Abstract
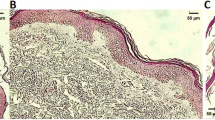
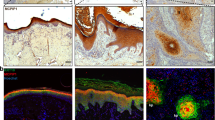
There is substantial evidence implicating the urokinase system in tissue remodeling during neo-vascularization, inflammation, tumor invasion, and metastasis. Regulated degradation of the extracellular matrix at the leading edge of migrating cells, mediated by uPA and uPAR, is required for tissue remodeling, invasiveness, and angiogenesis. Psoriasis and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) are the most common skin diseases. Pathogenesis of both of them is associated with keratinocyte hyperproliferation, inflammatory cell migration, and angiogenesis—processes in which the plasminogen system (uPA, uPAR, tPA, and PAI-1) plays a crucial role. In the present study, the comparative analysis of uPA, uPAR, tPA, and PAI-1 expression in the normal skin, in the biopsies of patients with psoriasis vulgaris, and BCC was carried out. uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 expression was up-regulated in the epidermis of psoriatic skin and in tumor cells in BCC. Increased uPAR expression was detected in the derma of psoriatic lesions and in the stroma surrounding tumor cells in BCC. Increased expression of uPA in epidermal cells in psoriasis and in tumor cells in BCC suggests an important role of the uPA system for aggressively proliferating and invading cells of epidermal origin. A possible activation of the stroma, as a result of uPA–uPAR interaction between tumor cells and the surrounding stroma, is suggested.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Horani RA (2014) Serpin regulation of fibrinolytic system; implications for applications in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem 12(2):91–125
Andreasen PA, Kjoller L, Christensen L, Duffy MJ (1997) The urokinase-type plasminogen activation system in cancer metastasis; a review. Int J Cancer 72:1–22
Barker JNWN (1991) Pathophysiology of psoriasis. Lancet 338:227–230
Bhushan M, Mclaughlin B, Weiss JB (1999) Level of endothelial cell stimulating angiogenesis factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 141:1054–1060
Blasi F, Vassalli J-D, Dano K (1987) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator; proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol 104:801–804
Blasi F, Carmeliet P (2002) uPAR; a versatile signaling orchestrator. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:932–943
Blasi F, Sidenius N (2010) The urokinase receptor; focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and signaling. FEBS Lett 584(9):1923–1930
Buo L, Meling GI, Karlsrud TS (1995) Antigen level of urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor at the tumor-host interface of colorectal adenocarcinomas are related to tumor aggressiveness. Hum Pathol 26:1133–1138
Chen CS, Jensen PJ (1996) Serum is a potent stimulator of keratinocyte tissue plasminogen activator expression. J Investig Dermatol 106(2):238–242
Choi J, Koo JY (2003) Quality of life issues in psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol 49:57–61
Collen D (1999) The plasminogen (fibrinolytic) system. Thromb Haemost 82(2):259–270
Collen D (2001) Role of the plasminogen system in fibrin-homeostasis and tissue remodelling. Hematology 1(1):1–9
Colman RW, Wu Y, Liu Y (2010) Mechanisms by which cleaved kininogen inhibits endothelial cell differentiation and signaling. Thromb Haemost 104:875–885
Creamer D, Allen M, Sousa A (1995) Altered vascular endothelium integrin expression in psoriasis. Am J Pathol 147:1661–1667
Creamer D, Jaggar M, Allen M (1997) Overexpression of angiogenic growth factor platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase in psoriatic epidermis. Br J Dermatol 137:8851–8855
Creamer D, Sullivan D, Bicknell R, Barker J (2002) Angiogenesis in psoriasis. Angiogenesis 5:231–236
Detmar M, Brown LF, Claffey KP (1994) Overexpression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor in psoriasis. J Exp Med 180:1141–1146
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM, Harbeck N, Thomssen C, Schmitt M (2014) uPA and PAI-1 as biomarkers in breast cancer: validated for clinical use in level-of-evidence-1 studies. Breast Cancer Res 16(4):428
Elder JT, Fisher GJ, Lindquist PB (1989) Overexpression of transforming growth factor-a in psoriatic epidermis. Science 243:811–814
Ettehadi P, Greaves MW, Wallach D (1994) Elevated tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a) biological activity in psoriatic lesions. Clin Exp Immunol 96:146–151
Feller L, Khammissa RA, Kramer B, Altini M, Lemmer J (2016) Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma of the head and face. Head Face Med 12:11
Fraki JE, Lazarus GS, Gilgor RS, Marchase P, Singer KH (1983) Correlation of epidermal plasminogen activator activity with disease activity in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 108:39–44
