Abstract
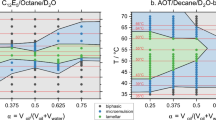
We describe full nanostructural characterization of the “one-phase corridor” in the “χ-cut” phase diagram of the isooctane-water-C12E5 system. We followed the nanostructural development from oil-in-water microemulsion to a bicontinuous microemulsion, and to water-in-oil microemulsion, as the oil content is increased, and temperature is raised accordingly. We used cryogenic-temperature transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM) and cryogenic-temperature scanning electron microscopy (cryo-SEM). In most of the composition range studied, we were able to apply both methodologies with similar results. This is a first report of nanostructural mapping of the entire composition range, from water-rich to oil-rich, of a microemulsion system, using well-controlled cryo-specimen preparation. The nanostructural sequence directly imaged here agrees well with theory and previous experimental work by nonimaging techniques, and some, partial electron microscopy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoar TP, Schulman JH (1943) Transparent water-in-oil dispersions: the oleopathic hydro-micelle. Nature 152:102–3
Scriven LE (1976) Equilibrium bicontinuous structure. Nature 263:123–5
Danielsson I, Lindman B (1981) The definition of microemulsion. Colloid Polym Sci 3:391–2
Friberg SE (1982) Comments on “the definition of microemulsion”. Colloids Surf A 2:201
Evans DF, Wennerström H (1999) The colloidal domain, 2nd edn. Wiley-VCH, New York
Komura S (2007) Mesoscale structures in microemulsions. J Phys Condens Matter 19:463101
Chen SJ, Evans DF, Ninham BW (1984) Properties and structure of three-component ionic microemulsions. J Phys Chem 88:1631–4
Lin T-L, Liu C-C, Roberts MF, Chen S-H (1991) Structure of mixed short-chain lecithin/long-chain lecithin aggregates studied by small-angle neutron scattering. J Phys Chem 95:6020–7
Fontell K, Ceglie A, Lindman B, Ninham B (1986) Some observations on phase diagrams and structure in binary and ternary systems of didodecyldimethylammonium bromide. Acta Chem Scand 40:247–56
Lenz U, Hoffmann H (1992) Dynamic behavior of ternary microemulsions consisting of didodecyldimethylammoniumbromide, water and hydrocarbon. Ber Bunnge Ph Chem 96:809–15
Sottmann T, Stubenrauch C (2009) Phase behavior, interfacial tension and microstructure of microemulsions. In: Stubenrauch C (ed) Microemulsions: background, new concepts, applications, perspectives. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Oxford, pp 1–47
Sottmann T, Strey R (2005) Microemulsions. In: Lyklema J (ed) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–96
Lichterfeld F, Schmeling T, Strey R (1986) Microstructure of microemulsions of the system water-n-tetradecane-alkyl polyglycol ether (C12E5). J Phys Chem 90:5762–6
Stubenrauch C, Sottmann T (2009) Microemulsions stabilized by sugar surfactants in sugar-based surfactants: fundamentals and application. C.C. Ruiz (ed.), CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Wolf L, Hoffmann H, Talmon Y, Teshigawara T, Watanabe K (2010) Cryo-TEM imaging of a novel microemulsion system of silicone oil with an anionic/nonionic surfactant mixture. Soft Matter 6:5367
Yaron PN, Reynolds PA, McGillivray DJ, Mata JP, White JW (2010) Nano- and microstructure of high-internal phase emulsions under shear. J Phys Chem B 114:3500–9
Kahlweit M, Lessner E, Strey R (1983) Influence of the properties of the oil and the surfactant on the phase behavior of systems of the type water–oil-nonionic surfactant. J Phys Chem 87:5032–40
Arleth L, Pedersen JS (2001) Droplet polydispersity and shape fluctuations in AOT [bis(2-ethylhexyl)sulfosuccinate sodium salt] microemulsions studied by contrast variation small-angle neutron scattering. Phys Rev E: Stat Phys Plasmas, Fluids 63:061406–1
Hirasaki GJ, Miller CA, Puerto M (2008) Recent advances in surfactant EOR. International Petroleum Technology Conference, IPTC 2008, December 3, 2008 - December 5. Soc Petrol Eng 1:130–64
Puerto M, Hirasaki GJ, Miller CA, Barnes JR (2010) Surfactant systems for EOR in high-temperature, high-salinity environments. 17th SPE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, IOR 2010, April 24, 2010 - April 28. Soc Petrol Eng (SPE) 1:356–75
Spernath A, Aserin A (2006) Microemulsions as carriers for drugs and nutraceuticals. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 128–130:47–64
Lutter S, Tiersch B, Koetz J, Boschetti-de-Fierro A, Abetz V (2007) Covalently closed microemulsions in presence of triblock terpolymers. J Colloid Interface Sci 311:447–55
Gayet F, Kalamouni CE, Lavedan P, Marty J, Brulet A, Viguerie NL (2009) Ionic liquid/oil microemulsions as chemical nanoreactors. Langmuir 25:9741–50
Kim D, Oh S, Lee J (1999) Preparation of ultrafine monodispersed indium-tin oxide particles in AOT-based reverse microemulsions as nanoreactors. Langmuir 15:1599–603
Eastoe J, Hollamby MJ, Hudson L (2006) Recent advances in nanoparticle synthesis with reversed micelles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 128–130:5–15
Talmon Y, Adrian M, Dubochet J (1986) Electron beam radiation damage to organic inclusions in vitreous, cubic, and hexagonal ice. J Microscopy 141:375–84
Kunieda H, Shinoda K (1982) Phase behavior in systems of nonionic surfactant/water/oil around the hydrophile-lipophile-balance temperature (HLB temperature). J Dispersion Sci Technol 3:233–44
