Abstract
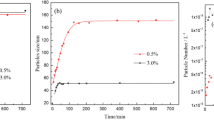
Monodisperse polystyrene microspheres with different functional groups have important applications in both the medical and analytical fields. In this study, we prepared monodisperse microspheres with sulfonic acid or carboxyl groups using soap-free emulsion polymerization (SFEP) with potassium persulfate as the initiator. A series of monodisperse polystyrene microspheres with sizes between 100 and 500 nm were successfully prepared by copolymerizing different types of ionic monomers at different concentrations. The microspheres were characterized by using dynamic light scattering (DLS), Zeta potential measurements (ZP), FT-IR spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The mechanism of the particle nucleation and growth were studied by combining the changes in particle size and the number of particles. The results showed that the addition of hydrophilic comonomers like sodium p-styrene sulfonate, acrylic acid, and methacrylic acid significantly improved the stability of the polystyrene microspheres and promoted particle nucleation, resulting in less particle aggregation and microspheres with smaller sizes.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prasath RA, Margarit-Puri K, Klapper M (2007) Emulsifier-free emulsion polymerization of styrene with 4-vinylbenzoic acid: kinetics and distribution of the carboxyl groups. Appl Polym Sci 103:2910–2919. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25066
Liu B, Bai Y, Sun C, Chen M, Cao Z, Du S, Xu L, Zhang M (2019) Synthesis of monodisperse, re-dispersable polymer particles by one-step high solid emulsion polymerization in the presence of reactive surfactant. J Dispers Sci Technol 2019:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1505527
Yaamoto T, Furuta R, Kawai Y (2019) Effect of initiator charge on dispersion stability of polymer particles formed by soap-free emulsion polymerization of 4-vinylaniline or 4-vinylpyridine. Chem Lett 48:208–210. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.180917
Liu B, Meng W, Wang P, Zhang M, Zhang H (2016) In situ charge neutralization-controlled particle coagulation and its effects on the particle size distribution in the one-step emulsion polymerization. Eur Polym J 83:278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.08.027
Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE (2001) Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Contr Release 70:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-3659(00)00340-0
Yang W, Yan S, Wei C, Wang Q (2010) Preparation of melamine molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres by precipitation polymerization. Acta Polym Sin 10:1163–1169. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1105.2010.09347
Li L, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2019) Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Asian J 4:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.200800300
Zhang S, Chen J, Taha M (2009) Synthesis of monodisperse styrene/methyl methacrylate/acrylic acid latex using surfactant-free emulsion copolymerization in air. J Appl Polym Sci 114:1598–1605. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30744
Bai F, Yang X, Li R, Huang B, Huang W (2006) Monodisperse hydrophilic polymer microspheres having carboxylic acid groups prepared by distillation precipitation polymerization. Polymer 47:5775–5784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2006.06.014
Ceska G (1974) The effect of carboxylic monomers on surfactant-free emulsion copolymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 18:427–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1974.070180210
Yan C, Cheng S, Feng L (1999) Kinetics and mechanism of emulsifier-free emulsion copolymerization: styrene-methyl methacrylate-acrylic acid system. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 37:2649–2656. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19990715)37:14<2649::AID-POLA40>3.0.CO;2-L
Abdollahi M (2007) Effect of carboxylic acid monomer type on particle nucleation and growth in emulsifier-free emulsion copolymerization of styrene-carboxylic acid monomer. Polym J 39:802–812. https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.PJ2006246
Wang H, Liu B, Zhang M, Du S, Wu G, Hu Y, Liu X (2020) Narrow-disperse, cross-linked polymer microspheres by one-step dispersion polymerization with a chain transfer agent. Polym Adv Technol 31:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4776
Wang P, Pan C (2001) Emulsion copolymerization of styrene with acrylic or methacrylic acids- distribution of the carboxylic group. Colloid Polym Sci 279:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960000407
Wen F, Zhang W, Zheng P, Zheng X, Yang X, Wang Y, Jang X, Wei G, Shi L (2008) One-stage synthesis of narrowly dispersed polymeric core-shell microspheres. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 46:1192–1202. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.22460
