Abstract
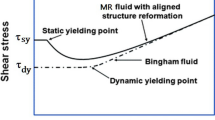
Magnetic poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/Fe3O4 composite nanoparticles were fabricated by Pickering emulsion polymerization using nano-sized iron oxide (Fe3O4) particles as a solid stabilizer that had been synthesized initially from a hydrothermal process. High-resolution scanning electron microscopy was applied to characterize the morphology of the materials. Fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy confirmed the chemical structure of both pure Fe3O4 and PMMA/Fe3O4 composites. The magnetic properties and atomic and molecular structure of a crystal of the materials were examined by vibration sample magnetometry and X-ray diffraction, respectively. The magnetorheological (MR) features of both pure Fe3O4 and PMMA/Fe3O4 nanoparticles dispersed in mineral oil under a magnetic field were characterized by a rotational rheometer. The dynamic yield stress was higher than the elastic stress under external magnetic field. The PMMA/Fe3O4 composite-based MR fluid showed good dispersion stability, while exhibiting typical MR characteristics for the applied magnetic field dependent yield stress with a slope of 1.5.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu YD, Choi HJ, Choi SB (2012) Controllable fabrication of silica encapsulated soft magnetic microspheres with enhanced oxidation-resistance and their rheology under magnetic field. Colloids Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp 403:133–138
Chand M, Shankar A, Noorjahan, Jain K, Pant RP (2014) Improved properties of bidispersed magnetorheological fluids. RSC Adv 4:53960–53966
de Vicente J, Ruiz-Lopez JA, Andablo-Reyes E, Segovia-Gutierrez JP, Hidalgo-Alvarez R (2011) Squeeze flow magnetorheology. J Rheol 55:753–779
Bica I, Anitas EM, Averis LME, Bunoiu M (2015) Magnetodielectric effects in composite materials based on paraffin, carbonyl iron and grapheme. J Ind Eng Chem 21:1323–1327
Li WH, Lynam C, Chen J, Liu B, Zhang XZ, Wallace GG (2007) Magnetorheology of single-walled nanotube dispersions. Mater Lett 61:3116–3118
Bunoiu M, Bica I (2016) Magnetorheological elastomer based on silicone rubber, carbonyl iron and Rochelle salt: effects of alternating electric and static magnetic fields intensities. J Ind Eng Chem 37:312–318
Li WH, Zhou Y, Tian TF (2010) Viscoelastic properties of MR elastomers under harmonic loading. Rheol Acta 49:733–740
Thirupathi G, Singh R (2014) Magneto-viscosity of MnZn-ferrite ferrofluid. Physica B 448:346–348
Yu M, Yang C, Bian X, Zhao S, Wang T, Liu S, Guo T (2016) Application of Fe78Si9B13 amorphous particles in magnetorheological fluids. RSC 6:22511–22518
Kim YJ, Liu YD, Seo Y, Choi HJ (2013) Pickering-emulsion-polymerized polystyrene/Fe2O3 composite particles and their Magnetoresponsive characteristics. Langmuir 29:4959–4965
Dong X, Tong Y, Ma N, Qi M, Ou J (2015) Properties of cobalt nanofiber-based magnetorheological fluids. RSC Adv 5:13958–13963
Cabuk M, Yavuz M, Unal HI (2016) Electrokinetic, electrorheological and viscoelastic properties of of polythiophene-graft-chitosan copolymer particles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 510:231–238
Yang J, Sun S, Li W, Du H, Alici G, Nakano M (2015) Development of a linear damper working with magnetorheological shear thickening fluids. J Intell Mater Sys Struct 26:1811–1817
Bica I, Liu YD, Choi HJ (2013) Physical characteristics of magnetorheological suspensions and their applications. J Ind Eng Chem 19:394–406
Piao SH, Kwon SH, Zhang WL, Choi HJ (2015) Celebrating soft Matter’s 10th anniversary: stimuli-responsive Pickering emulsion polymerized smart fluids. Soft Matter 11:646–654
Binks BP, Lumsdon SO (2000) Influence of particle wettability on the type and stability of surfactant-free emulsions. Langmuir 16:8622–8631
Liu H, Wei Z, Hu M, Deng Y, Tong Z, Wang C (2014) Fabrication of degradable polymer microspheres via pH-responsive chitosan-based Pickering emulsion photopolymerization. RSC Adv 4:29344–29351
Wei XR, Liu J, Yang Y, Deng L (2014) A general approach towards efficient catalysis in Pickering emulsions stabilized by amphiphilic RGO-silica hybrid materials. RSC Adv 4:35744–35749
Schrade A, Landfester K, Ziener U (2013) Pickering-type stabilized nanoparticles by heterophase polymerization. Chem Soc Rev 42:6823
