Abstract
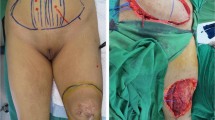
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a cutaneous sarcoma that has remained a challenge for oncologic and reconstructive surgeons due to a high rate of local recurrence. The objective of this study is to investigate the oncologic and reconstructive benefits of employing a multidisciplinary two-step approach to the treatment of DFSP. A retrospective review was conducted using a prospectively collected database of all patients who underwent resection and reconstruction of large DFSPs by a multidisciplinary team, including a Mohs micrographic surgeon, surgical oncologist, dermatopathologist, and plastic and reconstructive surgeon, at one academic institution from 1998–2018. Each patient underwent Mohs micrographic surgery for peripheral margin clearance (Step 1) followed by wide local excision (WLE) of the deep margin by surgical oncology and immediate reconstruction by plastic surgery (Step 2). 57 patients met inclusion criteria. Average defect size after WLE (Step 2): 87.3 cm2 (range 8.5–1073.5 cm2). Mean follow-up time was 37 months (range 0–138 months). There were no cases of recurrence. A two-step multidisciplinary surgical treatment approach for DFSP minimizes risk of recurrence, decreases patient discomfort, and allows immediate reconstruction after deep margin clearance.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data were collected from IRB approved retrospective chart review.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agostini T, Dini M, Quattrini Li A, Grassetti L, Mori A, Spinelli G et al (2013) A novel combined surgical approach to head and neck dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Cranio-Maxillo-Fac Surg 41(7):681–685
Allen A, Ahn C, Sangueza OP (2019) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Clin 37(4):483–488
Arnaud EJ, Perrault M, Revol M, Servant JM, Banzet P (1997) Surgical treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Plast Reconstr Surg 100(4):884–895
Barnes L, Coleman JA Jr, Johnson JT (1984) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol 110(6):398–404
Bertolli E, Campagnari M, Molina AS, Macedo MP, Pinto CA, Cunha IW et al (2015) Artificial dermis (Matriderm(R)) followed by skin graft as an option in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with complete circumferential and peripheral deep margin assessment. Int Wound J 12(5):545–547
Bogucki B, Neuhaus I, Hurst EA (2012) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a review of the literature. Dermatol Surg 38(4):537–551
Buck DW 2nd, Kim JY, Alam M, Rawlani V, Johnson S, Connor CM et al (2012) Multidisciplinary approach to the management of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Am Acad Dermatol 67(5):861–866
Campagnari M, Jafelicci AS, Carneiro HA, Brechtbuhl ER, Bertolli E, Duprat Neto JP (2017) Dermal substitutes use in reconstructive surgery for skin tumors: a single-center experience. Int J Surg Oncol 2017:9805980
Criscione VD, Weinstock MA (2007) Descriptive epidemiology of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in the United States, 1973 to 2002. J Am Acad Dermatol 56(6):968–973
Enzinger FM, Weiss SW (1995) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Soft Tissue Tumors 3:325–335
Foroozan M, Sei JF, Amini M, Beauchet A, Saiag P (2012) Efficacy of Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: systematic review. Arch Dermatol 148(9):1055–1063
Haycox CL, Odland PB, Olbricht SM, Casey B (1997) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP): growth characteristics based on tumor modeling and a review of cases treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. Ann Plast Surg 38(3):246–251
Kim BJ, Kim H, Jin US, Minn KW, Chang H (2015) Wide local excision for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a single-center series of 90 patients. Biomed Res Int 2015:642549
Kreicher KL, Kurlander DE, Gittleman HR, Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Bordeaux JS (2016) Incidence and survival of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in the United States. Dermatol Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/DSS.0000000000000300
Lemm D, Mügge L-O, Mentzel T, Höffken K (2009) Current treatment options in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135(5):653–665
Lowe GC, Onajin O, Baum CL, Otley CC, Arpey CJ, Roenigk RK et al (2017) A Comparison of Mohs micrographic surgery and wide local excision for treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with long-term follow-up: the mayo clinic experience. Dermatol Surg 43(1):98–106
McPeak CJ, Cruz T, Nicastri AD (1967) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: an analysis of 86 cases–five with metastasis. Ann Surg 166(5):803–816
Meguerditchian AN, Wang J, Lema B, Kraybill WG, Zeitouni NC, Kane JM 3rd (2010) Wide excision or Mohs micrographic surgery for the treatment of primary dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Am J Clin Oncol 33(3):300–303
Miller SJ, Alam M, Andersen JS, Berg D, Bichakjian CK, Bowen GM et al (2012) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 10(3):312–318
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2020). Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP) (Version 1. 2020). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx, Accessed 22 April 22 2020.
Pack GT (1951) Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. AMA Arch Surg 62(3):391–411
Parker TL, Zitelli JA (1995) Surgical margins for excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Am Acad Dermatol 32(2 Pt 1):233–236
Reha J, Katz SC (2016) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Surg Clin N Am 96(5):1031–1046
Roses DF, Valensi Q, LaTrenta G, Harris MN (1986) Surgical treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Surg Gynecol Obstetr 162(5):449–452
Rouhani P, Fletcher CD, Devesa SS, Toro JR (2008) Cutaneous soft tissue sarcoma incidence patterns in the US: an analysis of 12,114 cases. Cancer 113(3):616–627
Rutgers EJ, Kroon BB, Albus-Lutter CE, Gortzak E (1992) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: treatment and prognosis. Eur J Surg Oncol 18(3):241–248
Sartore L, Venezia ED, Della Puppa A, Bedogni A, Campana L, Giatsidis G (2015) Reconstructive strategies for dermatofibrosarcomas of the face: role of regenerative dermal templates. Head Neck 37(1):E8–11
Smola MG, Soyer HP, Scharnagl E (1991) Surgical treatment of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. A retrospective study of 20 cases with review of literature. Eur J Surg Oncol 17(5):447–453
Thway K, Noujaim J, Jones RL, Fisher C (2016) Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: pathology, genetics, and potential therapeutic strategies. Ann Diagn Pathol 25:64–71
Funding
No funding was provided in support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors had access to the information and certify its accuracy. Wayne, Chappell, Buck, Kim, Alam, Yoo, Gerami: intellectual design of study. Wayne, Chappell, Doe: Data Collection. Wayne, Chappell, Doe, Kim: Data Analysis. Chappell, Worley, Alam: drafting of the manuscript. All authors: revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors: final approval of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have nothing to disclose.
Statement of Prior Presentation
Plastic Surgery the Meeting (ASPS) 2019 in San Diego, CA.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chappell, A.G., Doe, S.C., Worley, B. et al. Multidisciplinary surgical treatment approach for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: an update. Arch Dermatol Res 313, 367–372 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-020-02124-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-020-02124-8