Abstract
Magnetic nanoparticles attached to hydrophilic polymer brushes containing immobilized Fe3+ ions were synthesized and used as a new strategy for phosphopeptide enrichment from digested tryptic proteins. To test the performance of nanoparticles in phosphopeptide enrichment, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) was used. Magnetic nanoparticles with the following features such as high adsorption capacity (about 360 mg/g), easy control and transfer by external magnetic field (high magnetic saturation, about 50 emu/g), excellent phosphopeptide recovery (93.4%) and no shadow effect (due to their non-porous structure), were synthesized. It has been shown that the presence of other proteins in high concentrations does not affect on the performance of nanoparticles. Furthermore, the lowest concentration of digested β-casein phosphopeptides detectable by nanoparticles was determined to be approximately 0.5 fmol µL− 1. The function of synthesized nanoparticles to enrich phosphopeptides in complex biological samples was also demonstrated by isolating four endogenous phosphopeptides from human serum.
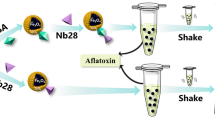
Graphical Abstract

A dispersion containing Fe-MNPs is added to a phosphopeptide solution. Then, using a magnet, particles containing phosphopeptides are separated from the solution









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Cantrell D (1996) T cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Immunol 14:259. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.259
Johnson SA, Hunter T (2005) Kinomics: methods for deciphering the kinome. Nat Methods 2:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth731
Fraser KB, Moehle MS, Alcalay RN, West AB, Consortium LC (2016) Urinary LRRK2 phosphorylation predicts parkinsonian phenotypes in G2019S LRRK2 carriers. Neurology 86:994–999. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002436
Dong M, Wu M, Wang F, Qin H, Han G, Dong J, Wu RA, Ye M, Liu Z, Zou H (2010) Coupling strong anion-exchange monolithic capillary with MALDI-TOF MS for sensitive detection of phosphopeptides in protein digest. Anal Chem 82:2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac902907w
Ashman K, Villar EL (2009) Phosphoproteomics and cancer research. Clin Transl Oncol 11:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-009-0369-z
Wang Z, Cheng G, Liu Y, Zhang J, Sun D, Ni J (2013) Novel 3D flowerlike hierarchical gamma-Fe2O3@xNH4F.yLuF3 core-shell microspheres tailor-made by a phase transformation process for the capture of phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B 1:4845–4854. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20743a
Posewitz MC, Tempst P (1999) Immobilized gallium(III) affinity chromatography of phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 71:2883–2892
Zhou H, Ye M, Dong J, Corradini E, Cristobal A, Heck AJ, Zou H, Mohammed S (2013) Robust phosphoproteome enrichment using monodisperse microsphere-based immobilized titanium (IV) ion affinity chromatography. Nat Protoc 8:461–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.010
Yao Y, Dong J, Dong M, Liu F, Wang Y, Mao J, Ye M, Zou H (2017) An immobilized titanium (IV) ion affinity chromatography adsorbent for solid phase extraction of phosphopeptides for phosphoproteome analysis. J Chromatogr A 1498:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.03.026
Chen J, Shinde S, Koch MH, Eisenacher M, Galozzi S, Lerari T, Barkovits K, Subedi P, Kruger R, Kuhlmann K, Sellergren B, Helling S, Marcus K (2015) Lowbias phosphopeptide enrichment from scarce samples using plastic antibodies. Sci Rep 5:11438. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11438
Zhou J (2018) Phosphopeptide enrichment with cross-linked os(II)(dmebpy)2Clderivatized acrylamide and vinylimidazole copolymer. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 32:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.7985
Tang R, Yu Y, Dong J, Yao Y, Ma S, Ou J, Ye M (2021) Facile preparation of bifunctional adsorbents for efficiently enriching N-glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta 1144:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.12.015
Najam-ul-Haq M, Saeed A, Jabeen F, Maya F, Ashiq MN, Sharif A (2014) Newly developed poly(allyl glycidyl ether/divinyl benzene) polymer for phosphopeptides enrichment and desalting of biofluids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3536–3545. https://doi.org/10.1021/am405718j
