Abstract
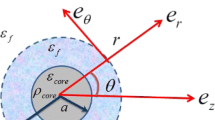
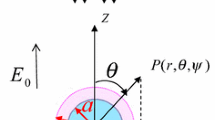
Electrophoresis of a soft particle with a charged polarizable core is analyzed theoretically. The soft particle is embedded in an uncharged hydrogel medium. The hydrodynamics in both the gel medium and the soft layer encapsulating the hard core are governed by the Darcy-Brinkman model. We have considered the numerical model based on the conservation principle of mass, momentum, and ion flux, leading to a coupled set of partial differential equations. A simplified approach under the weak field and low charge density consideration is also proposed. The subtle nonlinear effects arising due to the polarization and relaxation of the double layer and the convective transport of counterions induced by the immobile charge of soft layer are elucidated. These nonlinear effects have negligible impact when the bulk ionic concentration becomes high. The simplified model under the weak field consideration is independent of the core dielectric permittivity. However, the numerical model shows a strong dependence on core permittivity when the applied electric field is moderate. We have also addressed the ion partitioning effect when the dielectric permittivity of the soft layer is different from the gel medium. This creates a counterion saturation in the soft layer, and hence an augmentation in the electrophoresis.

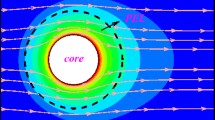
Distribution of counterion concentration and electric field lines around a charged soft particle in hydrogel medium







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen TH, Easter N, Gutierrez L, Huyett L, Defnet E, Mylon SE, Ferri JK, Viet NA (2011) The RNA core weakly influences the interactions of the bacteriophage MS2 at key environmental interfaces. Soft Matter 7(21):10449–10456
Win KY, Feng S-S (2005) Effects of particle size and surface coating on cellular uptake of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 26(15):2713–2722
Brown SD, Fiedler JD, Finn MG (2009) Assembly of hybrid bacteriophage qβ virus-like particles. Biochemistry 48(47):11155–11157
Šiber A, Podgornik R (2007) Role of electrostatic interactions in the assembly of empty spherical viral capsids. Phys Rev E 76(6):061906
Šiber A, Božič AL, Podgornik R (2012) Energies and pressures in viruses: contribution of nonspecific electrostatic interactions. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14(11):3746–3765
Stock-Ley PG, Stonehouse NJ, Valegård K (1994) Molecular mechanism of RNA phage morphogenesis. Int J Biochem 26(10-11):1249–1260
Duval JFL, Ohshima H (2006) Electrophoresis of diffuse soft particles. Langmuir 22(8):3533–3546
Duval JFL, Werner C, Zimmermann R (2016) Electrokinetics of soft polymeric interphases with layered distribution of anionic and cationic charges. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science 24:1–12
Ohshima H (1995) Electrophoresis of soft particles. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 62(2-3):189–235
Ohshima H (1994) Electrophoretic mobility of soft particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 163(2):474–483
Ohshima H (2002) Modified henry function for the electrophoretic mobility of a charged spherical colloidal particle covered with an ion-penetrable uncharged polymer layer. J Colloid Interface Sci 252(1):119–125
Ohshima H (2006) Electrophoresis of soft particles: analytic approximations. Electrophoresis 27 (3):526–533
Duval JFL, Gaboriaud F (2010) Progress in electrohydrodynamics of soft microbial particle interphases. Current Opinion in Colloid and Interface Science 15(3):184–195
Saville DA (2000) Electrokinetic properties of fuzzy colloidal particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 222(1):137–145
Hill RJ, Saville DA, Russel WB (2003) Polarizability and complex conductivity of dilute suspensions of spherical colloidal particles with charged (polyelectrolyte) coatings. J Colloid Interface Sci 263 (2):478–497
López-Viota J, Mandal S, Delgado AV, Toca-Herrera JL, Möller M, Zanuttin F, Balestrino M, Krol S (2009) Electrophoretic characterization of gold nanoparticles functionalized with human serum albumin (HSA) and creatine. J Colloid Interface Sci 332(1):215–223
Cametti C (2011) Dielectric properties of soft-particles in aqueous solutions. Soft Matter 7 (12):5494–5506
Yeh L-H, Fang K-Y, Hsu J-P, Tseng S (2011) Influence of boundary on the effect of double-layer polarization and the electrophoretic behavior of soft biocolloids. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 88 (2):559–567
Tseng S, Hsu J-P, Lo H-M, Yeh L-H (2013) Electrophoresis of a soft sphere in a necked cylindrical nanopore. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15(28):11758–11765
Dingari NN, Buie CR (2014) Theoretical investigation of bacteria polarizability under direct current electric fields. Langmuir 30(15):4375–4384
Moussa M, Caillet C, Town RM, Duval JFL (2015) Remarkable electrokinetic features of charge-stratified soft nanoparticles: Mobility reversal in monovalent aqueous electrolyte. Langmuir 31(20):5656–5666
Phan AD, Hoang TX (2019) The pH-dependent electrostatic interaction of a metal nanoparticle with the ms2 virus-like particles. Chem Phys Lett 730:84–88
Majee PS, Bhattacharyya S, Gopmandal PP, Ohshima H (2018) On gel electrophoresis of dielectric charged particles with hydrophobic surface: a combined theoretical and numerical study. Electrophoresis 39(5-6):794–806
Duval JFL, Zimmermann R, Cordeiro AL, Rein N, Werner C (2009) Electrokinetics of diffuse soft interfaces. IV. analysis of streaming current measurements at thermoresponsive thin films. Langmuir 25(18):10691–10703
