Abstract
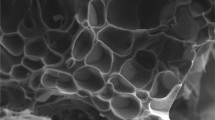
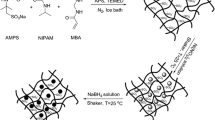
Thermosensitive poly(NIPAAm-co-AMPS) hydrogels were prepared by copolymerization of N-isopropyl acrylamide (NIPAAm) and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl 1-propansulfonic acid (AMPS) by employing N,N′-methylenebis(acrylamide) (BIS) as cross-linker. Uniformly distributed silver nanoparticles (Ag-NP) were obtained within hydrogel networks as nanoreactors via in situ reduction of silver nitrate (AgNO3) using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as reducing agent. The catalytic properties of Ag-NP-poly(NIPAAm-co-AMPS) hydrogels presented obvious temperature dependence upon the reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) in aqueous solution. Interestingly, the addition of α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) could further enhance the reduction rate and change the associated activation parameters. This advanced catalytic system with temperature dependence and α-CD synergetic effect presented promising applications in catalytic chemistry.

ᅟ











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kruifa CG, Anemac S, Zhuc C, Haveac P, Cokerc C (2015) Water holding capacity and swelling of casein hydrogels. Food Hydrocolloid 44:372–379
Wang Q, Yang Z, Wang L, Ma M, Xu B (2007) Molecular hydrogel-immobilized enzymes exhibit superactivity and high stability in organic solvents. Chem Commun 10:1032–1034
Lee J, Ko JH, Lin E, Wallace P, Ruch F, Maynard HD (2015) Trehalose hydrogels for stabilization of enzymes to heat. Polym Chem 6:3443–3448
Ahmed EM, Aggor FS (2010) Swelling kinetic study and characterization of crosslinked hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 117(4):2168–2174
Hamidia M, Azadia A, Rafieia P (2008) Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 60(15):1638–1649
Guo Q, Cao H, Li X, Liu S (2015) Thermosensitive hydrogel drug delivery system containing doxorubicin loaded CS–GO nanocarriers for controlled release drug in situ. Mater Technol 30(5):294–300
Westa JL, Hubbell JA (1995) Photopolymerized hydrogel materials for drug delivery applications. React Polym 25(2–3):139–147
Gariepy E, Leroux JC (2004) In situ-forming hydrogels—review of temperature-sensitive systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 58(2):409–426
Ma X, Li Y, Wang W, Ji Q, Xia Y (2013) Temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels by in situ polymerization with improved swelling capability and mechanical behavior. Eur Polym J 49(2):389–396
Qiu Y, Park K (2012) Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev 64:49–60
Yang J, Chen J, Pan D, Wan Y, Wang Z (2013) pH-sensitive interpenetrating network hydrogels based on chitosan derivatives and alginate for oral drug delivery. Carbohyd Polym 92(1):719–725
Zhang C, Losego MD, Braun PV (2013) Hydrogel-based glucose sensors: effects of phenylboronic acid chemical structure on response. Chem Mater 25(15):3239–3250
Choi E, Jun I, Chang H, Park KM, Shin H, Park KD, Park J (2012) Quantitatively controlled in situ formation of hydrogel membranes in microchannels for generation of stable chemical gradients. Lab Chip 12:302–308
Wang E, Desai MS, Lee SW (2013) Light-controlled graphene-elastin composite hydrogel actuators. Nano Lett 13(6):2826–2830
Inomata H, Goto S, Otake K, Saito S (1992) Effect of additives on phase transition of N-isopropylacrylamide gels. Langmuir 8:687–690
Gorelikov I, Field LM, Kumacheva E (2004) Hybrid microgels photoresponsive in the near-infrared spectral range. J Am Chem Soc 126:15938–15939
Holtz JH, Asher SA (1997) Polymerized colloidal crystal hydrogel films as intelligent chemical sensing materials. Nature 389:829–832
Hapiot F, Menuel S, Monflier E (2013) Thermoresponsive hydrogels in catalysis. ACS Catal 3(5):1006–1010
Gilbert B, Ono RK, Ching KA, Kim CS (2009) The effects of nanoparticle aggregation processes on aggregate structure and metal uptake. J Colloid Interf Sci 339(2):285–295
Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW (2009) Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25(24):13840–13851
Campbell CT, Parker SC, Starr DE (2002) The effect of size-dependent nanoparticle energetics on catalyst sintering. Science 298(5594):811–814
Burda C, Chen X, Narayanan R, El-Sayed MA (2005) Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Rev 105(4):1025–1102
Tam SK, Ng KM (2015) High-concentration copper nanoparticles synthesis process for screen-printing conductive paste on flexible substrate. J Nanoparticle Res 17:466
Lee N, Hyeon T (2012) Designed synthesis of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for efficient magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Chem Soc Rev 41:2575–2589
Gutes A, Hsia B, Sussman A, Mickelson W, Zettl A, Carraro C, Maboudian R (2012) Graphene decoration with metal nanoparticles: towards easy integration for sensing applications. Nanoscale 4:438–440
Liu J, Wang J, Zhu Z, Li L, Guo X, Lincoln SF, Prud’homme RK (2014) Cooperative catalytic activity of cyclodextrin and Ag nanoparticles immobilized on spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. AICHE J 60(6):1977–1982
Wu S, Kaiser J, Guo X, Li L, Lu Y, Ballauff M (2012) Recoverable platinum nanocatalysts immobilized on magnetic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(15):5608–5614