Saeed A, Najam-ul-Haq M, Jabeen F, Svec F (2013) High affinity phosphopeptides enrichment and desalting of biological materials on newly engineered poly(glycidyl propargyl ether/divinyl benzene). Anal Chem 85:8979–8986. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4015484
Lu Q, Chen C, Xiong Y, Li G, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang D, Zhu Z, Li X, Qing G, Sun T, Liang X (2020) High-efficiency phosphopeptide and glycopeptide simultaneous enrichment by hydrogen bond-based bifunctional smart polymer. Anal Chem 92:6269–6277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02643
Zhou H, Ye M, Dong J, Han G, Jiang X, Wu R, Zou H (2008) Specific phosphopeptide enrichment with immobilized titanium ion affinity chromatography adsorbent for phosphoproteome analysis. J Proteome Res 7:3957–3967. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr800223m
Zhou H, Xu S, Ye M, Feng S, Pan C, Jiang X, Li X, Han G, Fu Y, Zou H (2006) Zirconium phosphonate-modified porous silicon for highly specific capture of phosphopeptides and MALDI-TOF MS analysis. J Proteome Res 5:2431–2437. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr060162f
Ma S, Tang R, Yu Y, Zhang L, Zhang H, Ding W, Ou J (2021) Robust titanium phenolate-modified microspheres as reusable affinity materials for selectively capturing phosphopeptides from complicated biosamples. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9:17025–17033. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c05864
Wang Z, Cheng G, Liu Y, Zhang J, Sun D, Ni J (2012) Fabrication of novel hierarchical structured Fe3O4@LnPO4 (Ln¼Eu, Tb, Er) multifunctional microspheres for capturing and labeling phosphopeptides. Small 8:3456–3464. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200601
Tang R, Zhou J, Li X, Yu Y, Ma S, Ou J (2022) Facile one-pot preparation of phosphonate functional polythiophene based microsphere via Friedel-Crafts reaction for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides from milk. Anal Chim Acta 1190:339268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339268
Yan Y, Zheng Z, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X, Yang P (2013) Hydrophilic polydopaminecoated graphene for metal ion immobilization as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform for phosphoproteome analysis. Anal Chem 85:8483–8487. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401668e
Shi C, Deng C (2015) Immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography ZipTip pipette tip with polydopamine modification and Ti4 immobilization for selective enrichment and isolation of phosphopeptides. Talanta 143:464–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.039
Shi C, Deng C, Zou S, Zhang X (2014) Polydopamine-coated eppendorf tubes for Ti4 immobilization for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 127:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.03.054
Shi C, Lin Q, Deng C (2015) Preparation of on-plate immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform via dopamine chemistry for highly selective isolation of phosphopeptides with matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis. Talanta 135:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.12.041
Wang H, Tian Z (2018) Facile synthesis of titanium (IV) ion immobilized adenosine triphosphate functionalized silica nanoparticles for highly specific enrichment and analysis of intact phosphoproteins. J Chromatogr A 1564:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.06.013
Sun N, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X (2014) Size-Exclusive Magnetic Graphene/Mesoporous Silica Composites with Titanium(IV)-Immobilized pore walls for Selective Enrichment of endogenous phosphorylated peptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:11799–11804. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502529a
Hong Y, Yao Y, Zhao H, Sheng Q, Ye M, Yu C, Lan M (2018) Dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles with abundant Ti4 for phosphopeptide enrichment from cancer cells with 96% specificity. Anal Chem 90:7617–7625. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01369
Hussain D, Najam-ul-Haq M, Jabeen F, Ashiq MN, Athar M, Rainer M, Huck CW, Bonn GK (2013) Functionalized diamond nanopowder for phosphopeptides enrichment from complex biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 775:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.03.007
Zhao L, Qin H, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Wu RA, Zou H (2012) A poly(ethylene glycol)- brush decorated magnetic polymer for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Sci 3:2828–2838. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2sc20363d