Ganzetti G, Campanati A, Molinelli E, Offidani A (2016) Psoriasis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease: three different diseases on a unique background. World J Cardiol 8(2):120–131
Gilhar A, David M, Kalish RS, Weisinger G (1996) In vivo effects of cytokines on psoriatic skin grafted on nude mice; involvement of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Clin Exp Immunol 106(1):134–142
Gissler HM, Frank R, Kramer MD (1993) Immunohistochemical characterization of the plasminogen activator system in psoriatic epidermis. Br J Dermatol 128(6):612–618
Godi A (2004) New approaches to psoriasis treatment. Acta Dermatovenerol 13(2):50–57
Gramling MW, Church FC (2010) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is an aggregate response factor with pleiotropic effects on cell signaling in vascular disease and the tumor microenvironment. Thromb Res 125:377–381
Grondahl-Hansen J, Nielsen LS, Kristensen P, Grondahl-Hansen V, Andreasen PA, Dano K (1985) Plasminogen activator in psoriatic scales is of the tissue-type PA as identified by monoclonal antibodies. Br J Dermatol 113(3):257–263
Grondahl-Hansen J, Ralfkiaer E, Nielsen LS, Kristensen P, Frentz G, Dano K (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in psoriatic skin. J Investig Dermatol 88(1):28–32
Harbeck N, Kates RE, Schmitt M (2004) Urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor type 1 predict disease outcome and therapy response in primary breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 5(5):348–352
Heissig B, Dhahri D, Eiamboonsert S, Salama Y, Shimazu H, Munakata S, Hattori K (2015) Role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived fibrinolytic factor in tissue regeneration and cancer progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(24):4759–4770
Hildenbrand R, Schaaf A (2009) The urokinase-system in tumor tissue stroma of the breast and breast cancer cell invasion. Int J Oncol 34(1):15–23
Hohler T, Marker-Hermann E (2001) Psoriatic arthritis; clinical aspects, genetics and the role of T-cells. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13:273–279
Jensen PJ, Baird J, Morioka S, Lessin S, Lazarus GS (1988) Epidermal plasminogen activator is abnormal in cutaneous lesions. J Investig Dermatol 90(6):777–782
Jensen PJ, Baird J, Belin D, Vassalli JD, Busso N, Gubler P, Lazarus GS (1990) Tissue plasminogen activator in psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 95(5):13–14
Kauvar AN, Cronin T Jr, Roenigk R, Hruza G, Bennett R (2015) Consensus for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment: basal cell carcinoma, including a cost analysis of treatment methods. Dermatol Surg 41(5):550–571
Kuroda K, Sapadin A, Shoji T (2001) Altered expression of angiopoietins and Tie2 endothelium receptor in psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 116:713–720
Lanoue J, Goldenberg G (2016) Basal cell carcinoma: a comprehensive review of existing and emerging nonsurgical therapies. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 9(5):26–36
Leurer C, Rabbani SA (2015) Plasminogen activator system—diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic implications in breast cancer, a concise review of molecular pathology of breast cancer. In: Gunduz M (ed) A concise review of molecular pathology of breast cancer. ISBN 978-953-51-2030-8
Lomas A, Leonardi-Bee J, Bath-Hextall F (2012) A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol 166(5):1069–1080
Lotti T, Bonan P, Panconesi E (1989) Plasminogen activation in psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 146:36–38
Lotti T, Bonan P, Cannarozzo G, Fedi AM, Panconesi E (1990) Antipsoriatic therapies inhibit epidermal plasminogen activator activity. Int J Dermatol 29(7):528–530
Lupu M, Caruntu C, Ghita MA, Voiculescu V, Voiculescu S, Rosca AE, Caruntu A, Moraru L, Popa IM, Calenic B, Greabu M, Costea DE (2016) Gene expression and proteome analysis as sources of biomarkers in basal cell carcinoma. Dis Mark. doi:10.1155/2016/9831237
Lyons-Giordano B, Loskutoff D, Chen CS, Lazarus G, Keeton M, Jensen PJ (1994) Expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 2 in normal and psoriatic epidermis. Histochemistry 101(2):105–112
Maguire T, Chin D, Soutar D, Duffy MJ (2000) Low levels of urokinase plasminogen activator components in basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Int J Cancer 85:457–459
Mazar AP, Henkin J, Goldfarb RH (1999) The urokinase plasminogen activator system in cancer; implication for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Angiogenesis 3:15–32
Mazzieri R, Pietrogrande G, Gerasi L, Gandelli A, Colombo P, Moi D, Brombin C, Ambrosi A, Danese S, Mignatti P, Blasi F, D’Alessio S (2015) Urokinase receptor promotes skin tumor formation by preventing epithelial cell activation of notch. Cancer Res 75(22):4895–4909
Miller SJ, Jensen PJ, Dzubow LM, Lazarus GS (1992) Urokinase plasminogen activator is immunocytochemically detectable in squamous cell but not basal cell carcinomas. J Investig Dermatol 98(3):351–358