Brady JF (1994) Response to “Comment on ‘The rheological behavior of concentrated colloidal dispersions”’[j. chem. phys. 101, 1757 (1994)]. The Journal of Chemical Physics 101(2):1758–1758
Johansson L, Löfroth J-E (1993) Diffusion and interaction in gels and solutions. 4. hard sphere Brownian dynamics simulations. The Journal of chemical physics 98(9):7471–7479
Bhattacharyya S, De S, Gopmandal PP (2014) Electrophoresis of a colloidal particle embedded in electrolyte saturated porous media. Chem Eng Sci 118:184–191
Allison SA, Xin Y, Pei H (2007) Electrophoresis of spheres with uniform zeta potential in a gel modeled as an effective medium. J Colloid Interface Sci 313(1):328–337
Allison SA, Li F, Hill RJ (2014) The electrophoretic mobility of a weakly charged “soft”? sphere in a charged hydrogel: application of the lorentz reciprocal theorem. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 118(29):8827–8838
Tsai P, Huang C-H, Lee E (2011) Electrophoresis of a charged colloidal particle in porous media: boundary effect of a solid plane. Langmuir 27(22):13481–13488
Hsu J-P, Huang C-H, Tseng S (2012) Gel electrophoresis: importance of concentration-dependent permittivity and double-layer polarization. Chem Eng Sci 84:574–579
Hsu J-P, Huang C-H, Tseng S (2013) Gel electrophoresis of a charge-regulated, bi-functional particle. Electrophoresis 34(5):785–791
Li F, Hill RJ (2013) Nanoparticle gel electrophoresis: bare charged spheres in polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J Colloid Interface Sci 394:1–12
Li F, Allison SA, Hill RJ (2014) Nanoparticle gel electrophoresis: soft spheres in polyelectrolyte hydrogels under the debye–hückel approximation. J Colloid Interface Sci 423:129–142
Langlet J, Gaboriaud F, Gantzer C, Duval JFL (2008) Impact of chemical and structural anisotropy on the electrophoretic mobility of spherical soft multilayer particles: the case of bacteriophage ms2. Biophys J 94(8):3293–3312
Phan AD, Tracy DA, Nguyen TLH, Viet NA, Phan T-L, Nguyen TH (2013) Electric potential profile of a spherical soft particle with a charged core. The Journal of Chemical Physics 139(24): 244908
López-Garcıa JJ, Horno J, Grosse C (2003) Suspended particles surrounded by an inhomogeneously charged permeable membrane. solution of the Poisson–Boltzmann equation by means of the network method. J Colloid Interface Sci 268(2):371– 379
Delgado AV, González-Caballero F, Hunter RJ, Koopal LK, Lyklema J (2007) Measurement and interpretation of electrokinetic phenomena. Journal of colloid and Interface Science 309(2):194–224
Ganjizade A, Ashrafizadeh SN, Sadeghi A (2017) Effect of ion partitioning on the electrostatics of soft particles with a volumetrically charged core. Electrochem Commun 84:19–23
Poddar A, Maity D, Bandopadhyay A, Chakraborty S (2016) Electrokinetics in polyelectrolyte grafted nanofluidic channels modulated by the ion partitioning effect. Soft Matter 12(27):5968–5978
Andrews J, Das S (2015) Effect of finite ion sizes in electric double layer mediated interaction force between two soft charged plates. RSC Advances 5(58):46873–46880
Yezek LP, Duval JFL, van Leeuwen HP (2005) Electrokinetics of diffuse soft interfaces. III. interpretation of data on the polyacrylamide/water interface. Langmuir 21(14):6220–6227
Young MA, Jayaram B, Beveridge DL (1998) Local dielectric environment of b-DNA in solution: results from a 14 ns molecular dynamics trajectory. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 102(39):7666–7669
Coster HGL (1973) The double fixed charge membrane: solution-membrane ion partition effects and membrane potentials. Biophysical journal 13(2):133–142
Bhattacharyya S, Gopmandal PP (2011) Migration of a charged sphere at an arbitrary velocity in an axial electric field. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 390(1-3):86–94
Majee PS, Bhattacharyya S, Dutta P (2019) On electrophoresis of a ph-regulated nanogel with ion partitioning effects. Electrophoresis 40(5):699–709
Maurya SK, Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya S, Ohshima H (2018) Ion partitioning effect on the electrophoresis of a soft particle with hydrophobic core. Phys Rev E 98(2):023103
Fletcher CAJ (2012) Computational techniques for fluid dynamics 2: specific techniques for different flow categories. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Landon LEM (1966) Fluid mechanics. Pergamon, London
Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya S, Banerjee M, Ohshima H (2016) Electrophoresis of diffuse soft particles with dielectric charged rigid core grafted with charge regulated inhomogeneous polymer segments. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 504:116–125
Gopmandal PP, Bhattacharyya S, Ohshima H (2017) Effect of hydrophobic core on the electrophoresis of a diffuse soft particle. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 473(2199):20160942
Kumar B, Gopmandal PP, Sinha RK, Ohshima H (2019) Electrophoresis of hydrophilic/hydrophobic rigid colloid with effects of relaxation and ion size. Electrophoresis 40(9):1282–1292
Ohshima H (2019) Gel electrophoresis of a soft particle. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 271:101977. Elsevier
Funding
P. P. G. acknowledges the financial support received from the Science and Engineering Research Board, Government of India through the project grant (File no. MTR/2018/001021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barman, S.S., Bhattacharyya, S., Gopmandal, P.P. et al. Impact of charged polarizable core on mobility of a soft particle embedded in a hydrogel medium. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1729–1739 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04751-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04751-z