Olsson U, Shinoda K, Lindman B (1986) Change of the structure of microemulsions with the hydrophile-lipophile balance of nonionic surfactant as revealed by NMR self-diffusion studies. J Phys Chem 90:4083–8
Kahlweit M, Strey R (1986) Phase behavior of quinary systems water-oil-nonionic amphiphile-ionic amphiphile-electrolyte. J Phys Chem 90:5239–44
Talmon Y (1983) Staining and drying-induced artifacts in electron microscopy of surfactant dispersions. J Colloid Interface Sci 93:366–82
Bellare JR, Davis HT, Scriven LE, Talmon Y (1988) Controlled environment vitrification system: an improved sample preparation technique. Microsc Res Tech 10:87–111
Uhlmann DR (1972) A kinetic treatment of glass formation. J Non-Cryst Solids 7:337–48
Jahn W, Strey R (1988) Microstructure of microemulsions by freeze fracture electron microscopy. J Phys Chem 92:2294–301
Talmon Y (2007) Seeing giant micelles by cryogenic-temperature transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM). In: Zana R, Kaler EA (eds) Giant micelles. CRC Press, New York, pp 163–178
Cui H, Hodgdon TK, Kaler EW, Abezgauz L, Danino D, Lubovsky M, Talmon Y, Pochan DJ (2007) Elucidating the assembled structure of amphiphiles in solution via cryogenic transmission electron microscopy. Soft Matter 3:945–55
Zhong S, Pochan DJ (2010) Cryogenic transmission electron microscopy for direct observation of polymer and small-molecule materials and structures in solution. J Macromol Sci Polym Rev 50:287–320
Oostergetel GT, Esselink FJ, Hadziioannou G (1995) Cryo-electron microscopy of block copolymers in an organic solvent. Langmuir 11:3721–4
Danino D, Gupta R, Satyavolu J, Talmon Y (2002) Direct cryogenic-temperature transmission electron microscopy imaging of phospholipid aggregates in soybean oil. J Colloid Interface Sci 249:180–6
Davis VA, Parra-Vasquez ANG, Green MJ, Rai PK, Behabtu N, Prieto V, Booker RD, Schmidt J, Kesselman E, Zhou W, Fan H, Adams WW, Hauge RH, Fischer JE, Cohen Y, Talmon Y, Smalley RE, Pasquali M (2009) True solutions of single-walled carbon nanotubes for assembly into macroscopic materials. Nat Nanotechnol 4:830–4
Behabtu N, Lomeda JR, Green MJ, Higginbotham AL, Sinitskii A, Kosynkin DV, Tsentalovich D, Parra-Vasquez ANG, Schmidt J, Kesselman E, Cohen Y, Talmon Y, Tour JM, Pasquali M (2010) Spontaneous high-concentration dispersions and liquid crystals of graphene. Nat Nanotechnol 5:406–11
Bernheim-Groswasser A, Tlusty T, Safran SA, Talmon Y (1999) Direct observation of phase separation in microemulsion networks. Langmuir 15:5448–53
Note C, Ruffin J, Tiersch B, Koetz J (2007) The influence of polyampholytes on the phase behavior of microemulsion used as template for the nanoparticle formation. J Dispersion Sci Technol 28:155–64
Note C, Koetz J, Kosmella S (2006) Structural changes in poly(ethyleneimine) modified microemulsion. J Colloid Interface Sci 302:662–8
Issman L, Talmon Y (2012) Cryo-SEM specimen preparation under controlled temperature and concentration conditions. J Microsc 246:60–69
Ben-Barak I, Talmon Y (2012) Direct-imaging cryo-SEM of nanostructure evolution in didodecyl-dimethylammonium bromide-based microemulsions. Z Phys Chem 226:665–674
Kleinerman O, Parra-Vasquez AN, Green MJ, Behabtu N, Schmidt J, Kesselman E, Young CC, Cohen Y, Pasquali M, Talmon Y (2015) Cryogenic-temperature electron microscopy direct imaging of carbon nanotubes and graphene solutions in superacids. J Microsc 259:16–25
Kahlweit M, Strey R (1985) Phase behavior of ternary systems of the type H2O-oil-nonionic amphiphile microemulsions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 24:654–668
Talmon Y (2015) The study of nanostructured liquids by cryogenic-temperature electron microscopy- A status report. J Mol Liq 210 (Part A):2–8
Kahlweit M, Strey R, Haase D et al (1987) How to study microemulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 118:436–453
Clausen TM, Vinson PK, Minter JR, Davis HT, Talmon Y, Miller WG (1992) Viscoelastic micellar solutions: microscopy and rheology. J Phys Chem 96:474–484
Koifman N, Schnabel-Lubovsky M, Talmon Y (2013) Nanostructure formation in the lecithin/ isooctane/water System. J Phys Chem B 117:9558–9567
Fanun M (2009) Microemulsions, properties and applications. In: Surfactant Science Series vol. 144. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p 110
Wolf L, Hoffmann H, Teshigawara T, Okamoto T, Talmon Y (2012) Microemulsions with a HIPME structure. J Phys Chem B 116:2131–2137
Acknowledgments
Our work on microemulsions has been supported by a grant from the Israel Science Foundation (ISF). The cryo-EM work was performed at the Laboratory for Electron Microscopy of Soft Matter, supported by the Technion Russell Berrie Nanotechnology Institute (RBNI). The authors thank Dr. Ellina Kesselman and Ms. Judith Schmidt for help with some of the cryo-TEM work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to a dear friend and a superb colleague, Prof. Dr. Heinz Hoffmann on his 80th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davidovich, I., Issman, L., de Paula, C. et al. A cryogenic-electron microscopy study of the one-phase corridor in the phase diagram of a nonionic surfactant-based microemulsion system. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 3189–3197 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3773-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-015-3773-7