Nagy B, Ban J, Brdar B (1977) Fibrinolysis associated with human neoplasia; production of plasminogen activators by human tumors. Int J Cancer 19:614–620
Nickoloff BJ, Mitra RS, Varani J (1994) Aberrant production of interleukin-8 and thrombospondin-1 by psoriatic keratinocytes mediates angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 144:820–828
Nickoloff BJ (2000) Characterization of lymphocyte-dependent angiogenesis using a SCID mouse; Human skin model of psoriasis. J Investig Dermatol 5:67–73
Nielsen HJ, Christensen IJ, Svendsen MN, Hansen U, Werther K, Brunner N, Petersen LJ, Kristensen JK (2002) Elevated plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 decrease during improvement of psoriasis. Inflamm Res 51(11):563–567
Parfyonova YV, Plekhanova OS, Tkachuk VA (2002) Plasminogen activators in vascular remodeling and angiogenesis. Biochemistry (Moscow) 67(1):139–156
Plekhanova OS, Parfenova EV, Tkachuk VA (2015) Mechanisms of vascular remodeling following arterial injury. Kardiologiia 55(7):63–77
Quinn AG, Perkins W (2010) Non-melanoma skin cancer and other epidermal skin tumors. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C (eds) Rook’s textbook of dermatology. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Chichester
Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, Coldiron BM (2012) Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population. JAMA Dermatol 151(10):1081–1086
Rox JM, Reinartz J, Kramer MD (1996) Interleukin-1 beta upregulates tissue-type plasminogen activator in a keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT). Arch Dermatol Res 288(9):554–558
Ruano J, Suárez-Fariñas M, Shemer A, Oliva M, Guttman-Yassky E, Krueger JG (2016) Molecular and cellular profiling of scalp psoriasis reveals differences and similarities compared to skin psoriasis. PloS One 11(2):1–18
Santibanez JF (2013) Transforming growth factor-beta and urokinase-type plasminogen activator; dangerous partners in tumorigenesis. implications in skin cancer volume. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, UK, ISRN Dermatology. Article ID 597927
Sappino AP, Belin D, Huarte J, Hirschel-Scholz S, Saurat JH, Vassalli JD (1991) Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Investig 88(4):1073–1079
Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Thompson C (1997) Clinical impact of the plasminogen activation system in tumor invasion and metastasis; prognostic relevance and target for therapy. Thromb Hemost 78(1):285–296
Schmitt M, Mengele K, Napieralski R, Magdolen V, Reuning U, Gkazepis A (2010) Clinical utility of level-of-evidence-1 disease forecast cancer biomarkers uPA and its inhibitor PAI-1. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 10(8):1051–1067
Seetoo DQ, Crowe PJ, Russell PJ, Yang JL (2003) Quantitative expression of protein markers of plasminogen activation system in prognosis of colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 82(3):184–193
Spiers EM, Lazarus GS, Lyons-Giordano B (1994) Expression of plasminogen activator enzymes in psoriatic epidermis. J Investig Dermatol 102(3):333–338
Spiers EM, Lazarus GS, Lyons-Giordano B (1996) Expression of plasminogen activators in basal cell carcinoma. J Pathol 178:290–296
Teofoli P, Mancini A, Lotti T (1996) Cyclosporine A inhibits tPA mRNA transcription in A431 cell line. Skin Pharmacol 9(2):137–140
Tkachuk VA, Plekhanova OS, Beloglazova IB, Parfenova EV (2013) A role of multi-domain structure of urokinase in regulating vascular growth and remodeling. Ukr Biokhim Zh 85:18–45
Tsuboi R, Yamaguchi T, Kurita Y, Nakao H, Ishihara K (1988) Comparison of proteinase activities in squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell epithelioma, and seborrheic keratosis. J Investig Dermatol 90:869–872
Tutrone WD, Saini R, Weinberg JM (2004) Biological therapy for psoriasis; an overview of infliximab, etanercept, efalizumab and alefacept. I Drugs 7(1):45–49
Vassalli J-D (1994) The urokinase receptor. Fibrinolysis 8(1):172–181
Zhang Y, Kenny HA, Swindell EP, Mitra AK, Hankins PL, Ahn RW, Gwin K, Mazar AP, O’Halloran TV, Lengyel E (2013) Urokinase plasminogen activator system-targeted delivery of nanobins as a novel ovarian cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 12(12):2628–2639
Acknowledgements
Source of funding: Grant (No. 14-24-00086) of the Russian Science Foundation. The authors acknowledge that the work was carried out using equipment purchased with the funding from the Program of Development of M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Bioethical Committee of Russian Cardiology Research Center and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubina, K.A., Sysoeva, V.Y., Zagorujko, E.I. et al. Increased expression of uPA, uPAR, and PAI-1 in psoriatic skin and in basal cell carcinomas. Arch Dermatol Res 309, 433–442 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-017-1738-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00403-017-1738-z