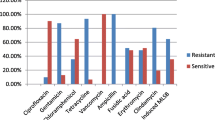
Abstract
Chronic hand eczema is a common chronic inflammatory skin disease that influences public health. Staphylococcus aureus colonization plays important roles in chronic hand eczema morbidity and progression, which also correlated to chronicity and severity of the disease. In this multicenter clinical trial, we aim to investigate the relationship between S. aureus colonization and chronic hand eczema. Eighty patient volunteers diagnosed with chronic hand eczema in 4 hospitals from 4 cities participated in this study. Staphylococcus aureus colonization was determined using Polymerase Chain Reaction and fluorescent labeling probe to rapidly detect the endemic thermostable nuclease gene nuc of S. aureus in clinical samples. All patients were treated with Halometasone Triclosan Cream for 2 weeks. The changes of clinical symptom scores were observed during the follow-up time. We found that the severity of chronic hand eczema was related to S. aureus colonization. Chronic hand eczema would remain severer than others if S. aureus colonization was not eliminated. Eliminating S. aureus colonization could provide good effectiveness in treatment of chronic hand eczema. Therefore, we make a proposal that detection and treatment of S. aureus should be considered in the clinical treatment of chronic hand eczema.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CHE:
-
Chronic hand eczema
- SA:
-
Staphylococcus aureus
- HECSI:
-
Hand Eczema Severity Index
- HEES:
-
Hand Eczema Extent Score
- IGA:
-
Investigator’s Global Assessment
- DLQI:
-
Dermatology Life Quality Index
- VAS:
-
Visual Analogue Scales
- SSRI:
-
Symptom Score Reducing Index
References
Diepgen TL, Andersen KE, Chosidow O, Coenraads PJ, Elsner P, English J, Fartasch M, Gimenez-Arnau A, Nixon R, Sasseville D et al (2015) Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention and treatment of hand eczema. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 13:e1–e22. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.12510
Diepgen TL, Agner T, Aberer W, Berth-Jones J, Cambazard F, Elsner P, McFadden J, Coenraads PJ (2007) Management of chronic hand eczema. Contact Dermat 57:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01179.x
de Leon FJ, Berbegal L, Silvestre JF (2015) Management of chronic hand eczema. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 106:533–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2015.04.005
Hanifin JM, Rogge JL (1977) Staphylococcal infections in patients with atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol 113:1383–1386. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.1977.01640100061009
Williams RE, Gibson AG, Aitchison TC, Lever R, Mackie RM (1990) Assessment of a contact-plate sampling technique and subsequent quantitative bacterial studies in atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 123:493–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1990.tb01455.x
Leyden JJ, Marples RR, Kligman AM (1974) Staphylococcus aureus in the lesions of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol 90:525–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1974.tb06447.x
Skov L, Baadsgaard O (2000) Bacterial superantigens and inflammatory skin diseases. Clin Exp Dermatol 25:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2230.2000.00575.x
McFadden JP, Noble WC, Camp RD (1993) Superantigenic exotoxin-secreting potential of staphylococci isolated from atopic eczematous skin. Br J Dermatol 128:631–632. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00257.x
Chen Y, Wang X, Zhang C, Shi W (2018) Detection and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus colonization in chronic hand eczema: a multicenter study. J Dermatol Treat. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2018.1476650
Held E, Skoet R, Johansen JD et al (2005) The hand eczema severity index (HECSI): a scoring system for clinical assessment of hand eczema. A study of inter- and intraobserver reliability. Br J Dermatol 152:302–307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.06305.x
Carlsson A, Svensson Å, Anderson CD et al (2016) Scoring of hand eczema: good reliability of hand eczema extent score. Acta dermato-venereol 97:193. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-2521
Pg VDV, van Gils RF, Boot CR et al (2013) A simple tool with which to study the course of chronic hand eczema in clinical practice: a reduced-item score. Contact Dermat 69:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.12041
Finlay AY, Khan GK (2010) Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)—a simple practical measure for routine clinical use. Clin Exp Dermatol 19:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.1994.tb01167.x
Zhu B, Edson-Heredia E, Guo J et al (2014) Itching is a significant problem and a mediator between disease severity and quality of life for patients with psoriasis: results from a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol 171:1215–1219. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.13065
Haslund P, Bangsgaard N, Jarlov JO, Skov L, Skov R, Agner T (2009) Staphylococcus aureus and hand eczema severity. Br J Dermatol 161:772–777. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09353.x
Mernelius S, Carlsson E, Henricson J, Lofgren S, Lindgren PE, Ehricht R, Monecke S, Matussek A, Anderson CD (2016) Staphylococcus aureus colonization related to severity of hand eczema. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35:1355–1361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-016-2672-2
Acknowledgements
We thank all the dermatologists from Beijing Friendship Hospital Capital Medical University, Jiangsu Province Hospital, Shanghai General Hospital and Wuhan No. 1 Hospital those offer their help in this study. Funding and Halometasone Triclosan Cream of this work were supplied by Lansen Pharmaceutical Holdings Limited, Ningbo, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WS and LL designed the study; XW, WX, YC, CZ, LC and YL collected, analyzed, and interpreted the data; XW, WS and LL drafted the manuscript. All the authors critically read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xu, W., Chen, Y. et al. Staphylococcus aureus colonization and chronic hand eczema: a multicenter clinical trial. Arch Dermatol Res 311, 513–518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01924-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01924-x