Abstract
Objective
This dual-institutional, retrospective study aimed to determine the clinicopathological risk factors for para-aortic lymph node (LN) metastasis among women who underwent radical hysterectomy with systematic pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy for 2009 FIGO stage IB1-IIA2 cervical cancer.
Methods
Institutional cervical cancer databases of two high-volume gynecologic cancer centers in Ankara, Turkey were retrospectively analyzed. Women with 2009 FIGO stage IB1-IIA2 cervical cancer that had undergone radical hysterectomy with pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy between January 2006 and December 2018 were included in the study. Patient data were analyzed with respect to para-aortic LN involvement and all potential clinicopathological risk factors for para-aortic LN metastasis were investigated.
Results
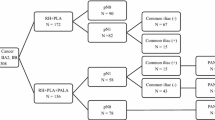
A total of 522 women met the inclusion criteria. Pelvic LN metastasis was detected in 190 patients (36.4%), para-aortic LN metastasis in 48 patients (9.2%), isolated para-aortic LN metastasis in 4 (0.8%), and both pelvic and para-aortic LN metastasis in 44 (8.4%) women, respectively. The independent risk factors identified for para-aortic LN involvement included parametrial invasion (odds ratio [OR]: 3.57, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.65–7.72; p = 0.001), metastasized pelvic LN size > 1 cm (OR: 4.51, 95% CI: 1.75–11.64; p = 0.002), multiple pelvic LN metastases (OR: 3.83, 95% CI: 1.46–10.01; p = 0.006), and common iliac LN metastasis (OR: 2.97, 95% CI: 1.01–8.68; p = 0.04). A total of 196 (37.5%) patients exhibited at least one risk factor for para-aortic nodal disease.
Conclusion
Parametrial invasion, metastasized pelvic LN size > 1 cm, multiple pelvic LN metastases, and common iliac LN metastasis seem to be independent predictors of para-aortic LN involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh N, Arif S (2004) Histopathologic parameters of prognosis in cervical cancer—a review. Int J Gynecol Cancer 14(5):741–750. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1048-891X.2004.014504.x
Tsuruga T, Fujimoto A, Kawana K, Mori M, Hasumi Y, Kino N, Tomio K, Miura S, Tanikawa M, Sone K, Miyamoto Y, Ikeda Y, Kojima S, Adachi K, Nagasaka K, Matsumoto Y, Arimoto T, Oda K, Nakagawa S, Horie K, Yasugi T, Yokota H, Osuga Y, Fujii T (2016) Radical hysterectomy with or without para-aortic lymphadenectomy for patients with stage IB2, IIA2, and IIB cervical cancer: outcomes for a series of 308 patients. Int J Clin Oncol 21(2):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-015-0907-3
Han X, Wen H, Ju X, Chen X, Ke G, Zhou Y, Li J, Xia L, Tang J, Liang S, Wu X (2017) Predictive factors of para-aortic lymph nodes metastasis in cervical cancer patients: a retrospective analysis based on 723 para-aortic lymphadenectomy cases. Oncotarget 8(31):51840–51847. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16025
Koh WJ, Abu-Rustum NR, Bean S, Bradley K, Campos SM, Cho KR, Chon HS, Chu C, Clark R, Cohn D, Crispens MA, Damast S, Dorigo O, Eifel PJ, Fisher CM, Frederick P, Gaffney DK, Han E, Huh WK, Lurain JR, Mariani A, Mutch D, Nagel C, Nekhlyudov L, Fader AN, Remmenga SW, Reynolds RK, Tillmanns T, Ueda S, Wyse E, Yashar CM, McMillian NR, Scavone JL (2019) Cervical cancer, version 3.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 17(1):64–68. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.0001
Ayhan A, Tuncer ZS, Ayhan A (1990) Effect of paraaortic lymphadenectomy on 5-year survival in early stage cervical cancer. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 30(4):378–380
Patsner B, Sedlacek TV, Lovecchio JL (1992) Para-aortic node sampling in small (3-cm or less) stage IB invasive cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol 44(1):53–54
Hackett TE, Olt G, Sorosky JI, Podczaski E, Harrison TA, Mortel R (1995) Surgical predictors of para-aortic metastases in early-stage cervical carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 59(1):15–19. https://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.1995.1261
Benedetti-Panici P, Maneschi F, Scambia G, Greggi S, Cutillo G, D'Andrea G, Rabitti C, Coronetta F, Capelli A, Mancuso S (1996) Lymphatic spread of cervical cancer: an anatomical and pathological study based on 225 radical hysterectomies with systematic pelvic and aortic lymphadenectomy. Gynecol Oncol 62(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.1996.0184
Michel G, Morice P, Castaigne D, Leblanc M, Rey A, Duvillard P (1998) Lymphatic spread in stage Ib and II cervical carcinoma: anatomy and surgical implications. Obstet Gynecol 91(3):360–363
Sakuragi N, Satoh C, Takeda N, Hareyama H, Takeda M, Yamamoto R, Fujimoto T, Oikawa M, Fujino T, Fujimoto S (1999) Incidence and distribution pattern of pelvic and paraaortic lymph node metastasis in patients with Stages IB, IIA, and IIB cervical carcinoma treated with radical hysterectomy. Cancer 85(7):1547–1554
