Abstract
Introduction
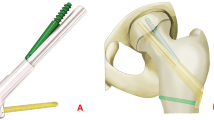
Posterior comminution of the femoral neck fracture is a major cause of delayed and non-union owing to the loss of the buttressing effect against the posterior rotation. When a femoral neck fracture with posterior comminution is anatomically reduced, only the anterior portions of the femoral neck fracture surfaces are brought into contact leaving a posterior defect. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the use of fibular strut grafting and dynamic hip screw (DHS) for fresh femoral neck fractures with posterior comminution in young patient less than 50 years.
Materials and methods
Between October 2012 and March 2016, 35 patients aged 20–50 years, 30 men and 5 women underwent fixation using DHS and fibular strut grafts for Garden grades III (25 patients) and IV (10 patients) femoral neck fractures with posterior comminution. All fractures were reduced by closed methods, and no hip was aspirated. Clinical and radiological outcomes were evaluated.
Results
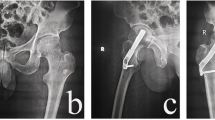
All patients were in the age group of 20–50 years (mean 37 years). The mean delay in presentation after injury was 1 day. The mean final follow-up for these 35 patients was 27.2 months. Healing of the femoral neck was attained in 34 cases, with an average time to union of 4.8 months (range 4–8 months). One patient underwent arthroplasty due to failure of fixation. According to the Harris hip score, outcome was good to excellent in 30 patients, fair in 4, and poor in 1.
Conclusions
In our study, only one patient developed non-union and no patients had avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Closed reduction, fibular strut grafts, and DHS fixation is a reliable procedure for femoral neck fractures with posterior comminution in young adults.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagi ON, Dhillon MS (2003) Management of neglected/ununited fractures of the femoral neck in young adults. Curr Orthop 17:394–402
Lifeso R, Young D (1990) The neglected hip fracture. J Orthop Trauma 4:287–292
Leung PC, Shen WY (1993) Fracture of the femoral neck in younger adults: a new method of treatment for delayed and nonunions. Clin Orthop 295:156–160
Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM, Christie J (1995) Hip fractures in adults younger than 50 years of age: epidemiology and results. Clin Orthop 312:238–246
Dedrick DK, Mackenzie JR, Burney RE (1986) Complications of femoral neck fracture in young adults. J Trauma 26:932–937
Swiontkowski MF, Winquist RA, Hansen ST (1984) Fractures of the femoral neck in patients between the ages of twelve and forty-nine years. J Bone Jt Surg Am 66:837–846
Protzman RB, Burkhalter WE (1976) Femoral neck fractures in young adults. J Bone Jt Surg Am 58:689–695
Huang C-H (1986) Treatment of neglected femoral neck fractures in young adults. Clin Orthop 206:117–126
Mittal Ravi, Banerjee Sumit (2012) Proximal femoral fractures: principles of management and review of literature. J Clin Orthop Trauma 3:15–23
Bosch U, Schreiber T, Krettek C (2002) Reduction and fixation of displaced intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop 339:59–71
Parker MJ (2000) The management of the intracapsular fractures of the proximal femur. J Bone Jt Surg (Br) 82:937–941
Gautum VK, Anand S, Dhaon BK (1998) Management of displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults (a group at risk). Injury 29:215–218
Bray TJ (1997) Femoral neck fracture fixation. Clin Orthop 339:20–31
Atin Jaiswal KK, Pruthi RK Goyal et al (2013) Evaluation of osteosynthesis with dual fibular bone grafting for neglected femoral neck fractures. J Clin Orthop Trauma 4:58–69
Ye Ye, Hao Jiandong, Mauffrey Cyrill et al (2015) Optimizing stability in femoral neck fracture fixation. Trauma Update 38(10):625–630
Asnis SE, Wanek-Sgaglione L (1994) Intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck: results of cannulated screw fixation. J Bone Jt Surg (Am) 76:1793–1803
Parker MJ (1994) Parallel garden screws for intracapsular femoral fractures. Injury 25:383–385
Lazaro LE, Birnbaum JF, Farshad-Amacker NA et al (2016) Endosteal biologic augmentation for surgical fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma 30(2):81–88
Weil YA, Khoury A, Zuaiter I et al (2012) Femoral neck shortening and varus collapse after navigated fixation of intracapsular femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma 26:19–23
Lorich D, Lazaro L, Boraih S (2013) Master technique in orthopaedic surgery: femoral neck fracture open reduction and internal fixation. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Boraiah S, Paul O, Hammoud S et al (2010) Predictable healing of femoral neck fractures treated with intraoperative compression and length-stable implants. J Trauma 69:142–147
Wendt M, Cass J, Trousdale R (2013) Incidence of radiographic cam-type impingement in young patients (<50) after femoral neck fracture treated with reduction and internal fixation. HSSJ 9:113–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Adham Elgeidi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Abed El-Negery declares that he has no conflict of interest. M. Serry Abdellatif declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nabil El Moghazy declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elgeidi, A., El Negery, A., Abdellatif, M.S. et al. Dynamic hip screw and fibular strut graft for fixation of fresh femoral neck fracture with posterior comminution. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 137, 1363–1369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2758-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2758-z