Wang Q, He X, Chen X, Zhu G, Wang R, Feng Y (2017) Pyridoxal 5 ‘-phosphate mediated preparation of immobilized metal affinity material for highly selective and sensitive enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Chromatogr A 1499:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.03.085
Wang H, Jiao F, Gao F, Lv Y, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Shen Y, Zhang Y, Qian X (2017) Titanium (IV) ion-modified covalent organic frameworks for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 166:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.043
Liu Y, Xia C, Fan Z, Jiao F, Gao F, Xie Y, He Z, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Shen Y, Qian X, Qin W (2020) Novel two-dimensional MoS2-Ti4 nanomaterial for efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides and large-scale identification of histidine phosphorylation by mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 92:12801–12808. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00618
Li JY, Cao Z, Hua Y, Wei G, Yu XZ, Shang W, Lian H (2020) Solvothermal synthesis of novel magnetic nickel based iron oxide nanocomposites for selective capture of global- and mono-phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 92:1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04053
Ding F, Zhao Y, Liu H, Zhang W (2020) Core-shell magnetic microporous covalent organic framework with functionalized Ti(Iv) for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Analyst 145:4341–4351. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00038h
Gao C, Bai J, He Y, Zheng Q, Ma W, Lei Z, Zhang M, Wu J, Fu F, Lin Z (2019) Postsynthetic functionalization of Zr4-immobilized core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:13735–13741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03330
Chu H, Zheng H, Miao A, Deng C, Sun N (2023) Probing region-resolved heterogeneity of phosphoproteome in human lens by hybrid metal organic frameworks. Chin Chem Lett 34:107716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2022.07.059
Chen L, Ou J, Wang H, Liu Z, Ye M, Zou H (2016) Tailor-made stable zr(IV)-based metal-organic frameworks for laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis of small molecules and simultaneous enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:20292–20300. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b06225
He Y, Zheng Q, Lin Z (2021) Ti+ 4-immobilized hierarchically porous zirconiumorganic frameworks for highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 188:150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04760-x
Pu C, Zhao H, Gu Q, Zheng Y, Lan M (2020) Targeted immobilization of titanium (IV) on magnetic mesoporous nanomaterials derived from metal-organic frameworks for high-efficiency phosphopeptide enrichment in biological samples. Microchim Acta 187:568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04556-5
Hart SR, Waterfield MD, Burlingame AL, Cramer R (2002) Factors governing the solubilization of phosphopeptides retained on ferric NTA IMAC beads and their analysis by MALDI TOFMS. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 13:1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(02)00432-4
Hong Y, Zhan Q, Pu C, Sheng Q, Zhao H, Lan M (2018) Highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides from HeLa cells using hollow magnetic macro/mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles. Talanta 187:223–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.05.031
Zhang Y, Yu X, Wang X, Shan W, Yang P, Tang Y (2004) Zeolite nanoparticles with immobilized metal ions: isolation and MALDI-TOF-MS/MS identification of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 2882–2883. https://doi.org/10.1039/B411336E
Rembsum A, Dreyer W (1980) Immunomicrospheres: reagents for cell labeling and separation. Science 208:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.6768131
Li D, Tang J, Wei C, Guo J, Wang S, Chaudhary D, Wang C (2012) Doxorubicin-conjugated mesoporous magnetic colloidal nano crystal clusters stabilized by polysaccharide as a smart anticancer drug vehicle. Small 8:2690–2697. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200272
Salimi K, Usta DD, Koçer I, Çelikad E, Tuncel A (2017) Highly selective magnetic affinity purification of histidine-tagged proteins by Ni2+ carrying monodisperse composite microspheres. RSC Adv 7:8718. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA27736E