Takeda N, Sakuragi N, Takeda M, Okamoto K, Kuwabara M, Negishi H, Oikawa M, Yamamoto R, Yamada H, Fujimoto S (2002) Multivariate analysis of histopathologic prognostic factors for invasive cervical cancer treated with radical hysterectomy and systematic retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 81(12):1144–1151
Huang H, Liu J, Li Y, Wan T, Feng Y, Li Z, Huang Q (2011) Metastasis to deep obturator and para-aortic lymph nodes in 649 patients with cervical carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol 37(11):978–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2011.08.128
Del Carmen MG, Pareja R, Melamed A, Rodriguez J, Greer A, Clark RM, Rice LW (2018) Isolated para-aortic lymph node metastasis in FIGO stage IA2-IB2 carcinoma of the cervix: revisiting the role of surgical assessment. Gynecol Oncol 150(3):406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.07.010
Matsuo K, Grubbs BH, Mikami M (2018) Quality and quantity metrics of pelvic lymph node metastasis and risk of para-aortic lymph node metastasis in stage IB-IIB cervical cancer. J Gynecol Oncol 29(1):e10. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2018.29.e10
Matsuo K, Shimada M, Saito T, Takehara K, Tokunaga H, Watanabe Y, Todo Y, Morishige KI, Mikami M, Sugiyama T (2018) Risk stratification models for para-aortic lymph node metastasis and recurrence in stage IB-IIB cervical cancer. J Gynecol Oncol 29(1):e11. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2018.29.e11
Inoue T, Morita K (1995) Long-term observation of patients treated by postoperative extended-field irradiation for nodal metastases from cervical carcinoma stages IB, IIA, and IIB. Gynecol Oncol 58(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.1995.1175
Chantalat E, Vidal F, Leguevaque P, Lepage B, Mathevet P, Deslandres M, Motton S (2015) Cervical cancer with paraaortic involvement: do patients truly benefit from tailored chemoradiation therapy? A retrospective study on 8 French centers. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 193:118–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2015.07.017
Matsuo K, Machida H, Blake EA, Takiuchi T, Mikami M, Roman LD (2017) Significance of uterine corpus tumor invasion in early-stage cervical cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 43(4):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2017.01.017
Du R, Li L, Ma S, Tan X, Zhong S, Wu M (2018) Lymph nodes metastasis in cervical cancer: incidences, risk factors, consequences and imaging evaluations. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.12997
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN, Sankaranarayanan R (2018) Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 143(Suppl 2):22–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12611
Zigras T, Lennox G, Willows K, Covens A (2017) Early cervical cancer: current dilemmas of staging and surgery. Curr Oncol Rep 19(8):51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-017-0614-5
Benedetti Panici P, Basile S, Angioli R (2009) Pelvic and aortic lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer: the standardization of surgical procedure and its clinical impact. Gynecol Oncol 113(2):284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.12.014
Verleye L, Vergote I, Reed N, Ottevanger PB (2009) Quality assurance for radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer: the view of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Gynecological Cancer Group (EORTC-GCG). Ann Oncol 20(10):1631–1638. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp196
Sakuragi N, Takeda N, Hareyama H, Fujimoto T, Todo Y, Okamoto K, Takeda M, Wada S, Yamamoto R, Fujimoto S (2000) A multivariate analysis of blood vessel and lymph vessel invasion as predictors of ovarian and lymph node metastases in patients with cervical carcinoma. Cancer 88(11):2578–2583
Lentz SE, Muderspach LI, Felix JC, Ye W, Groshen S, Amezcua CA (2004) Identification of micrometastases in histologically negative lymph nodes of early-stage cervical cancer patients. Obstet Gynecol 103(6):1204–1210. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000125869.78251.5e
Ouldamer L, Marret H, Acker O, Barillot I, Body G (2012) Unusual localizations of sentinel lymph nodes in early stage cervical cancer: a review. Surg Oncol 21(3):e153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2012.04.003
Hwang L, Bailey A, Lea J, Albuquerque K (2015) Para-aortic nodal metastases in cervical cancer: a blind spot in the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics staging system: current diagnosis and management. Future Oncol 11(2):309–322. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon.14.200
Ouldamer L, Fichet-Djavadian S, Marret H, Barillot I, Body G (2012) Upper margin of para-aortic lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 91(8):893–900. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0412.2012.01443.x
