Abstract
Background
There is a lack of sufficient evidence regarding efficacy and safety of amlodipine on treating hypertension during pregnancy.
Objective
To compare antihypertensive efficacy, pregnancy outcome and safety of amlodipine with nifedipine on hypertension during pregnancy.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, clinicaltrials.gov, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wanfang Database and China Biology Medicine disc of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) up to April l5, 2021 was conducted on RCTs comparing amlodipine to nifedipine for the treatment of hypertension during pregnancy. Screening, data extraction, and quality assessment were done by two independent reviewers. To estimate relative effects from all available evidence, a meta-analysis was conducted.
Results
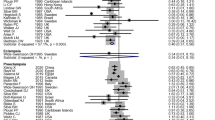
Seventeen RCTs were included. Amlodipine was found the efficacy is slightly superior to nifedipine on treating hypertension during pregnancy (RR 1.06, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.10) with a decreased risk for maternal side effects (RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.29 to 0.61). Subgroup analysis found amlodipine can get a better control on SBP (RR − 11.68, 95% CI − 17.98 to − 5.37) and DBP (RR − 7.44, 95% CI − 13.81 to − 1.06) compared with intermediate-/long-acting nifedipine. In addition, there was no difference between amlodipine and nifedipine on pregnancy outcomes including caesarean section, premature labour, placental abruption, FGR, fetal distress, neonatal asphyxia.
Conclusions
Given the results of this systematic review and meta-analysis, amlodipine can be effectively and safely used for hypertension during pregnancy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lale S et al (2014) Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis[J]. Lancet Glob Health 2:e323–e333
Abalos E, Duley L, Steyn DW et al (2018) Antihypertensive drug therapy for mild to moderate hypertension during pregnancy[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:D2252
Magee LA, Abalos E, Von Dadelszen P et al (2011) How to manage hypertension in pregnancy effectively[J]. Br J Clin Pharmacol 72:394–401
(2019) ACOG practice bulletin No. 203: chronic hypertension in pregnancy[J]. Obstet Gynecol 133(1):e26–e50
Butalia S, Audibert F, Cote AM et al (2018) Hypertension Canada’s 2018 guidelines for the management of hypertension in pregnancy[J]. Can J Cardiol 34(5):526–531
Toal CB (2004) Formulation dependent pharmacokinetics-does the dosage form matter for nifedipine[J]? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 44:82–86
(2019) ACOG Committee Opinion No. 767: emergent therapy for acute-onset, severe hypertensionduring pregnancy and the postpartum period[J]. Obstet Gynecol 133(2):e174–e180
Shekhar S, Gupta N, Kirubakaran R et al (2016) Oral nifedipine versus intravenous labetalol for severe hypertension during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BJOG 123(1):40–47
Fares H, DiNicolantonio JJ, O’Keefe JH et al (2016) Amlodipine in hypertension: a first-line agent with efficacy for improving blood pressure and patient outcomes[J]. Open Heart 3(2):e473
Morgan JL, Kogutt BK, Meek C et al (2018) Pharmacokinetics of amlodipine besylate at delivery and during lactation[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens 11:77–80
Xiaoli C (2015) Clinical study on amlodipine medication treatment of gestational hypertension[J]. China Continu Med Educ 7(13):171–172
Yifeng G, Miaoni Li (2013) Therapeutic effect analysis of amlodipine in 40 cases of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Inter Med 8(4):356–357
Bojin G (2015) Efficacy comparison between amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Cardiovasc Dis Prev 4(8):28–29
Hu S, Zhang H, Luan J, Li X (2015) Efficacy comparison between amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Chin Foreign Womens Health Res 7:165
Jin Ju (2018) Clinical effect of amlodipine in the treatment of pregnant patients with hypertension[J]. Health 12(8):82–83
Guiying Li, Hongxia S (2016) Contrastive observation of amlodipine and nibendipine in the treatment of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Chin Foreign Womens Health Res 23:166–172
Wei L (2015) Clinical effect of amlodipine in the treatment of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. J Prev Treat Cardiovasc Dis 8:26–27
