Abstract
Water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) are synthesized from oleate-stabilized particles (IONPs-OA) by replacing oleate moieties with 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid (3,4-DHB) and polyethyleneimine (PEI). Investigation of the obtained composite nanoparticles by TEM, SEM, and AFM methods demonstrated that the parent IONPs-OA particles have a narrow size distribution and that the size of the magnetite core (4.3 nm) was retained in the polyethyleneimine modified IONPs-PEI nanoparticles (4.5 nm). IONPs-PEI exist in the form of separate nanoparticles distributed in the bulk polymer matrix as well as elongated chains (up to 20 nm in length) consisting of 3–6 nanoparticles, and mostly in the form of large clusters (~ 150 nm). The NMR relaxometric properties of IONPs-PEI in the water at various pHs are determined. Relaxivity of such modified nanoparticles remains constant over a wide pH range (3–9) and decreases only in strongly alkaline solutions due to the destruction processes. In the presence of physiological amounts of NaCl (0.15 M), the relaxivity of IONPs-PEI solutions is reduced by 37%. The effect of the addition of various iron(III) chelators is analyzed. Tiron (disodium 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonate) is the only ligand which destroys the polymer-bound IONP system in solution, dissolving the iron oxide core, while other ligands (3,4-DHB, 2,4-DHB, citric acid) do not reduce the relaxation of the composite aqueous solution. The developed polyethyleneimine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles can be regarded as a promising model of a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

ᅟ








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao G (2004) Nanostructures & nanomaterials: synthesis, properties & applications, Imperial college press
Sanchez C, Belleville P, Popall M, Nicole L (2011) Applications of advanced hybrid organic–inorganic nanomaterials: from laboratory to market. Chem Soc Rev 40(2):696–753
Barreto JA, O’Malley W, Kubeil M, Graham B, Stephan H, Spiccia L (2011) Nanomaterials: applications in cancer imaging and therapy. Adv Mater 23(12)
Edelstein A S, Cammaratra R (1998) Nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties and applications, CRC press
Fu C, Ravindra NM (2012) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and applications. Bioinspired, Biomimetic and Nanobiomaterials 1(4):229–244
Laurent S, Forge D, Port M, Roch A, Robic C, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2008) Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev 108(6):2064–2110
Rossi LM, Costa NJ, Silva FP, Wojcieszak R (2014) Magnetic nanomaterials in catalysis: advanced catalysts for magnetic separation and beyond. Green Chem 16(6):2906–2933
Teja AS, Koh P-Y (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55(1–2):22–45
Cornell R, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurences and uses.--Willey-VCH Verlag GmbH & co
Cullity BD, Graham CD (2011) Introduction to magnetic materials, John Wiley & Sons
Xu C, Xu K, Gu H, Zheng R, Liu H, Zhang X, Guo Z, Xu B (2004) Dopamine as a robust anchor to immobilize functional molecules on the iron oxide shell of magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126(32):9938–9939
Wen X, Yang J, He B, Gu Z (2008) Preparation of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles under mild conditions. Curr Appl Phys 8(5):535–541
Sun S, Zeng H (2002) Size-controlled synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 124(28):8204–8205
Lu Y, Yin Y, Mayers BT, Xia Y (2002) Modifying the surface properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles through a sol-gel approach. Nano Lett 2(3):183–186
Lai CW, Low FW, Tai MF, Abdul Hamid SB (2017) Iron oxide nanoparticles decorated oleic acid for high colloidal stability. Adv Polym Technol
Chanana M, Jahn S, Georgieva R, Lutz J-F, Baumler H, Wang D (2009) Fabrication of colloidal stable, thermosensitive, and biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles and study of their reversible agglomeration in aqueous milieu. Chem Mater 21(9):1906–1914
Aeineh N, Salehi F, Akrami M, Nemati F, Alipour M, Ghorbani M, Nikfar B, Salehian F, Riyahi Alam N, Sadat Ebrahimi SE, Foroumadi A, Khoobi M, Rouini M, Dibaei M, Haririan I, Ganjali MR, Safaei S (2018) Glutathione conjugated polyethylenimine on the surface of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a theranostic agent for targeted and controlled curcumin delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 29(10):1109–1125. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2018.1427013