Cauvin S, Colver PJ, Bon SAF (2005) Pickering stabilized Miniemulsion polymerization: preparation of clay armored latexes. Macromolecules 38:7887
Dao TD, Erdenedelger G, Jeong HM (2014) Water-dispersible graphene designed as a Pickering stabilizer for the suspension polymerization of poly(methyl methacrylate)/graphene coreeshell microsphere exhibiting ultra-low percolation threshold of electrical conductivity. Polymer 55:4709–4719
Lee KY, Blaker JJ, Heng JYY, Murakami R, Bismarck A (2014) pH-triggered phase inversion and separation of hydrophobised bacterial cellulose stabilised Pickering emulsions. React Funct Polym 85:208–213
Lin Z, Yu D, Li Y (2015) Study on the magnetic ODSA-in-Water Pickering emulsion stabilized by Fe3O4 nanoparticle. Colloid Polym Sci 293:125–134
Dinsmore AD, Hsu MF, Nikolaides MG, Marquez M, Bausch AR, Weitz DA (2002) Colloidosomes: selectively permeable capsules composed of colloidal particles. Science 298:1006–1009
Wei ZJ, Yang Y, Yang R, Wang CY (2012) Alkaline lignin extracted from furfural residues for pH-responsive Pickering emulsions and their recyclable polymerization. Green Chem 14:3230–3236
Deng Y, Qi D, Deng C, Zhang X, Zhao D (2008) Superparamagnetic high-magnetization microspheres with a Fe3O4@SiO2 Core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 Shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130:28–29
Shen LH, Bao JF, Wang D, Wang YX, Chen ZW, Ren L, Zhou X, Ke XB, Chen M, Yang AQ (2013) One-step synthesis of monodisperse, water-soluble ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles for potential bioapplication. Nano 5:2133
Choi HJ, Jang IB, Lee JY, Pich A, Bhattacharya S, Adler HJ (2005) Magnetorheology of synthesized core–shell structured nanoparticle. IEEE T Magn 41:3448–3450
Liu YD, Choi HJ (2015) Magnetorheology of core–shell typed dual-coated carbonyl iron particle fabricated by a sol–gel and self-assembly process. Mater Res Bull 69:92–97
Quan XM, Liu YD, Choi HJ (2015) Magnetorheology of iron associated magnetic metal-organic framework nanoparticle. J Appl Phys 117:17C732
Monfreda M, Varani F, Cattaruzza F, Ciambrone S, Proposito A (2015) Fast profiling of cocaine seizures by FTIR spectroscopy and GC-MS analysis of minor alkaloids and residual solvents. Sci Justice 55:456–466
Mohammad AA, Ali RA (2016) Fe3O4@B-MCM-41:a new magnetically recoverable nanostructured catalyst for the synthesis of polyhydroquinolines. J Magn Magn Mater 398:205–214
Khanlou HM, Ang BC, Talebian S, Barzani MM, Silakhori M, Fauzi H (2015) A systematic study of maghemite/PMMA nano-fibrous composite via an electrospinning process: synthesis and characterization. Measurement 70:179–187
Chae HS, Piao SH, Choi HJ (2015) Fabrication of spherical Fe3O4 particles with a solvothermal method and their magnetorheological characteristics. J Ind Eng Chem 29:129–133
Wang J, Yang J, Li X, Wang D, Wei B, Song H, Li X, Fu S (2016) Preparation and photocatalytic properties of magnetically reusable Fe3O4@ZnO core/shell nanoparticles. Phys E 75:66–71
Feng J, Mao J, Wen X, Tu M (2011) Ltrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 509:9093–9097
Safari J, Zarnegar Z, Hekmatara H (2016) Green synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and survey their magnetic properties, synthesis and reactivity in inorganic, metal-organic, and nano-metal. Chemistry 46:1047–1052
Zhu J, He J, Du X, Lu R, Huang L, Ge X (2011) A facile and flexible process of b-cyclodextrin grafted on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and host–guest inclusion studies. Appl Surf Sci 257:9056–9062
Cheng Q, Pavlinek V, He Y, Li C, Saha P (2009) Electrorheological characteristics of polyaniline/titanate composite nanotube suspensions. Colloid Polym Sci 287:435–441
Buron H, Mengual O, Meunier G, Cayré I, Snabre P (2004) Optical characterization of concentrated dispersions: applications to laboratory analyses and on-line process monitoring and control. Polym Int 53:1205–1209
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Korea (#10047791).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C.Y., Piao, S.H. & Choi, H.J. Pickering emulsion polymerized magnetite-poly(methyl methacrylate) composite particles and their magnetorheology. Colloid Polym Sci 295, 959–966 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-017-4086-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-017-4086-9