Deng W, Li R, Zhang M, Gong L, Kan C (2010) Influences of MAA on the porous morphology of P(St-MAA) latex particles produced by batch soap-free emulsion polymerization followed by stepwise alkali/acid post-treatment. J Colloid Interface Sci 349:122–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.05.033
Meincke T, Jordan M, Vogel N, Robin N (2018) On the size-determining role of the comonomer in the nucleation and growth of cationic polystyrene latex via emulsion polymerization. Macromol Chem Phys 219:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.201700457
Liu Z, Xiao H, Wiseman N (2000) Emulsifier-free emulsion copolymerization of styrene with quaternary ammonium cationic monomers. J Appl Polym Sci 76:1129–1140. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(20000516)76:7<1129::AID-APP17>3.0.CO;2-O
Zhang J, Zhao X, Wang Y, Zhu L, Yang L, Li G, Sha S (2017) Synthesis of vertically-aligned zinc oxide nanowires and their application as a photocatalyst. Nanomaterials 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7010009
De La Rosa L, Sudol E, El-Aasser M, Klein A (1999) Emulsion polymerization of styrene using reaction calorimeter. I. Above and below critical micelle concentration. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 37:4054–4065. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19991115)37:22<4054::AID-POLA4>3.0.CO;2-7
Polpanich D, Tangboriboonrat P, Elaïssari A (2005) The effect of acrylic acid amount on the colloidal properties of polystyrene latex. Colloid Polym Sci 284:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-005-1366-6
Kang K, Kan C, Du Y, Liu D (2006) Study on soap-free P(MMA-EA-AA or MAA) latex particles with narrow size distribution. Polym Adv Technol 17:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.714
Zhang J, Cheng S, Lu G, Cha S (2009) Kinetics and particle nucleation mechanism of St/BA/QBVPBr emulsifier-free cationic emulsion polymerization. J Appl Polym Sci 111:2092–2098. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29276
Li Z, Cheng H, Han C (2012) Mechanism of narrowly dispersed latex formation in a surfactant-free emulsion polymerization of styrene in acetone–water mixture. Macromolecules 45:3231–3239. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma202535j
Kobayashi M, Juillerat F, Galletto P, Bowen P, Borkovec M (2005) Aggregation and charging of colloidal silica particles: effect of particle size. Langmuir 21:5761–5769. https://doi.org/10.1021/la046829z
Zhao X, Sun M, Duan Y, Hao H (2020) Superhydrophobic coatings based on raspberry-like nanoparticles and their applications on cotton. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 602:125039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125039
Yamamoto T, Nakayama M, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2006) Growth mechanism of soap-free polymerization of styrene investigated by AFM. J Colloid Interface Sci 297(1):112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.10.025
Nagao D, Yamada Y, Inukai S, Ishii H, Konno M, Gu S (2015) Quantitative understanding of the self-sharpening of growing polymer particle size distributions in soap-free emulsion polymerization. Polym. 68:176–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.05.020
Bai Y, Luo X, Han Y, Liu B, Zhang J, Zhang M (2020) Facile synthesis of narrow particle size distribution, high solid content, cationic polymer latexes by macroemulsion polymerization-based particle coagulation mechanism. J Macromol Sci, Part A: Pure Appl Chem 57:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2019.1673175
Zhang B, Lu J, Liu X, Jin H, He G, Guo X (2018) Synthesis of controllable carboxylated polystyrene microspheres by two-step dispersion polymerization with hydrocarbon alcohols. Int J Polym Sci 2018:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8702597
Fariascepeda L, Herreraordonez J, Hernandezmartinez A, Estevez M, Rosalesmarines L (2017) Super-enhanced particle nucleation in styrene emulsion polymerization in the presence of sodium styrene sulfonate. Colloid Interface Sci 500:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.015
Arunbabu D, Sanga Z, Seenimeera K, Jana T (2009) Emulsion copolymerization of styrene and sodium styrene sulfonate: kinetics, monomer reactivity ratios and copolymer properties. Polym Int 58:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.2497
Adelnia H, Pourmahdian S (2014) Soap-free emulsion polymerization of poly (methyl methacrylate-co-butyl acrylate): effects of anionic comonomers and methanol on the different characteristics of the latexes. Colloid Polym Sci 292:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-013-3043-5
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.51903017) and People’s Goverment of Jilin Province Development and Reform Commission Program of China (2019C041-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Xu, L., Liu, Y. et al. Preparation of monodisperse polystyrene microspheres with different functional groups using soap-free emulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 1095–1102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04830-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04830-9