Bats AS, Mathevet P, Buenerd A, Orliaguet I, Mery E, Zerdoud S, Le Frere-Belda MA, Froissart M, Querleu D, Martinez A, Leblanc E, Morice P, Darai E, Marret H, Gillaizeau F, Lecuru F (2013) The sentinel node technique detects unexpected drainage pathways and allows nodal ultrastaging in early cervical cancer: insights from the multicenter prospective SENTICOL study. Ann Surg Oncol 20(2):413–422. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2597-7
Ditto A, Martinelli F, Lo Vullo S, Reato C, Solima E, Carcangiu M, Haeusler E, Mariani L, Lorusso D, Raspagliesi F (2013) The role of lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer patients: the significance of the number and the status of lymph nodes removed in 526 cases treated in a single institution. Ann Surg Oncol 20(12):3948–3954. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3067-6
Lv X, Chen L, Yu H, Zhang X, Yan D (2012) Intra-operative frozen section analysis of common iliac lymph nodes in patients with stage IB1 and IIA1 cervical cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 285(3):811–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-011-2038-z
Choi HJ, Ju W, Myung SK, Kim Y (2010) Diagnostic performance of computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography or positron emission tomography/computer tomography for detection of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer: meta-analysis. Cancer Sci 101(6):1471–1479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01532.x
Ramirez PT, Jhingran A, Macapinlac HA, Euscher ED, Munsell MF, Coleman RL, Soliman PT, Schmeler KM, Frumovitz M, Ramondetta LM (2011) Laparoscopic extraperitoneal para-aortic lymphadenectomy in locally advanced cervical cancer: a prospective correlation of surgical findings with positron emission tomography/computed tomography findings. Cancer 117(9):1928–1934. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25739
Leblanc E, Katdare N, Narducci F, Bresson L, Gouy S, Morice P, Ferron G, Querleu D, Martinez A (2016) Should systematic infrarenal para-aortic dissection be the rule in the pretherapeutic staging of primary or recurrent locally advanced cervix cancer patients with a negative preoperative para-aortic PET Imaging? Int J Gynecol Cancer 26(1):169–175. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000000588
Sironi S, Buda A, Picchio M, Perego P, Moreni R, Pellegrino A, Colombo M, Mangioni C, Messa C, Fazio F (2006) Lymph node metastasis in patients with clinical early-stage cervical cancer: detection with integrated FDG PET/CT. Radiology 238(1):272–279. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2381041799
Jover R, Lourido D, Gonzalez C, Rojo A, Gorospe L, Alfonso JM (2008) Role of PET/CT in the evaluation of cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110(3 Suppl 2):S55–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.05.023
Leblanc E, Gauthier H, Querleu D, Ferron G, Zerdoud S, Morice P, Uzan C, Lumbroso S, Lecuru F, Bats AS, Ghazzar N, Bannier M, Houvenaeghel G, Brenot-Rossi I, Narducci F (2011) Accuracy of 18-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography in the pretherapeutic detection of occult para-aortic node involvement in patients with a locally advanced cervical carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18(8):2302–2309. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1583-9
Gouy S, Morice P, Narducci F, Uzan C, Gilmore J, Kolesnikov-Gauthier H, Querleu D, Haie-Meder C, Leblanc E (2012) Nodal-staging surgery for locally advanced cervical cancer in the era of PET. Lancet Oncol 13(5):e212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70011-6
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA: conceptualized and designed the study, prepared the draft manuscript. MMM: conceptualized and designed the study, analyzed and interpreted the data, prepared the draft manuscript. KA: collected the data, performed statistical analyses, edited and reviewed the manuscript. YAT: collected the data, edited and reviewed the manuscript. EK: controlled the quality of the data, analyzed and interpreted the data, edited and reviewed the manuscript. MÖ: controlled the quality of the data, analyzed and interpreted the data, performed statistical analyses, edited and reviewed the manuscript. All co-authors revised the manuscript critically and approved the final version to be published. MÖ accepts full responsibility for the work and/or the conduct of the study, had access to the data, and oversaw the decision to publish.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or academic support of relationships that could pose any potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayhan, A., Aslan, K., Öz, M. et al. Para-aortic lymph node involvement revisited in the light of the revised 2018 FIGO staging system for cervical cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet 300, 675–682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05232-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05232-7