Ai H (2011) Layer-by-layer capsules for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(9):772–788
Drake P, Cho H-J, Shih P-S, Kao C-H, Lee K-F, Kuo C-H, Lin X-Z, Lin Y-J (2007) Gd-doped iron-oxide nanoparticles for tumour therapy via magnetic field hyperthermia. J Mater Chem 17(46):4914
Gupta AK, Gupta M (2005) Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26(18):3995–4021
Ni D, Bu W, Ehlerding EB, Cai W, Shi J (2017) Engineering of inorganic nanoparticles as magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem Soc Rev 46(23):7438–7468
Schladt TD, Schneider K, Schild H, Tremel W (2011) Synthesis and bio-functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles for medical diagnosis and treatment. Dalton Trans 40(24):6315–6343
Song X, Gong H, Yin S, Cheng L, Wang C, Li Z, Li Y, Wang X, Liu G, Liu Z (2014) Ultra-small Iron oxide doped polypyrrole nanoparticles for in vivo multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. Adv Funct Mater, 24 (9)
Thorat ND, Lemine OM, Bohara RA, Omri K, El Mir L, Tofail SA (2016) Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocargoes for combined cancer thermotherapy and MRI applications. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(31):21331–21339
Sosa-Acosta JR, Silva JA, Fernández-Izquierdo L, Díaz-Castañón S, Ortiz M, Zuaznabar-Gardona JC, Díaz-García AM (2018) Iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) with potential applications in plasmid DNA isolation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 545:167–178
Zaaeri F, Khoobi M, Rouini M, Akbari Javar H (2017) pH-responsive polymer in a core–shell magnetic structure as an efficient carrier for delivery of doxorubicin to tumor cells. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater, 1–11
Belanova AA, Gavalas N, Makarenko YM, Belousova MM, Soldatov AV, Zolotukhin PV (2018) Physicochemical properties of magnetic nanoparticles: implications for biomedical applications in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Res Treat 41(3):139–143. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485020
Petri-Fink A, Steitz B, Finka A, Salaklang J, Hofmann H (2008) Effect of cell media on polymer coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): colloidal stability, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 68(1):129–137
Mosaiab T, Jeong CJ, Shin GJ, Choi KH, Lee SK, Lee I, In I, Park SY (2013) Recyclable and stable silver deposited magnetic nanoparticles with poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)-catechol coated iron oxide for antimicrobial activity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 33(7):3786–3794
Soares PI, Sousa AI, Ferreira IM, Novo CM, Borges JP (2016) Towards the development of multifunctional chitosan-based iron oxide nanoparticles: optimization and modelling of doxorubicin release. Carbohydr Polym 153:212–221
Cai H, An X, Cui J, Li J, Wen S, Li K, Shen M, Zheng L, Zhang G, Shi X (2013) Facile hydrothermal synthesis and surface functionalization of polyethyleneimine-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(5):1722–1731
Goon IY, Lai LM, Lim M, Munroe P, Gooding JJ, Amal R (2009) Fabrication and dispersion of gold-shell-protected magnetite nanoparticles: systematic control using polyethyleneimine. Chem Mater 21(4):673–681
Korpany KV, Habib F, Murugesu M, Blum AS (2013) Stable water-soluble iron oxide nanoparticles using Tiron. Mater Chem Phys 138(1):29–37
Korpany KV, Majewski DD, Chiu CT, Cross SN, Blum AS (2017) Iron oxide surface chemistry: effect of chemical structure on binding in benzoic acid and catechol derivatives. Langmuir 33(12):3000–3013
Berry CC, Wells S, Charles S, Curtis AS (2003) Dextran and albumin derivatised iron oxide nanoparticles: influence on fibroblasts in vitro. Biomaterials 24(25):4551–4557
Xie J, Xu C, Kohler N, Hou Y, Sun S (2007) Controlled PEGylation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoparticles for reduced non-specific uptake by macrophage cells. Adv Mater 19(20):3163–3166
Do MA, Yoon GJ, Yeum JH, Han M, Chang Y, Choi JH (2014) Polyethyleneimine-mediated synthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with enhanced sensitivity in T2 magnetic resonance imaging. Colloids Surf B 122:752–759