Zizhen R (2014) Clinical effect analysis of amlodipine in the treatment of pregnant patients with hypertension[J]. Jilin Med Sci 35(27):6006–6007
Wang F (2016) Comparison of curative effect between amlodipine and nifedipine on pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Cardiovasc Dis J Integr Tradi Chin Western Med 4(11):63–66
Hong W (2018) Amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of hypertension complicated by pregnancy[J]. China & Foreign Med Treat 37(19):107–108
Zifen W, Haixiang S, Lili G (1997) Clinical analysis of amlodipine in the treatment of hypertension during pregnancy[J]. J Linyi Med Coll 4:291–293
Hui X (2016) Effect analysis of amlodipine in the treatment of pregnant patients with hypertension[J]. Cardiovasc Dis J Integr Tradi Chin Western Med 4(25):72–74
Yunxia X, Huiping Z (2017) Clinical effect of amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of pregnancy hypertension[J]. Ningxia Med J 39(4):357–359
Yuan Y (2016) Comparison of clinical effects between amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of 48 cases of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. World Latest Med Infor 16(41):96–99
Junsu Z (2018) Effect of amlodipine and nifedipine on pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Cardiovasc Dis J Integr Tradi Chin Western Med 6(35):125–126
Zhang Y (2019) Clinical analysis of amlodipine in the treatment of pregnancy complicated with hypertension[J]. Electronic J Pract Gynecol Endocrinol 6(16):119–120
Li Z (2017) Efficacy comparison between amlodipine and nifedipine in the treatment of pregnancycomplicated with hypertension[J]. World Clin Med 11(21):100
Weber-Schoendorfer C, Hannemann D, Meister R et al (2008) The safety of calcium channel blockers during pregnancy: a prospective, multicenter, observational study[J]. Reprod Toxicol 26(1):24–30
Salama M, Rezk M, Gaber W et al (2019) Methyldopa versus nifedipine or no medication for treatment of chronic hypertension during pregnancy: a multicenter randomized clinical trial[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens 17:54–58
Webster LM, Myers JE, Nelson-Piercy C et al (2017) Labetalol versus nifedipine as antihypertensivetreatment for chronic hypertension in pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Hypertension 70(5):915–922
Huang QF, Sheng CS, Li Y et al (2019) A randomized controlled trial on the blood pressure-lowering effect of amlodipine and nifedipine-GITS in sustained hypertension[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 21(5):648–657
Malachias MV, Figueiredo CE, Sass N et al (2016) 7th Brazilian guideline of arterial hypertension: chapter 9 – arterial hypertension in pregnancy. Arq Bras Cardiol 107(3 Suppl 3):49–52
Magee LA, Brown MA, Hall DR et al (2021) The 2021 International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy classification, diagnosis & management recommendations for international practice[J]. Pregnancy Hypertens 27:148–169
Cifkova R, Johnson MR, Kahan T et al (2020) Peripartum management of hypertension: a position paper of the ESC Council on Hypertension and the European Society of Hypertension[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 6(6):384–393
(2019) Hypertension in pregnancy: diagnosis and management. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), London
Mito A, Murashima A, Wada Y et al (2019) Safety of Amlodipine in Early Pregnancy[J]. J Am Heart Assoc 8(15):e12093
Funding
This study was supported by Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation (A2020161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJ, QS wrote the protocol. YJ performed the search. YJ and QS independently selected eligible studies and extracted data. Differences of opinion were registered and resolved by consensus with DP, SS. YJ and QS performed the meta-analyses. YJ, MZ, DP, SS, QS participated in the interpretation of the data and writing of the review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared. Completed disclosure of interests form available to view online as supporting information.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not needed for this meta-analysis.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Mei, Z., Shi, S. et al. Nifedipine or amlodipine? The choice for hypertension during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet 306, 1891–1900 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-022-06504-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-022-06504-5