Horak D, Rittich B, Safar J, Spanova A, Lenfeld J, Benes MJ (2001) Properties of RNase A immobilized on magnetic poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) Microspheres. Biotechnol Prog 17:447. https://doi.org/10.1021/bp0100171
Huang W, Kim J-B, Bruening ML, Baker GL (2002) Functionalization of surfaces by water-accelerated atom-transfer radical polymerization of hydroxyethyl methacrylate and subsequent derivatization. Macromolecules 35:1175–1179. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma011159e
Ulbricht M, Yang H (2005) Porous polypropylene membranes with different carboxyl polymer brush layers for reversible protein binding via surface-initiated graft copolymerization. Chem Mater 17:2622–2631. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0485714
Brown HR, Char K, Deline VR (1990) Enthalpy-driven swelling of a polymer brush. Macromolecules 23:3383–3385. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00215a029
Andruzzi L, Senaratne W, Hexemer A, Sheets ED, Ilic B et al (2005) Oligo(ethylene glycol) containing polymer brushes as bioselective surfaces. Langmuir 21:2495–2504. https://doi.org/10.1021/la047574s
Ma HW, Hyun JH, Stiller P, Chilkoti A (2004) Non-fouling oligo(ethylene glycol)-functionalized polymer brushes synthesized by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Adv Mater 16:338–341. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200305830
Zhang Z, Chen SF, Jiang SY (2006) Dual-functional biomimetic materials: nonfouling poly(carboxybetaine) with active functional groups for protein immobilization. Biomacromolecules 7:3311–3315. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060750m
Shirzadi Z, Baharvand H, Nikpour Nezhati M, Sajedi RH (2020) Synthesis of nonlinear polymer brushes on magnetic nanoparticles as an affinity adsorbent for his-tagged xylanase purification. Colloid Polym Sci 298:1597–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04749-7
Asara JM, Allison J (1999) Enhanced detection of phosphopeptides in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using ammonium salts. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 10:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1044-0305(98)00129-9
Chang CK, Wu CC, Wang YS, Chang HC (2008) Selective extraction and Enrichment of Multiphosphorylated peptides using polyarginine-coated Diamond nanoparticles. Anal Chem 80:3791–3797. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac702618h
Hu Y, Guo S, Ma H, Ye N, Ren X (2013) Preparation and loading buffer study of polyvinyl alcohol-based immobilized Ti4+ affinity chromatography for phosphopeptide enrichment. J Sep Sci 36:3563–3570. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300622
Boersema PJ, Raijmakers R, Lemeer S, Mohammed S, Heck AJR (2009) Multiplex peptide stable isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Nat Protoc 4:484–494. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.21
Xiong Z, Zhang L, Fang C, Zhang Q, Ji Y, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Zou H (2014) Ti4+-immobilized multilayer polysaccharide coated magnetic nanoparticles for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B 2:4473. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TB00479E
Chen Y, Xiong Z, Peng L, Gan Y, Zhao Y, Shen J, Qian J, Zhang L, Zhang W (2015) Facile preparation of core–shell magnetic metal–organic framework nanoparticles for the selective capture of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:16338–16347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03335
Hu L, Zhou H, Li Y, Sun S, Guo L, Ye M, Tian X, Gu J, Yang S, Zou H (2009) Profiling of endogenous serum phosphorylated peptides by Titanium (IV) immobilized mesoporous silica particles Enrichment and MALDI-TOFMS detection. Anal Chem 81:94–104. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac801974f
Acknowledgements
We appreciate Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute and the Department of Chemistry of Islamic Azad University, Central Tehran Branch for their support.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Z. Shirzadi, H. Baharvand, M. Nikpour Nezhati, H. Ahmad Panahi and R. H. Sajedi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Zahra Shirzadi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare They have their consent to participate and publish of this article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shirzadi, Z., Baharvand, H., Nezhati, M.N. et al. Nonlinear polymer brush modified magnetic nanoparticles in phosphopeptides enrichment. Colloid Polym Sci 302, 911–923 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-024-05244-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-024-05244-z