retrospective analysis and two cases of life-threatening upper airway obstruction from an interrupted trial. Anesth Analg 86:678
Shlizerman L, Ashkenazi D (2005) Peripheral facial nerve paralysis after peritonsillar infiltration of bupivacaine: a case report. Am J Otolaryngol 26:406–407
Weksler N, Nash M, Rozentsveig V, Schwartz JA, Schily M, Gurman GM (2001) Vocal cord paralysis as a consequence of peritonsillar infiltration with bupivacaine. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 45:1042–1044
Alsarraf R, Sie KC (2000) Brain stem stroke associated with bupivacaine injection for adenotonsillectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 122:572–573
Kadar AA, Obaid MA (2003) Effect on post-operative pain after local application of bupivacaine in the tonsillar fossa; a prospective single blind controlled trial. J Pak Med Assoc 53:422–426
Violaris NS, Tuffin JR (1989) Can post-tonsillectomy pain be reduced by topical bupivacaine? Double blind controlled trial. J Laryngol Otol 103:592–593
Ozmen AO, Ozmen S (2011) Topical bupivacaine compared to lidocaine with epinephrine for post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: a randomized controlled study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75(1):77–80
Beyer JE, McGrath PJ, Berde CB (1990) Discordance between self report and behavioral pain measures in 3–7 year old children following surgery. J Pain Symptom Manage 5:350–356
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haksever, M., Özmen, S., Akduman, D. et al. Topical bupivacaine compared to bupivacaine infiltration for post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: a prospective randomized controlled clinical study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 2555–2559 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3022-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3022-6