Abstract
Background
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition with systemic manifestations that have a detrimental impact on a patient’s quality of life, affecting social, psychological, and sexual aspects of life. Complete clearance of lesions is a meaningful end goal of treatment; however, it is often difficult for patients to achieve. In this literature review, we summarized past studies that compared patients who achieved complete clearance to those who were almost clear to highlight the effect of complete clearance on psychological distress, social stigma, self-esteem, and interpersonal relationships in adult patients with psoriasis.
Methods
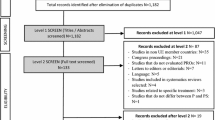
A literature search was performed through the PubMed database using the keywords “clearance of psoriasis”, “complete clearance of psoriasis”, “psychological impact psoriasis”, “social impact psoriasis”, and “stigma of psoriasis”. Age (< 18) and language (only articles written in English were included) were the only exclusion criteria to include adult patients only. The information was then collected and evaluated to compare complete clearance and almost complete clearance of psoriasis.
Results
Of the patients with complete skin clearance (sPGA of 0), 61.4–91.1% reported a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) of 0, indicating no detectable impact of psoriasis on quality of life, compared to 45.7–48.3% who were almost clear. Patients who were completely clear felt psoriasis had less of an effect on their leisure activities and daily living compared to patients who were almost clear. Patient perceptions of disease severity also differed between the two groups, with the majority (65.5%) of those achieving complete clearance reporting a Psoriasis Symptom Inventory (PSI) of 0, which is consistent with their disease being “not at all severe”, compared to 32.6% of those who were almost but not completely clear. While patients with complete clearance achieve a DLQI of 0 at a higher rate than those who have only almost complete clearance, the difference in the mean DLQI between patients with sPGA of 0 (completely clear) and sPGA of 1 (almost clear) is less than the minimal clinically important difference (MCID of 3–5) of the DLQI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blauvelt A, Wu JJ, Armstrong A, Menter A, Liu C, Jacobson A (2020) Importance of complete skin clearance in psoriasis as a treatment goal: implications for patient-reported outcomes. J Drugs Dermatol 19(5):487–492
Aghaei S, Moradi A, Ardekani GS (2009) Impact of psoriasis on quality of life in Iran. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 75(2):220. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.48689
Feldman SR, Malakouti M, Koo JY (2014) Social impact of the burden of psoriasis: effects on patients and practice. Dermatol Online J 20(8):13030/qt48r4w8h2
Strober B, Papp KA, Lebwohl M et al (2016) Clinical meaningfulness of complete skin clearance in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 75(1):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.03.026
Norris D, Photiou L, Tacey M et al (2017) Biologics and dermatology life quality index (DLQI) in the Australasian psoriasis population. J Dermatol Treat 28(8):731–736. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2017.1329501
Karamata VV, Gandhi AM, Patel PP, Sutaria A, Desai MK (2017) A study of the use of drugs in patients suffering from psoriasis and their impact on quality of life. Indian J Pharmacol 49(1):84–88. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijp.IJP_166_16
Rasmussen MK, Enger M, Dahlborn AK et al (2019) The importance of achieving clear or almost clear skin for patients: results from the Nordic countries of the global. Acta Derm Venereol 99(2):158–163. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-3048
Korman NJ, Malatestinic W, Goldblum OM et al (2020) Assessment of the benefit of achieving complete versus almost complete skin clearance in psoriasis: a patient’s perspective. J Dermatol Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2020.1772454
Al-Suwaidan SN, Feldman SR (2000) Clearance is not a realistic expectation of psoriasis treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol 42(5 Pt 1):796–802. https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2000.103983
Feldman SR, Bushnell DM, Klekotka PA et al (2016) Differences in psoriasis signs and symptom severity between patients with clear and almost clear skin in clinical practice. J Dermatol Treat 27(3):224–227. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2015.1093589
Viswanathan HN, Chau D, Milmont CE et al (2015) Total skin clearance results in improvements in health-related quality of life and reduced symptom severity among patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. J Dermatol Treat 26(3):235–239. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2014.943687