Bi C, Liang Y, Shen L, Tian S, Zhang K, Li Y, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2018) Maltose-functionalized hydrophilic magnetic nanoparticles with polymer brushes for highly selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. ACS Omega 3(2):1572–1580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.7b01788
Chertok B, David AE, Yang VC (2010) Polyethyleneimine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for brain tumor drug delivery using magnetic targeting and intra-carotid administration. Biomaterials, 31 (24), 6317–24
Luo D, Shahid S, Hasan SM, Whiley R, Sukhorukov GB, Cattell MJ (2018) Controlled release of chlorhexidine from a HEMA-UDMA resin using a magnetic field. Dent Mater 34(5):764–775
Shen T, Zhu W, Yang L, Liu L, Jin R, Duan J, Anderson JM, Ai H (2018) Lactosylated N-alkyl polyethylenimine coated iron oxide nanoparticles induced autophagy in mouse dendritic cells. Regen Biomater 5:141–149
Thünemann AF, Schütt D, Kaufner L, Pison U, Möhwald H (2006) Maghemite nanoparticles protectively coated with poly (ethylene imine) and poly (ethylene oxide)-b lock-poly (glutamic acid). Langmuir 22(5):2351–2357
Schweiger C, Pietzonka C, Heverhagen J, Kissel T (2011) Novel magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles coated with poly(ethylene imine)-g-poly(ethylene glycol) for potential biomedical application: synthesis, stability, cytotoxicity and MR imaging. Int J Pharm 408(1–2):130–137
Shen M, Wang SH, Shi X, Chen X, Huang Q, Petersen EJ, Pinto RA, Baker Jr JR, Weber Jr WJ (2009) Polyethyleneimine-mediated functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotubes: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro toxicity assay. J Phys Chem C 113(8):3150–3156
Chen B, Liu Y, Chen S, Zhao X, Meng X, Pan X (2016) Magnetically recoverable cross-linked polyethylenimine as a novel adsorbent for removal of anionic dyes with different structures from aqueous solution. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 67:191–201
Saharan P, Chaudhary GR, Mehta SK, Umar A (2014) Removal of water contaminants by iron oxide nanomaterials. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14(1):627–643
Jiang W, Wu Y, He B, Zeng X, Lai K, Gu Z (2010) Effect of sodium oleate as a buffer on the synthesis of superparamagnetic magnetite colloids. J Colloid Interface Sci 347(1):1–7
Jiang W, Lai K-L, Hu H, Zeng X-B, Lan F, Liu K-X, Wu Y, Gu Z-W (2011) The effect of [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] molar ratio and iron salts concentration on the properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the water/ethanol/toluene system. J Nanopart Res 13(10):5135–5145
Yuen AK, Hutton GA, Masters AF, Maschmeyer T (2012) The interplay of catechol ligands with nanoparticulate iron oxides. Dalton Trans 41(9):2545–2559
Na HB, Palui G, Rosenberg JT, Ji X, Grant SC, Mattoussi H (2011) Multidentate catechol-based polyethylene glycol oligomers provide enhanced stability and biocompatibility to iron oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 6(1):389–399
Huang Q, Fang L, Chen X, Saleem M (2011) Effect of polyethyleneimine on the growth of ZnO nanorod arrays and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Alloys Compd 509(39):9456–9459
Hossaini Nasr S, Tonson A, El-Dakdouki MH, Zhu DC, Agnew D, Wiseman R, Qian C, Huang X (2018) Effects of nanoprobe morphology on cellular binding and inflammatory responses: Hyaluronan-conjugated magnetic nanoworms for magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerotic plaques. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(14):11495–11507
Dodoo S, Steitz R, Laschewsky A, von Klitzing R (2011) Effect of ionic strength and type of ions on the structure of water swollen polyelectrolyte multilayers. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(21):10318–10325
Acknowledgments
The reported study was funded by RFBR, according to the research project no. 18-33-00441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given their approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
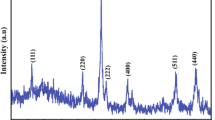
Additional XRD, TEM, SEM, and relaxivity data for characterization of investigated IONPs.
ESM 1
(PDF 1187 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solodov, A.N., Shayimova, J.R., Burilova, E.A. et al. Polyethyleneimine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles: their synthesis and state in water and in solutions of ligands. Colloid Polym Sci 296, 1983–1993 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4425-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-018-4425-5