Scott RW, Wilson OM, Crooks RM (2005) Synthesis, characterization, and applications of dendrimer-encapsulated nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 109(2):692–704
Saravanan G, Hara T, Yoshikawa H, Yamashita Y, Ueda S, Kobayashi K, Abe H (2012) Post-synthesis dispersion of metal nanoparticles by poly(amidoamine) dendrimers: size-selective inclusion, water solubilization, and improved catalytic performance. Chem Commun 48:7441–7443
Wang D, Xin HL, Hovden R, Wang H, Yu Y, Muller DA, DiSalvo FJ (2013) Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Nat Mater 12:81–87
Lu Y, Mei Y, Drechsler M, Ballauff M (2006) Thermosensitive core–shell particles as carriers for Ag nanoparticles: modulating the catalytic activity by a phase transition in networks. Angew Chem Int Edit 45:813–816
Ballauff M, Lu Y (2007) “Smart” nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and applications. Polymer 48(7):1815–1823
Lu Y, Mei Y, Ballauff M, Drechsler M (2006) Thermosensitive core–shell particles as carrier systems for metallic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 110(9):3930–3937
Lu Y, Proch S, Schrinner M, Drechsler M, Kempe R, Ballauff M (2009) Thermosensitive core–shell microgel as a “nanoreactor” for catalytic active metal nanoparticles. J Mater Chem 19:3955–3961
Zhang J, Xu S, Kumacheva E (2004) Polymer microgels: reactors for semiconductor, metal, and magnetic nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 126(25):7908–7914
Sahiner N, Ozay O, Aktas N, Inger E, He J (2011) The on demand generation of hydrogen from Co–Ni bimetallic nano catalyst prepared by dual use of hydrogel: as template and as reactor. Int J Hydrog Energy 36(23):15250–15258
Peppas NA, Hilt JZ, Khademhosseini A, Langer R (2006) Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv Mater 18:1345–1360
Liu J, Wang J, Wang Y, Liu C, Li L, Guo X, Lincoln SF (2015) A thermosensitive hydrogel carrier for nickel nanoparticles. Colloids and Interface Sci Commun 4:1–4
Sahiner N, Ozay H, Ozay O, Aktas N (2010) New catalytic route: hydrogels as templates and reactors for in situ Ni nanoparticle synthesis and usage in the reduction of 2-and 4-nitrophenols. Appl Catal A 385(1–2):201–207
Kim JH, Lee TR (2004) Thermo- and pH-responsive hydrogel-coated gold nanoparticles. Chem Mater 16(19):3647–3651
Li G, Wen Q, Zhang T, Ju Y (2013) Synthesis and properties of silver nanoparticles in chitosan-based thermosensitive semi-interpenetrating hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 127(4):2690–2697
Kim JH, Lee TR (2007) Hydrogel-templated growth of large gold nanoparticles: synthesis of thermally responsive hydrogel–nanoparticle composites. Langmuir 23(12):6504–6509
Faraga RK, EL-Saeeda S, Abdel-Raoufa ME (2015) Synthesis and investigation of hydrogel nanoparticles based on natural polymer for removal of lead and copper(II) ions. Desalin Water Treat: 1–11
Uematsul Y, Araki T (2012) Effects of strongly selective additives on volume phase transition in gels. J Chem Phys 137(2):024902
Xue C, Palaniappan K, Arumugam G, Hackney SA, Liu J, Liu H (2007) Sonogashira reactions catalyzed by water-soluble, β-cyclodextrin- capped palladium nanoparticles. Catal Lett 116(3–4):94–100
Park C, Kim H, Kim S, Kim C (2009) Enzyme responsive nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers and synergistic effects in release of guests. J Am Chem Soc 131(46):16614–16615
He J, Dominik S, Andreas O, Andrij P, Yan L (2015) Cyclodextrin modified microgels as “nanoreactor” for the generation of Au nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic activity. J Mater Chem A 3:6187–6195
Wong YT, Yang C, Ying KC, Jia G (2002) Synthesis of a novel β-cyclodextrin-functionalized diphosphine ligand and its catalytic properties for asymmetric hydrogenation. Organometallics 21(9):1782–1787
Machut C, Patrigeon J, Tilloy S, Bricout H, Hapiot F, Monflier E (2007) Self-assembled supramolecular bidentate ligands for aqueous organometallic catalysis. Angew Chem 119(17):3100–3102
Gassensmith JJ, Smaldone RA, Forgan RS, Wilmer CE, Cordes DB, Botros YY (2012) Polyporous metal-coordination frameworks. Org Lett 14(6):1460–1463
Chen X, Parker S, Zou G, Su W, Zhang Q (2010) β-Cyclodextrin functionalized silver nanoparticles for the naked eye detection of aromatic isomers. ACS Nano 4(11):6387–6394
Chen X, Cheng X, Gooding JJ (2012) Detection of trace nitroaromatic isomers using indium tin oxide electrodes modified using β-cyclodextrin and silver nanoparticles. Anal Chem 84(20):8557–8563
Devi LB, Mandal AB (2013) Self-assembly of Ag nanoparticles using hydroxypropyl cyclodextrin: synthesis, characterisation and application for the catalytic reduction of p-Nitrophenol. RSC Adv 3:5238–5253
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge NSFC Grants (51403062 and 51273063), the Australian Research Council Grant DP110103177, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013 M541485), 111 Project Grant (B08021), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, and the Open Project of Engineering Research Center of Materials-Oriented Chemical Engineering of Xinjiang Bingtuan (2015BTRC001) for support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Wang, J., Wang, Y. et al. Synergetic catalytic effect of α-cyclodextrin on silver nanoparticles loaded in thermosensitive hydrogel. Colloid Polym Sci 294, 1087–1095 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3867-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-016-3867-x