Takeshita J, Callis Duffin K, Shin DB et al (2014) Patient-reported outcomes for psoriasis patients with clear versus almost clear skin in the clinical setting. J Am Acad Dermatol 71(4):633–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2014.05.001
Basra MK, Salek MS, Camilleri L, Sturkey R, Finlay AY (2015) Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): further data. Dermatology 230(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1159/000365390
Reich K, Griffiths CE (2008) The relationship between quality of life and skin clearance in moderate-to-severe psoriasis: lessons learnt from clinical trials with infliximab. Arch Dermatol Res 300(10):537–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-008-0885-7
Egeberg A, Thyssen JP (2019) Factors associated with patient-reported importance of skin clearance among adults with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 81(4):943–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2019.06.018
Kouwenhoven TA, van der Ploeg JAM, van de Kerkhof PCM (2020) Treatment goals in psoriasis from a patient perspective: a qualitative study. J Dermatol Treat 31(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2018.1544408
Armstrong A, Jarvis S, Boehncke WH et al (2018) Patient perceptions of clear/almost clear skin in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: results of the Clear About Psoriasis worldwide survey. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 32(12):2200–2207. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.15065
Ogbechie-Godec O, Azarchi S, Lee J, Cohen DE, Neimann A, Nagler AR (2019) Validated patient-reported outcome measurements for psoriasis may not reflect patients’ current preferences. J Am Acad Dermatol 80(5):1445–1447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.09.019
Kauf TL, Yang JC, Kimball AB et al (2015) Psoriasis patients’ willingness to accept side-effect risks for improved treatment efficacy. J Dermatol Treat 26(6):507–513. https://doi.org/10.3109/09546634.2015.1034071
Hawro M, Maurer M, Weller K et al (2017) Lesions on the back of hands and female gender predispose to stigmatization in patients with psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 76(4):648–54.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.10.040
Sampogna F, Tabolli S, Abeni D (2007) The impact of changes in clinical severity on psychiatric morbidity in patients with psoriasis: a follow-up study. Br J Dermatol 157(3):508–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08071.x
Böhm D, Stock Gissendanner S, Bangemann K et al (2013) Perceived relationships between severity of psoriasis symptoms, gender, stigmatization and quality of life. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27(2):220–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2012.04451.x
Kamata M, Tada Y (2020) Efficacy and safety of biologics for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and their impact on comorbidities: a literature review. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051690
Fairchild AO, Reed SD, Johnson FR, Anglin G, Wolka AM, Noel RA (2017) What is clearance worth? Patients’ stated risk tolerance for psoriasis treatments. J Dermatol Treat 28(8):709–715. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2017.1329499
Elewski BE, Puig L, Mordin M et al (2017) Psoriasis patients with psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) 90 response achieve greater health-related quality-of-life improvements than those with PASI 75–89 response: results from two phase 3 studies of secukinumab. J Dermatol Treat 28(6):492–499. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2017.1294727
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NB wrote the main manuscript text and EB, MC, and SF contributed by editing the manuscript. MC prepared Tables 1, 2 and NB, EB, and SF contributed by editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Feldman has received research, speaking and/or consulting support from Eli Lilly and Company, GlaxoSmithKline/Stiefel, AbbVie, Janssen, Alovtech, vTv Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Samsung, Pfizer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Amgen Inc, Dermavant, Arcutis, Novartis, Novan, UCB, Helsinn, Sun Pharma, Almirall, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Mylan, Celgene, Valeant, Menlo, Merck & Co, Qurient Forte, Arena, Biocon, Accordant, Argenx, Sanofi, Regeneron, the National Biological Corporation, Caremark, Advance Medical, Suncare Research, Informa, UpToDate and the National Psoriasis Foundation. He is also the founder and majority owner of www.DrScore.com [drscore.com] and the founder and part owner of Causa Research. Nicole D. Boswell, Esther A. Balogh and Madison K. Cook have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Boswell, N.D., Cook, M.K., Balogh, E.A. et al. The impact of complete clearance and almost complete clearance of psoriasis on quality of life: a literature review. Arch Dermatol Res 315, 699–706 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-022-02420-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-022-02420-5